Un VIPoma VIPoma A VIPoma is a rare neuroendocrine tumor arising primarily in the pancreas that releases large amounts of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). This process leads to chronic watery diarrhea with concomitant hypokalemia and dehydration, as well as wheezing and flushing (known as Verner-Morrison or WDHA syndrome). VIPoma es un tumor Tumor Inflammation neuroendocrino poco frecuente que surge principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el páncreas y que libera grandes cantidades de polipéptido intestinal vasoactivo. Este proceso da lugar a diarrea acuosa crónica con hipopotasemia y deshidratación concomitante, así como a sibilancias y sofocos, lo que se conoce como síndrome de Verner-Morrison o diarrea acuosa crónica con hipopotasemia y aclorhidria (Watery (acuosa), Diarrhea (diarrea), Hypokalemia (hipopotasemia), Achlorhydria (aclorhidria); WDHA, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria tumores surgen de forma esporádica, pero algunos se asocian a neoplasia endocrina múltiple 1. El diagnóstico se establece midiendo los LOS Neisseria niveles séricos de polipéptido intestinal vasoactivo. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento médico de los LOS Neisseria síntomas y la extirpación quirúrgica completa del tumor Tumor Inflammation cuando es posible.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Un VIPoma VIPoma A VIPoma is a rare neuroendocrine tumor arising primarily in the pancreas that releases large amounts of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). This process leads to chronic watery diarrhea with concomitant hypokalemia and dehydration, as well as wheezing and flushing (known as Verner-Morrison or WDHA syndrome). VIPoma es un tumor Tumor Inflammation neuroendocrino poco frecuente que segrega polipéptido intestinal vasoactivo.
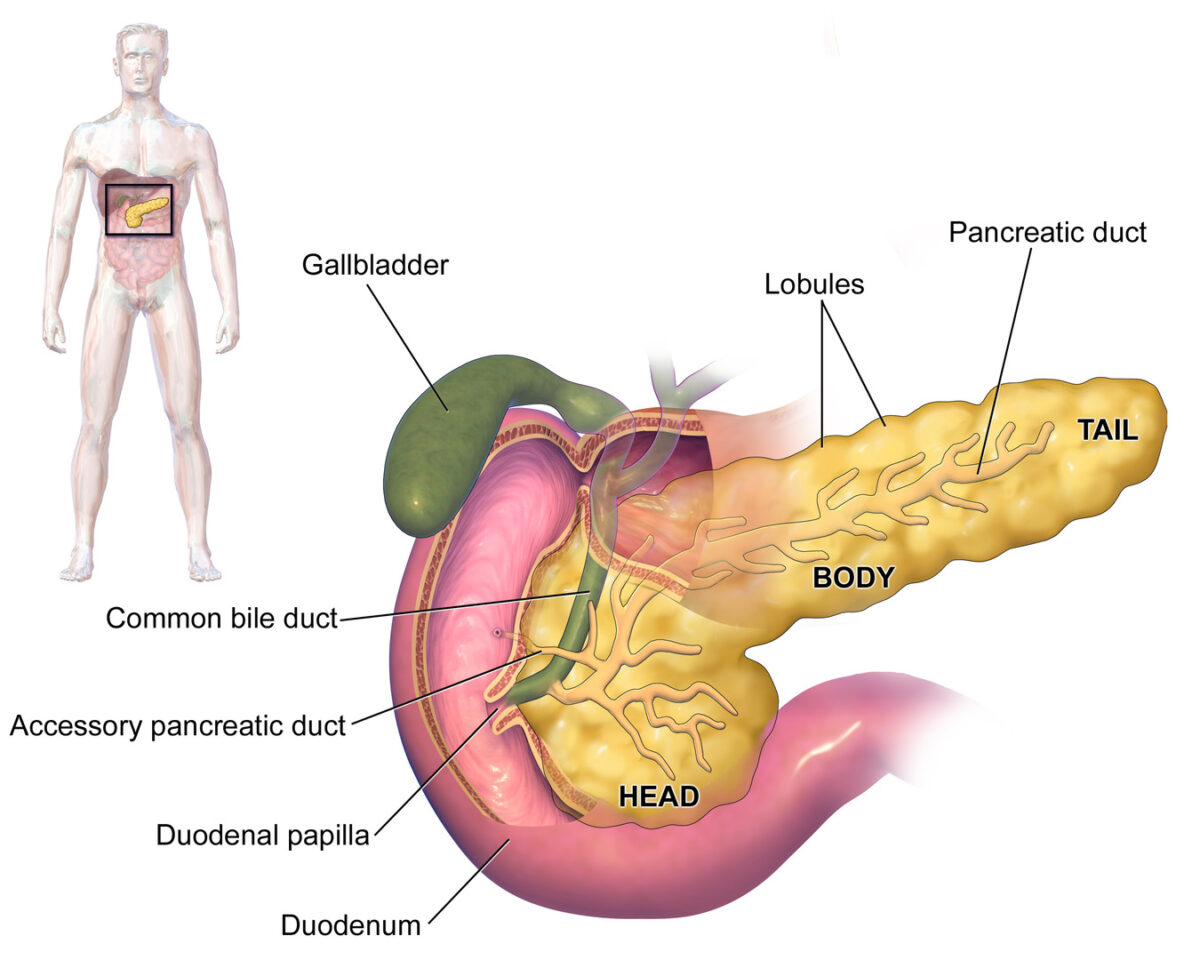
Anatomía del páncreas
Imagen: “Blausen 0699 PancreasAnatomy2” por Blausen. Licencia: CC BY 3.0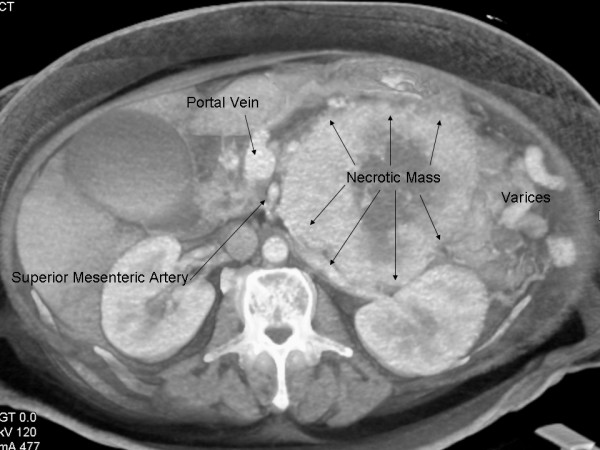
Tomografía computarizada que muestra un gran VIPoma pancreático necrótico
Imagen: “Multi-visceral resection of pancreatic VIPoma in a patient with sinistral portal hypertension” por Joyce DL, Hong K, Fishman EK, Wisell J, Pawlik TM. Licencia: CC BY 2.0