La tripanosomiasis africana, o enfermedad del sueño africana, es una infección parasitaria causada por el protozoo Trypanosoma brucei Trypanosoma brucei African trypanosomiasis, or African sleeping sickness, is a parasitic infection caused by the protozoa Trypanosoma brucei. There are 2 notable subtypes, T. brucei gambiense and T. brucei rhodesiense. Transmission is primarily vector borne through the tsetse fly. Trypanosoma brucei/African trypanosomiasis. Hay 2 subtipos notables, T. brucei gambiense T. brucei gambiense A hemoflagellate subspecies of parasitic protozoa that causes gambian or West african sleeping sickness in humans. The vector host is usually the tsetse fly (glossina). Trypanosoma brucei/African trypanosomiasis y T. brucei rhodesiense. La transmisión es principalmente por vectores a través de la mosca tsetsé. Las infecciones iniciales se presentan con inflamación localizada (chancro), linfadenopatía cervical, fiebre intermitente y otros hallazgos inespecíficos. Si no se trata, se produce afectación del SNC, que se caracteriza por trastornos del sueño, cambios de comportamiento, coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma y muerte. El diagnóstico se confirma mediante la identificación de tripanosomas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum frotis de sangre o serología. El tratamiento depende del subtipo y el estadio de la enfermedad. El tratamiento y la prevención precoz son claves para evitar secuelas a largo plazo y la muerte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
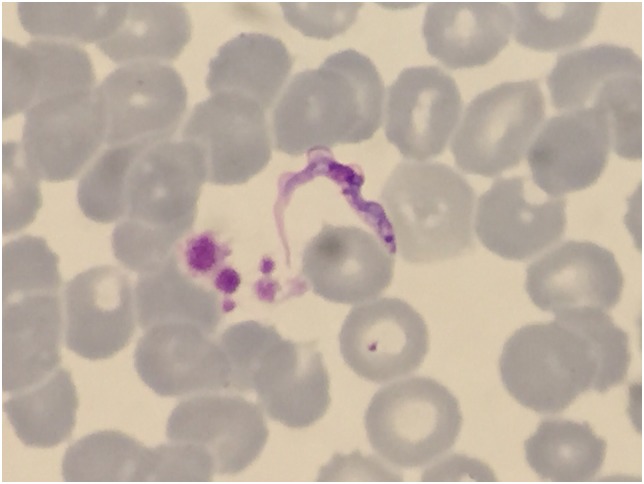
Tripanosomas en una gota delgada de sangre teñida con Giemsa de un viajero que regresa de Tanzania
Imagen: “Trypanosomes in a Giemsa-stained thin blood film from a Spanish traveler returning from Tanzania” por Joan Gómez-Junyent et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0T. brucei causa la tripanosomiasis africana, también conocida como enfermedad del sueño africana.
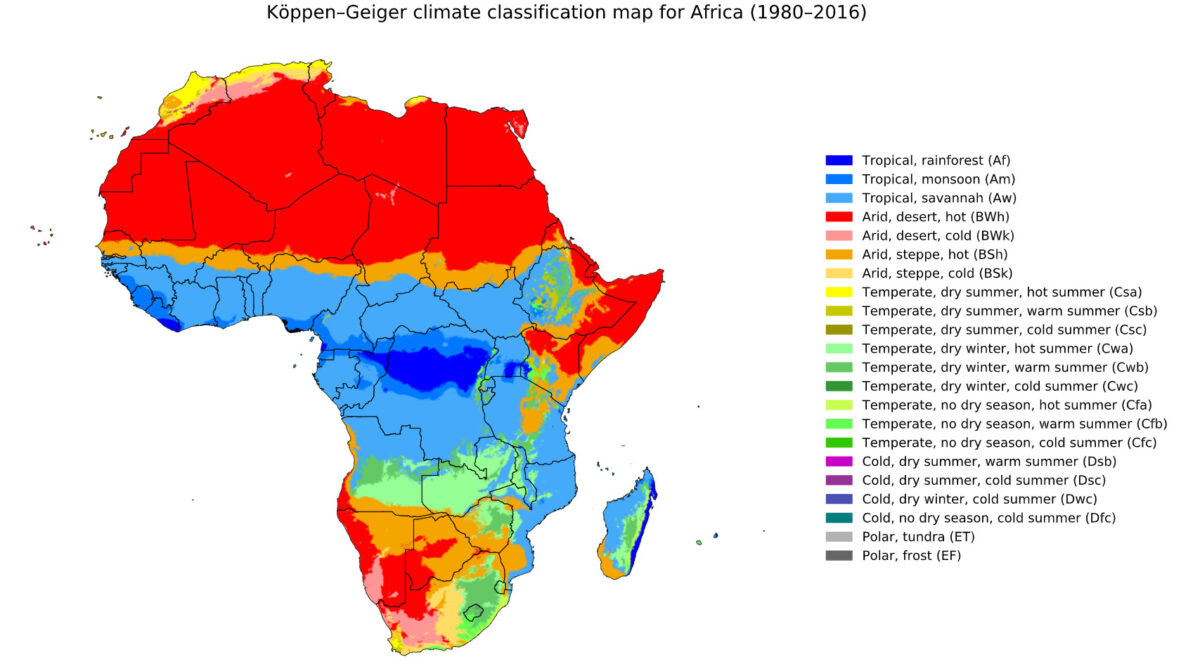
Distribución geográfica de la tripanosomiasis africana: T. brucei solo se encuentra en las áreas azules.
