El tejido adiposo es un tipo especializado de tejido conectivo que tiene funciones estructurales y metabólicas muy complejas, como el almacenamiento de energía, la homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death de la glucosa y una multitud de capacidades endocrinas. Los LOS Neisseria adipocitos y sus células estromales y macrófagos asociados expresan múltiples hormonas, factores de crecimiento y citoquinas. Existen tres tipos de tejido adiposo: el tejido adiposo blanco, el tejido adiposo pardo y el tejido adiposo beige o “brite”, que es una forma transitoria. El tejido adiposo pardo está presente sobre todo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el feto y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños pequeños, y su principal objetivo es la termogénesis. Los LOS Neisseria pequeños depósitos de tejido adiposo pardo persisten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vida adulta. El tejido adiposo blanco es el principal tejido adiposo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria adultos, y desempeña un papel en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varios estados de enfermedad, sobre todo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la obesidad, síndrome metabólico y diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus de tipo 2.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El tejido adiposo es un tipo de tejido conectivo laxo compuesto principalmente por células denominadas adipocitos.
Dos tipos clásicos:
3er tipo transitorio, recientemente descrito:
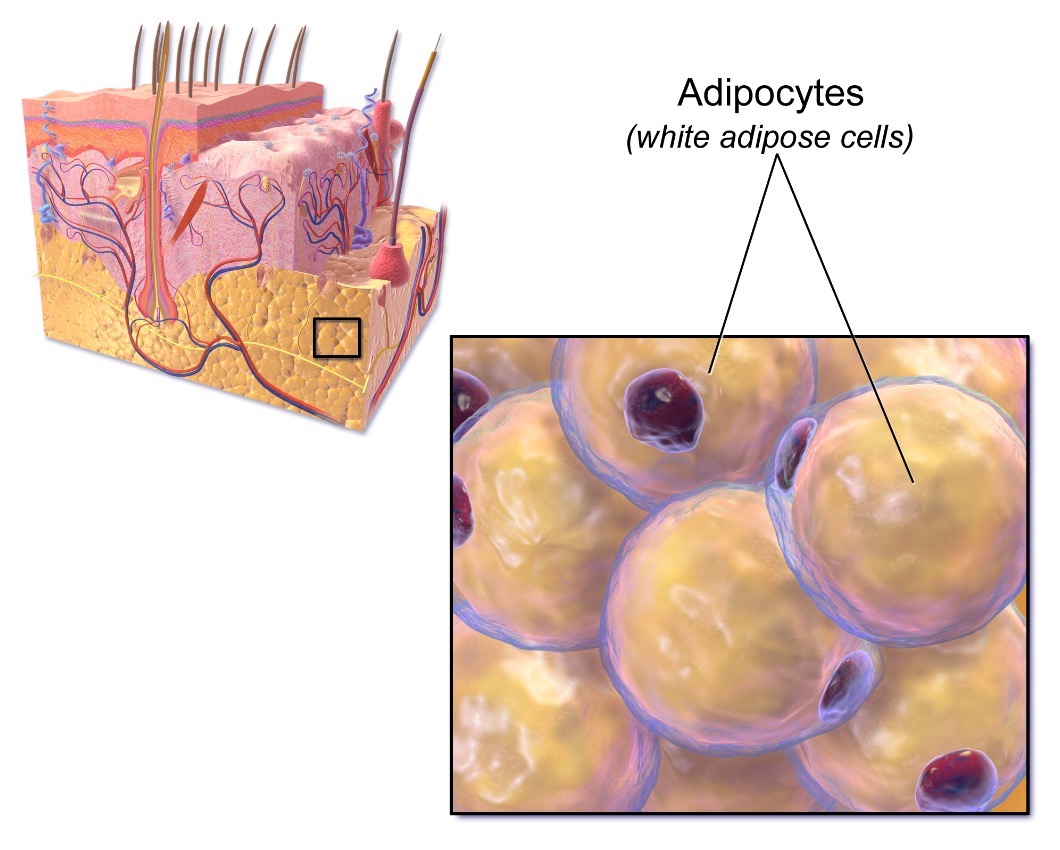
Tejido adiposo subcutáneo
Imagen: “Adipose Tissue” por Bruce Blaus. Licencia: Dominio Público, editado por Lecturio.Tejido adiposo blanco:
Tejido adiposo pardo o marrón:
Mujeres:
Hombres:
Tejido adiposo blanco:
