La tuberculosis (TB) es una enfermedad infecciosa causada por bacterias del complejo Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Las bacterias generalmente atacan los pulmones, pero también pueden dañar otras partes del cuerpo. Aproximadamente el 30% de las personas a nivel mundial están infectadas con este patógeno, y la mayoría alberga una infección latente. La tuberculosis se propaga por el aire cuando una persona con infección pulmonar activa tose o estornuda. M. tuberculosis es una bacteria ácido-alcohol resistente de crecimiento lento que puede sobrevivir en los macrófagos, lo que permite una infección latente que puede permanecer asintomática durante décadas, representando un desafío para el diagnóstico, la terapia y la prevención. El diagnóstico se establece con la prueba cutánea de la tuberculina, el cultivo de esputo y la imagenología pulmonar. El pilar del tratamiento son los medicamentos antimicobacterianos.
Last updated: Mar 25, 2022
La tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis ( TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis) es una enfermedad infecciosa que afecta a los LOS Neisseria pulmones y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ocasiones, a otros órganos. La tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis es causada por las bacterias del complejo Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis.
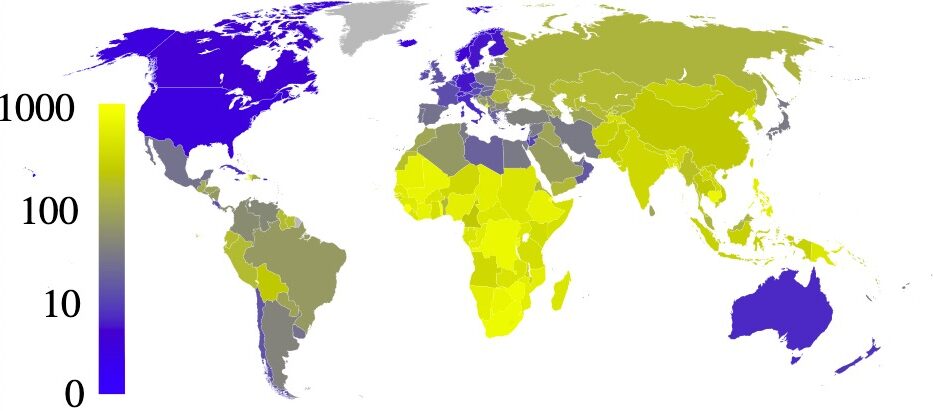
Prevalencia estimada de tuberculosis por cada 100 000 habitantes en 2007, por país
Imagen: “Estimated prevalence of tuberculosis” por Eubulides. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl complejo M. tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis es un grupo de especies que pueden causar TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos u otros animales.
Especies clave:
Caracteristicas:
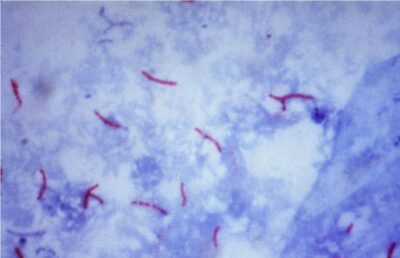
Tinción ácido-alcohol resistente de M. tuberculosis
Imagen: “Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria” por CDC/Dr. George P. Kubica. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoFactores de virulencia:
Transmisión:
Enfermedad activa primaria:
Infección latente:
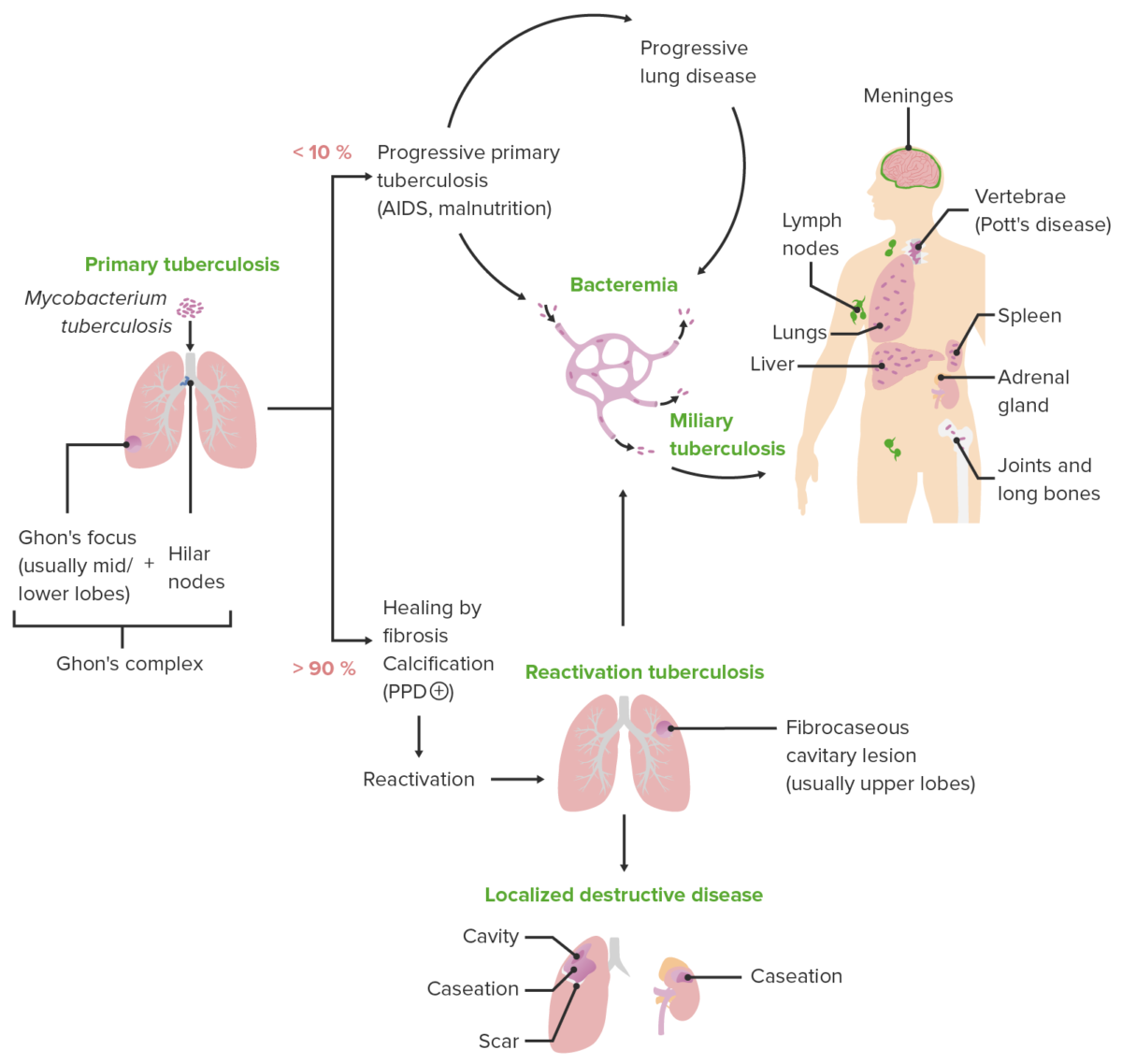
Diagrama esquemático que representa las diversas presentaciones clínicas de la tuberculosis junto con los mecanismos patológicos característicos de cada presentación
