La esofagitis es la inflamación o irritación del esófago. Los LOS Neisseria principales tipos de esofagitis son la inducida por medicamentos, la infecciosa, la eosinofílica, la corrosiva y por reflujo ácido del estómago. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar odinofagia, disfagia y dolor Dolor Inflammation torácico retroesternal. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante endoscopia y biopsia. Se obtienen pruebas de laboratorio y de imagenología, dependiendo del grado de daño y de la afectación de otros sistemas. El tratamiento de la esofagitis depende de la etiología subyacente e incluye cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dieta, evitar los LOS Neisseria agentes causantes, terapia con antibióticos o uso de inhibidores de la bomba de protones. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos graves, como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las lesiones por corrosión, la cirugía puede ser necesaria. Si no se trata, la esofagitis puede dar lugar a complicaciones como estenosis, metaplasia Metaplasia A condition in which there is a change of one adult cell type to another similar adult cell type. Cellular Adaptation del esófago y desarrollo de malignidad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Para recordar las causas comunes de la esofagitis: “PIECE” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés)
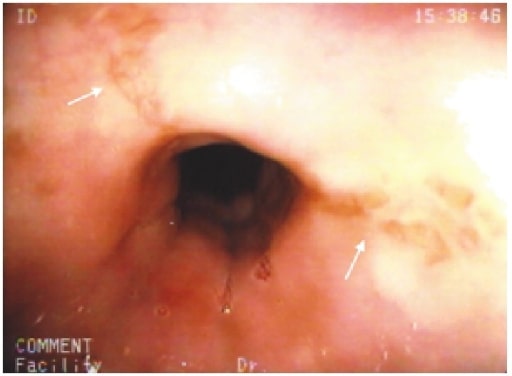
Erosiones estrelladas en el esófago medial (flechas blancas) en un paciente con esofagitis inducida por cloxacilina
Imagen: “Cloxacillin: A New Cause of Pill-Induced Esophagitis” por Zezos P, Harel Z, Saibil F. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El diagnóstico se realiza mediante una endoscopia superior.
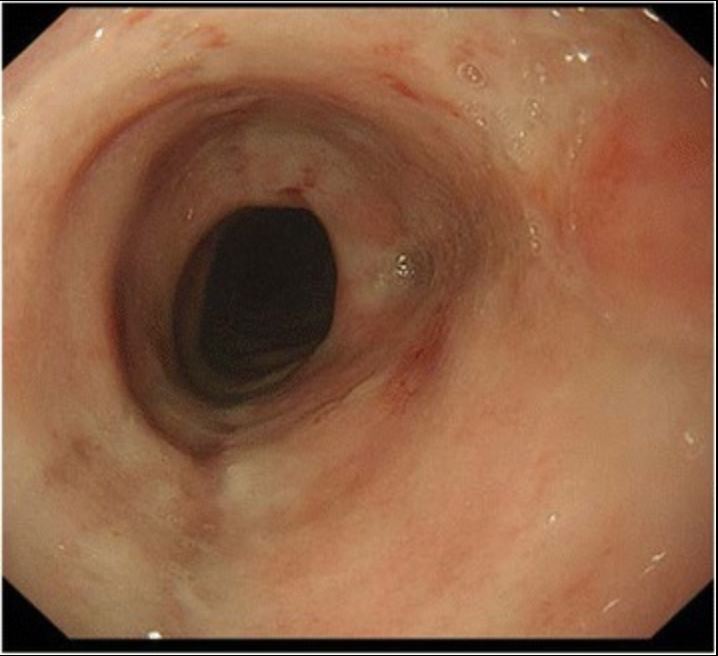
Hallazgos de una endoscopia gastrointestinal superior en un paciente con esofagitis por citomegalovirus. Se observa una úlcera con una base blanca en el esófago.
Imagen: “Cytomegalovirus esophagitis developing during chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer” por Journal of Medical Case Reports. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El diagnóstico se realiza mediante una endoscopia superior.
Endoscopia digestiva alta de un paciente que muestra numerosas lesiones en la superficie esofágica de color amarillo-blanquecino, pleomórficas y pequeñas placas circulares aisladas con erosiones centrales.
Imagen: “Herpetic esophagitis in immunocompetent medical student” por Marinho AV, Bonfim VM, de Alencar LR, Pinto SA, de Araújo Filho JA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0El diagnóstico se realiza mediante una endoscopia superior.
La esofagogastroduodenoscopia ilustra lesiones blancas difusas en el esófago características de la esofagitis por Candida.