Imagen: “T. brucei is only found in the blue areas” por Beck, HE et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0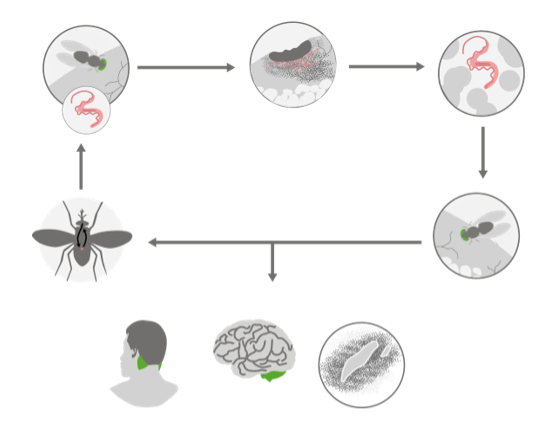
Imagen que ilustra la patogenia de la tripanosomiasis africana
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0La tripanosomiasis africana tiene 2 estadios: el estadio hemolinfático y estadio neurológica
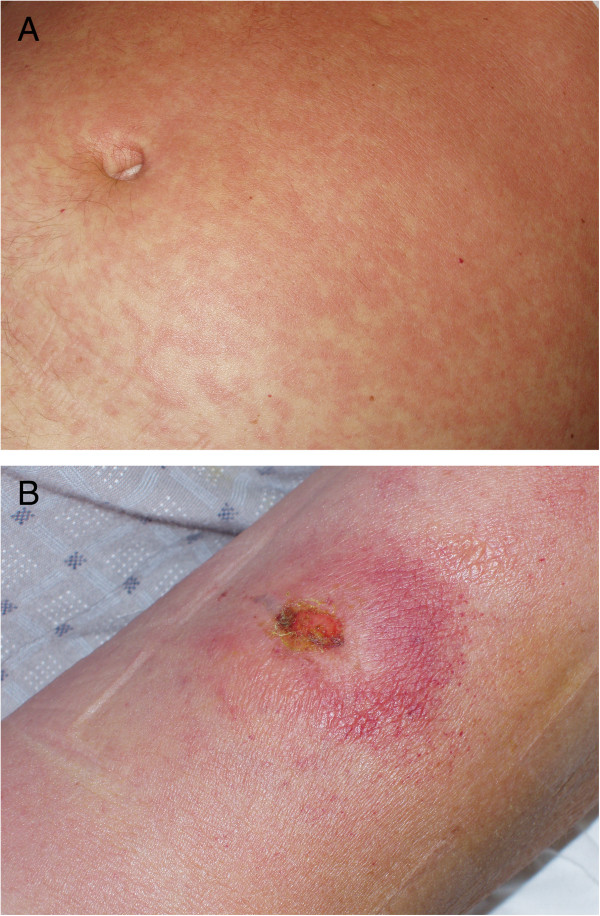
Manifestaciones cutáneas de la tripanosomiasis africana:
A: una erupción fina y rosada en el abdomen
B: chancro tripanosómico en el brazo izquierdo del paciente que se produce en el lugar de la inoculación
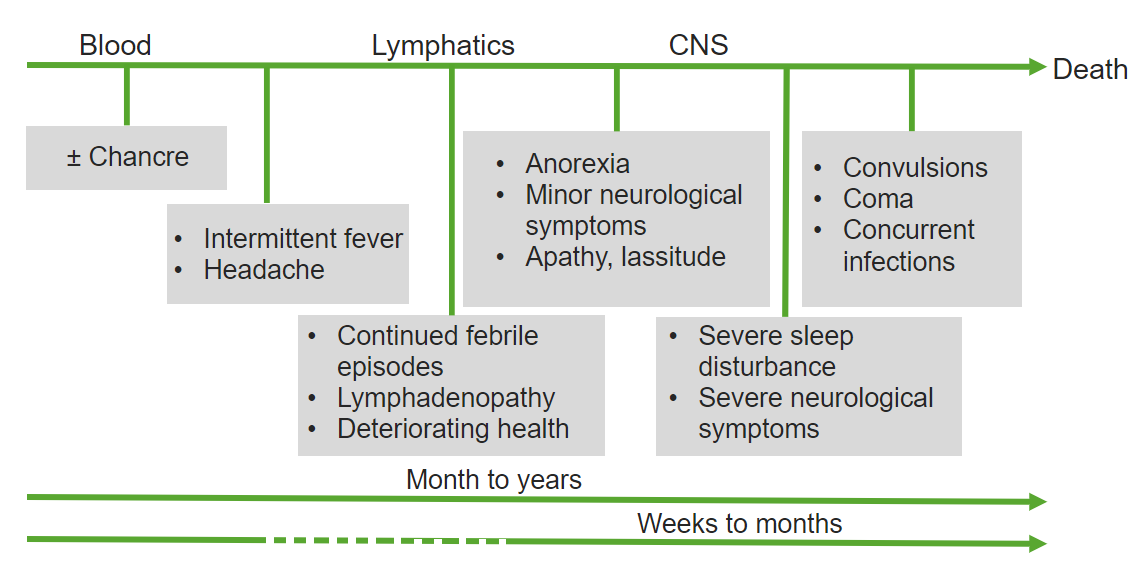
Imagen que muestra el curso temporal de la tripanosomiasis africana desde la infección inicial hasta la enfermedad crónica meses o años después (dependiendo de la subespecie involucrada)