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0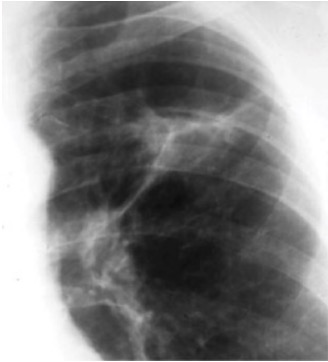
Radiografía de tórax del complejo de Ghon de TB activa (pulmón izquierdo)
Imagen: “Ghon’s complex” por Basem Abbas Al Ubaidi. Licencia: CC BY 4.0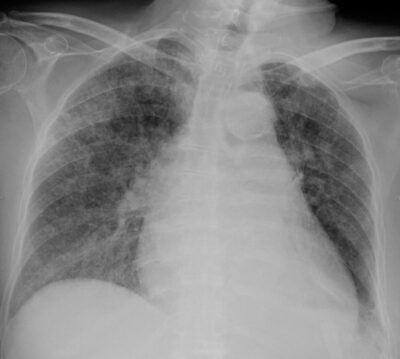
Radiografía de tórax de infiltrados miliares difusos, característicos de la TB miliar
Imagen: “Chest radiograph of miliary tuberculosis” por Benjamín Herreros et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0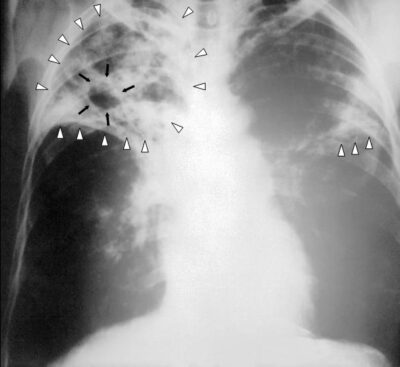
Radiografía de tórax de un paciente con tuberculosis: infiltrados reticulares bilaterales (triángulos blancos) y lesión cavitaria (flechas negras) en el lóbulo superior derecho
Imagen: “An anteroposterior X-ray” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Licencia: Dominio Público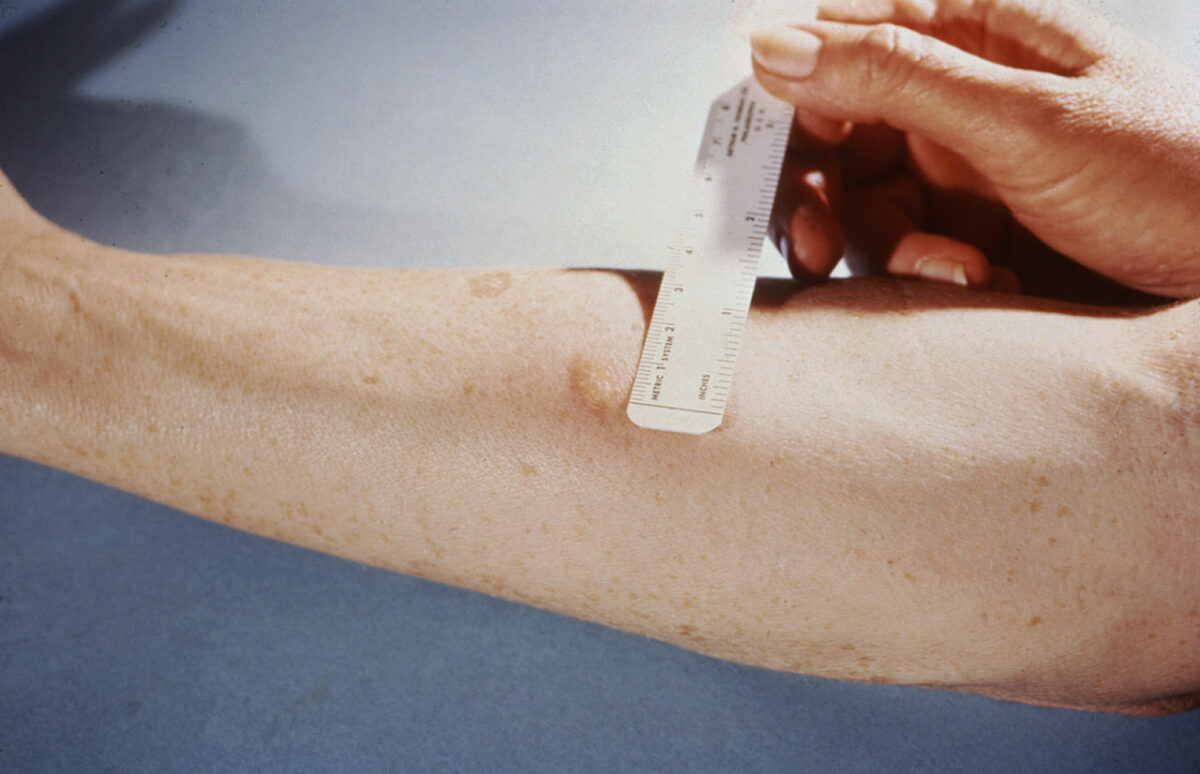
Medición de la reacción a una prueba cutánea de la tuberculina
Imagen: “Mendel-Mantoux-Test” por Public Health Image Library. Licencia: Dominio Público| Fase inicial | Fase de estabilización | |
|---|---|---|
| TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis activa |
|
|
| TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis latente | Opciones de tratamiento:
|
|