Imagen: “Epigastric Distress Caused by Esophageal Candidiasis” por Chen KH, Weng MT, Chou YH, Lu YF, Hsieh CH. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El diagnóstico se realiza mediante una endoscopia superior.
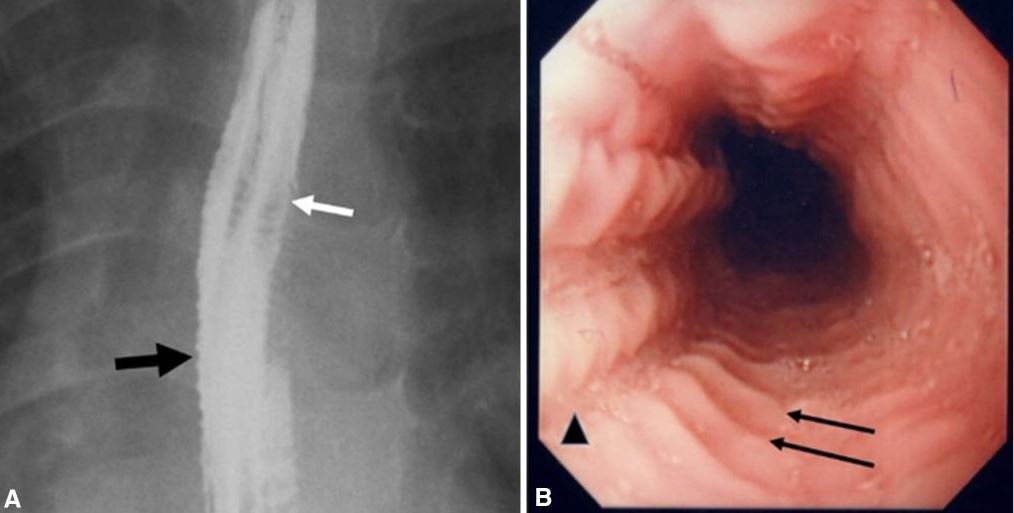
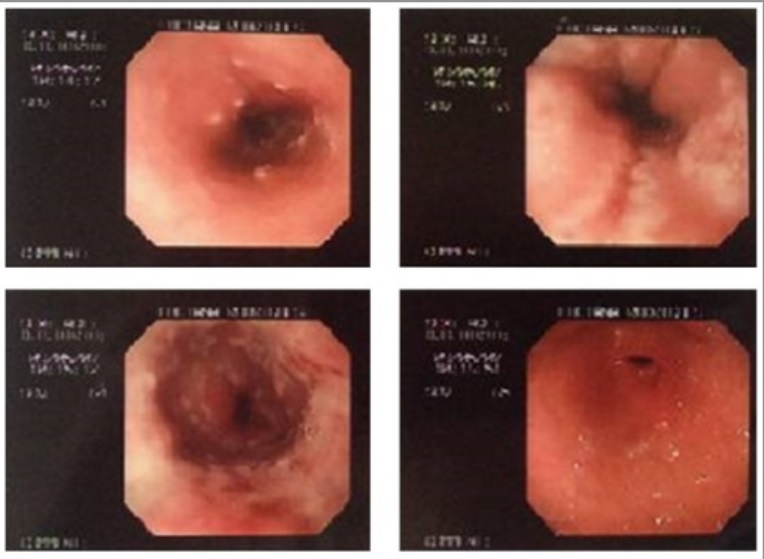
Imágenes de la esofagitis eosinofílica:
A. Esofagograma en un paciente con antecedente de impactaciones alimentarias recurrentes y disfagia que muestra múltiples anillos esofágicos (flecha blanca), dando la apariencia de un esófago corrugado o anillado e irregularidad de la mucosa (flecha negra).
