Nursing Knowledge
A burn is tissue damage caused by excessive heat, electricity, radioactivity, or corrosive chemicals that denature (break down) the proteins in the skin cells. All burns cause homeostatic imbalances in the body and are graded according to their severity.
Burns are classified based on their depth (superficial–full thickness; first–third-degree burns), size of total body surface area (TBSA), and location (with some areas considered more serious than others due to higher potential for complications).
| Superficial | Superficial partial thickness | Deep partial thickness | Full thickness |
| Only epidermis; red without blisters | Dermis; blisters (very painful) | Burnt area is stiff; injury extends to all layers of the skin. | Burn is black and leads to loss of the burnt part. Injury to deeper tissues is present (muscle, tendons, bone). |
TBSA stands for Total Body Surface Area. It is used to estimate the percentage of the body surface that has been burned. This is an important part of initial burn assessment as it helps to determine the severity of the burn, guides fluid resuscitation, and aids in planning further treatment.
A common method to estimate the TBSA in adults is the “Rule of Nines”, which divides the body into sections of 9% (or multiples thereof). For example, each arm represents 9% of the body (4.5% front/back), each leg 18% (9% front/back), the torso 18% front and 18% back, and the head 9%.
In children, due to the proportionally larger head size, different percentages are used, often requiring specific pediatric burn charts.
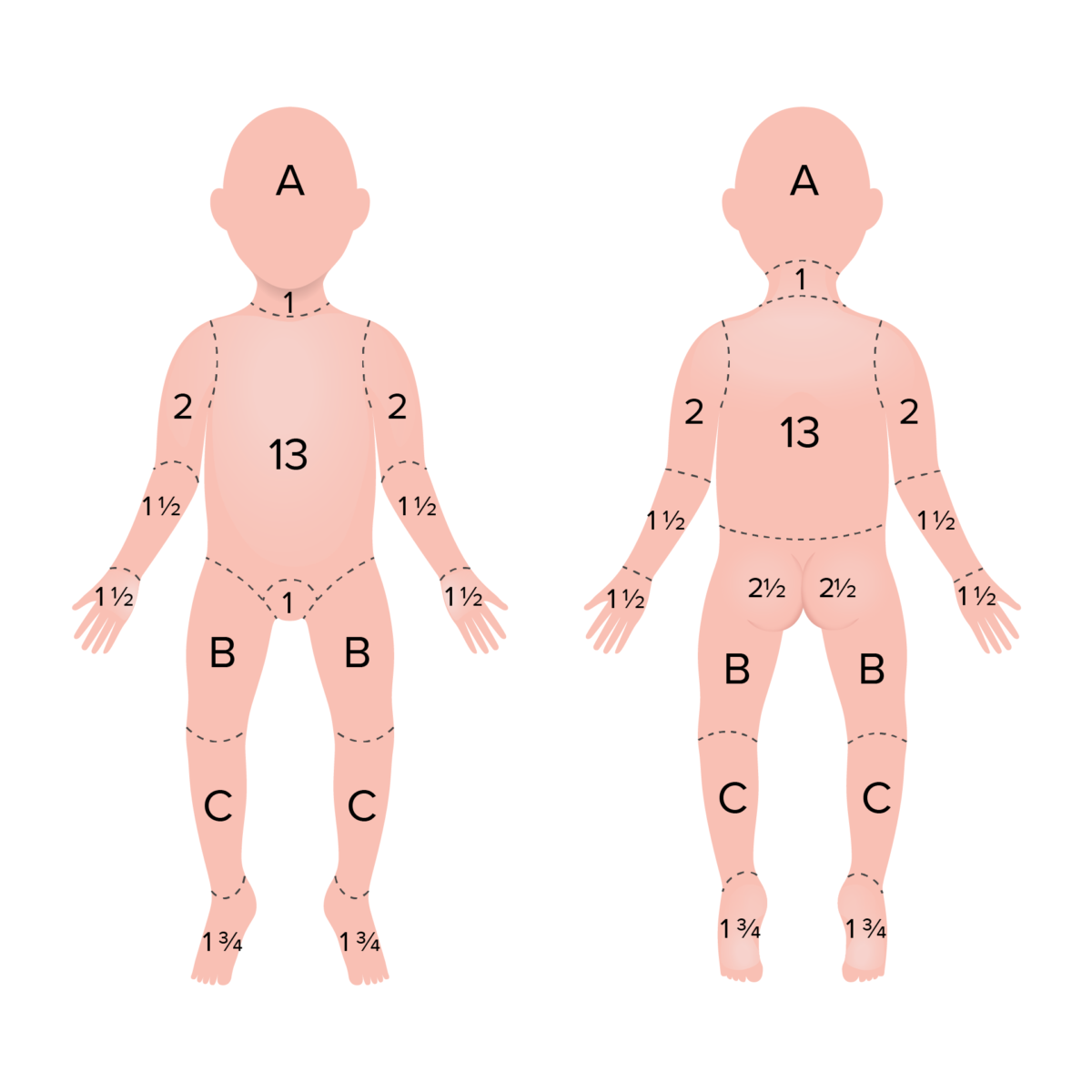
Rule of 9 in children used to determine the TBSA of burn: percentages adjusted to more closely resemble adults
Area A represents 8.5% TBSA in a 1 year old, 6.5% in a 5 year old, 5.5% in a 10 year old and 4.5% in a 15 year old.
Area B represents 3.25% TBSA in a 1 year old, 4.0% in a 5 year old, 4.5% in a 10 year old and 4.5% in a 15 year old.
Area C represents 2.5% TBSA in a 1 year old, 2.75% in a 5 year old, 3.0% in a 10 year old and 3.25% in a 15 year old.
Caring for a client with second-degree burns involves:
Nursing diagnoses for burns can be quite diverse, depending on the severity and location of the burn. Some common nursing diagnoses for burns might include:
Burn unit nurses are critical care nurses specialized on treating clients with burn injuries.
They may work in a specialized burn unit, emergency department, intensive care unit, or outpatient care setting. This role requires strong clinical skills, a compassionate approach, and the ability to support clients and families through potentially long and difficult recovery processes.
To become a burn unit nurse, you will likely first need to gain a couple of years of acute or critical care experience after obtaining your nursing license. A certification like the Certified Wound Care Nurse credential or the Certified Pediatric Emergency Nurse can also help when applying for positions in burn units.
RELATED TOPIC:
Free Download
Master the topic with a unique study combination of a concise summary paired with video lectures.
Your free account gives you access to:
or