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Protozoos | Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles | Leishmania Leishmania Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The disease is endemic to Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Mediterranean, and South and Central America. Clinical presentation varies, dependent on the pathogenicity of the species and the host’s immune response. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis | Trypanosoma | Trichomonas Trichomonas A genus of parasitic flagellate eukaryotes distinguished by the presence of four anterior flagella, an undulating membrane, and a trailing flagellum. Nitroimidazoles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características |
|
|
|
|
| Formas |
|
|
|
|
| Transmisión |
|
|
|
|
| Clínico |
|
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
Depende del síndrome clínico:
|
Depende de la enfermedad clínica:
|
|
| Prevención |
|
|
|
|
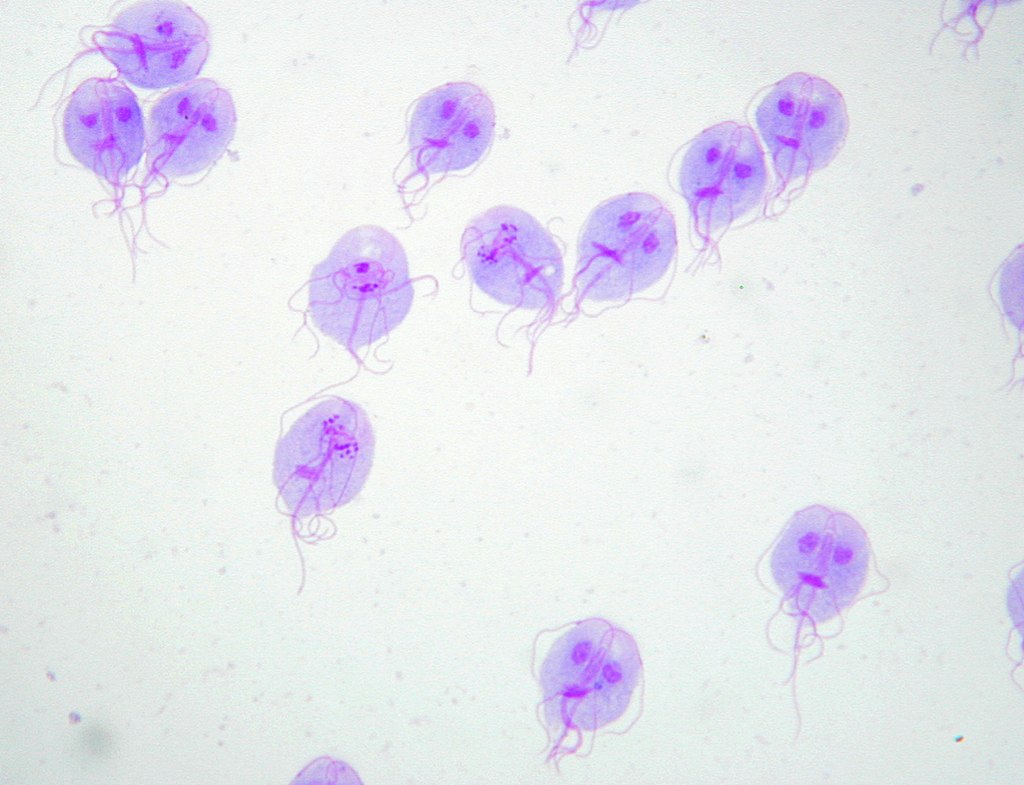
Tinción de Giemsa de trofozoítos de Giardia lamblia
Imagen: “Trophozoites of Giardia lamblia” por Eva Nohýnková, Department of Tropical Medicine, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Hospital Bulovka, Czech Republic. Licencia: CC BY 4.0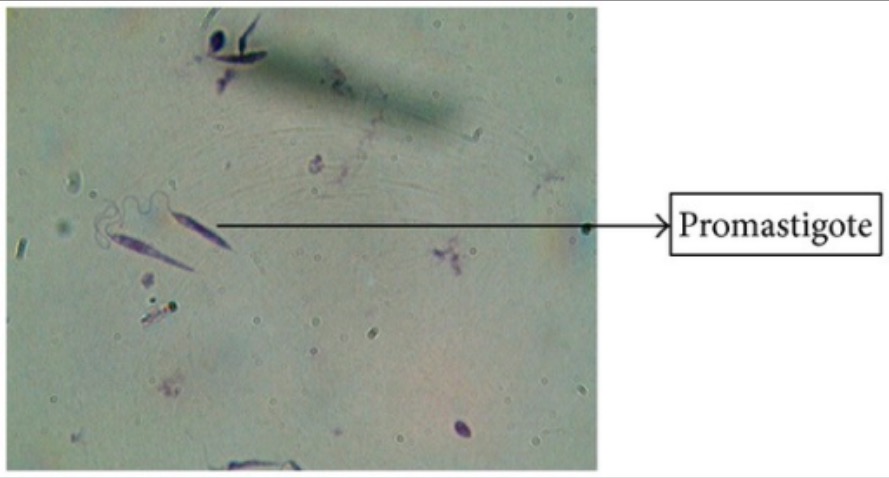
Tinción de Giemsa de promastigotes de Leishmania
Imagen: “Giemsa stain” por Arriyadh Community College, King Saud University, P.O. Box 28095, Riyadh 11437, Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 3.0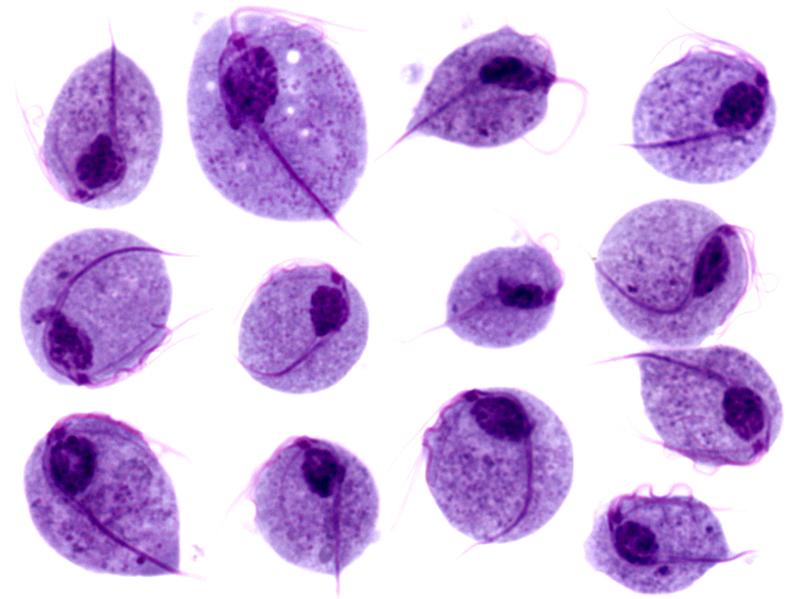
Imágenes microscópicas de trofozoítos de Trichomonas vaginalis
Imagen: “Trichomonas protozoa” por isis325. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.