B. La endoscopia muestra múltiples anillos transversales (flechas) y surcos en la mucosa (cabeza de flecha).
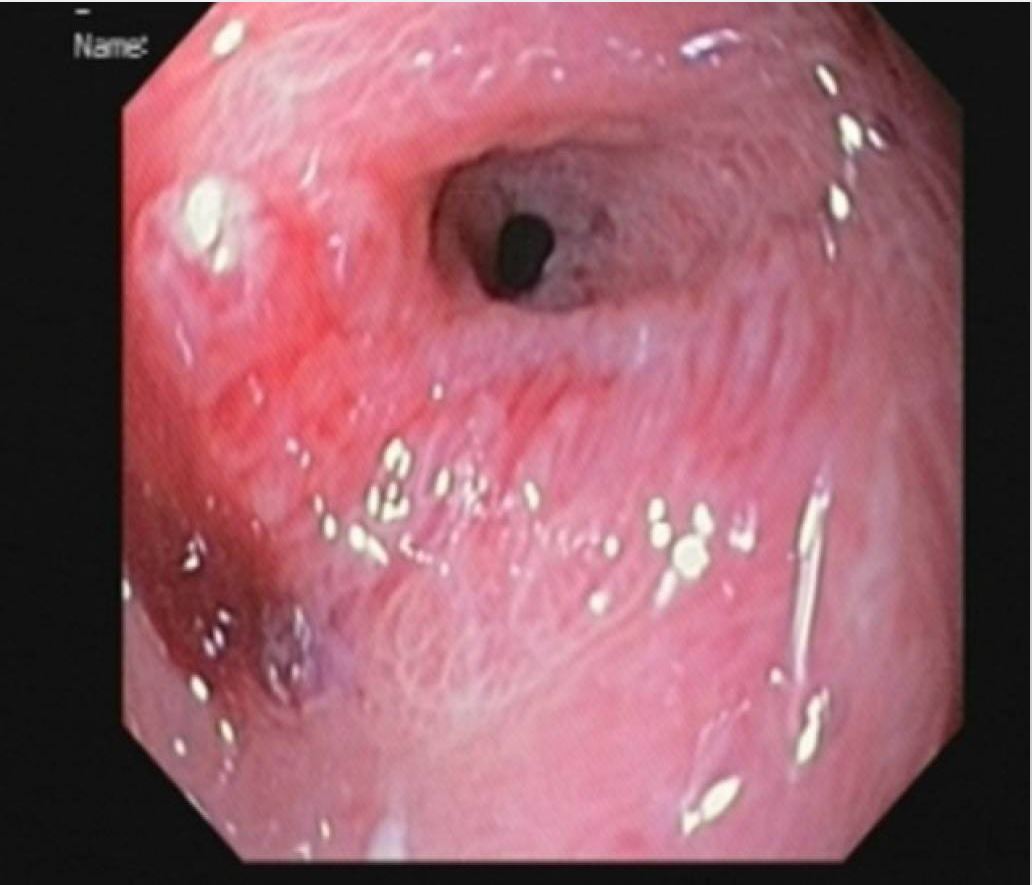
Hallazgo en la endoscopia superior de un niño con ingestión de álcali: Estenosis pilórica desarrollada 2 meses después de la lesión.
Imagen: “Pyloric stenosis after 2 months” por Dehghani SM, Aldaghi M, Javaherizadeh H. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La esofagitis por reflujo también se conoce como enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico (ERGE).
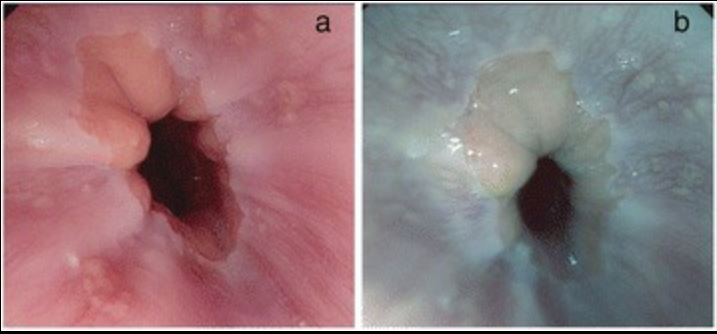
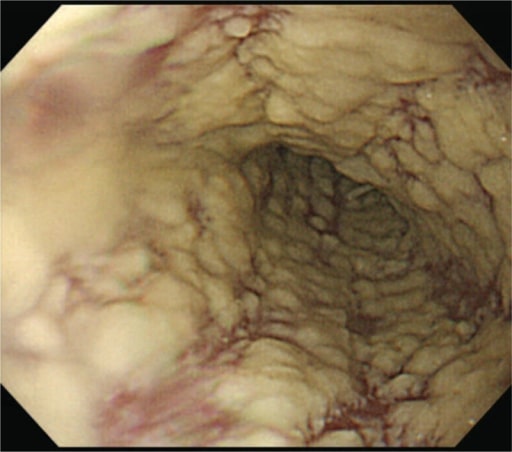
Esofagitis por reflujo en la endoscopia superior:
A: imagen de alta definición de los cambios esofágicos observados en la ERGE
B: imagen con realce de tono de la ERGE