Tejido adiposo pardo:
Beige: tejido adiposo de color marrón más claro que el marrón
Tejido adiposo blanco:
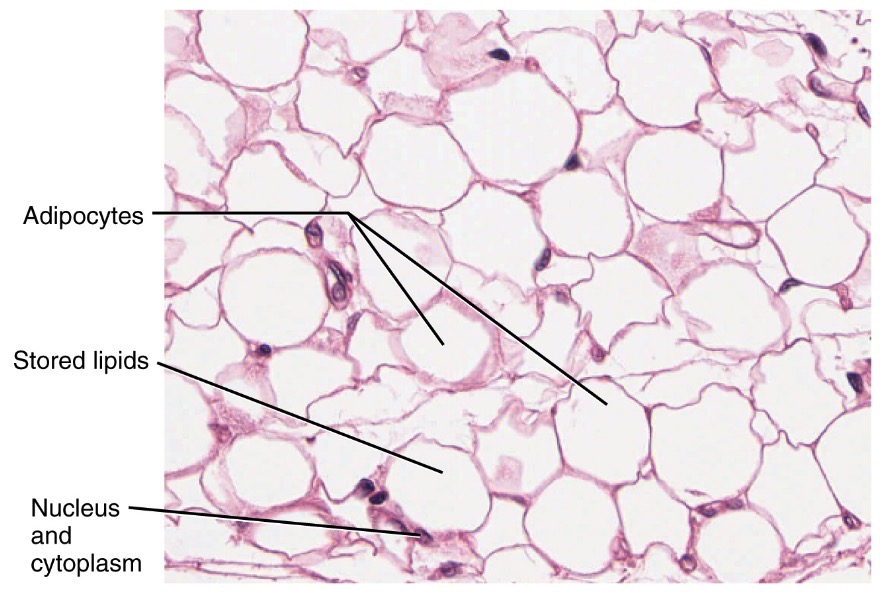
Tejido adiposo blanco: células con núcleos aplanados que se localizan en la periferia
Imagen: “White adipose tissue” por OpenStax College, Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax CNX. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Tejido adiposo pardo o marrón:
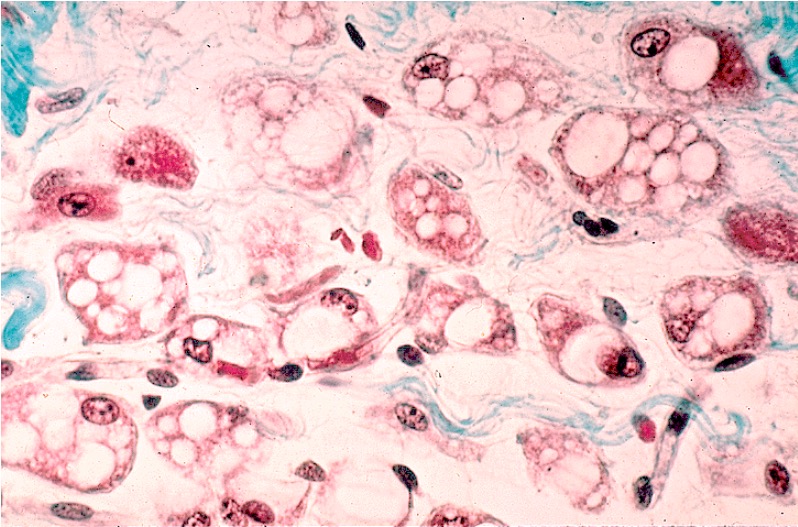
Tejido adiposo pardo o marrón:
El tejido adiposo pardo contiene adipocitos multivacuolados y tiene un color marrón característico debido a una marcada vascularización (4–5 veces más que el tejido adiposo blanco) y numerosas mitocondrias. Los adipocitos son más pequeños que los del tejido adiposo blanco y el núcleo está situado en el centro; los adipocitos blancos también están dispersos dentro del tejido adiposo marrón normal.
Grasa beige:
El tejido adiposo produce una serie de hormonas y citoquinas.
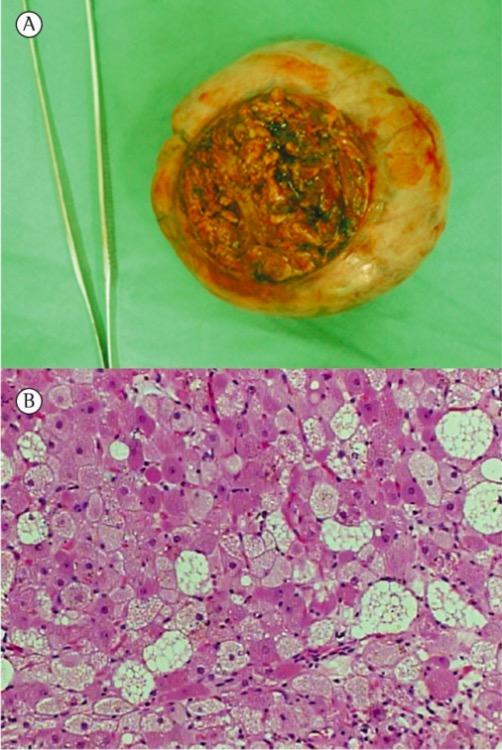
Hibernoma:
A: fotografía de un espécimen bruto, que muestra una masa bien circunscrita, encapsulada, blanda, de color marrón a amarillo, que mide 10 × 9 × 5 cm.
B: Histológicamente, el tumor consta de 2 tipos de células tumorales: células con citoplasma eosinófilo intenso y granular y células claras multivacuoladas llenas de gotas de lípidos, sin evidencia de atipia celular o mitosis (tinción de hematoxilina y eosina; aumento, ×200).
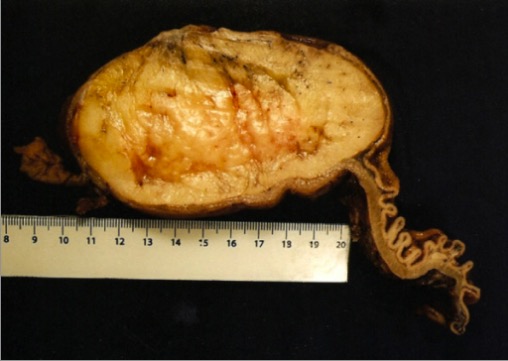
La superficie de corte de un lipoma submucoso gástrico gigante, que mide 12 × 8 × 6 cm:
Obsérvese la superficie amarilla homogénea en este espécimen fijado con formol, que tiende a blanquear los colores de los tejidos. El patrón histológico demostró un tejido adiposo bien diferenciado rodeado por una cápsula fibrosa.
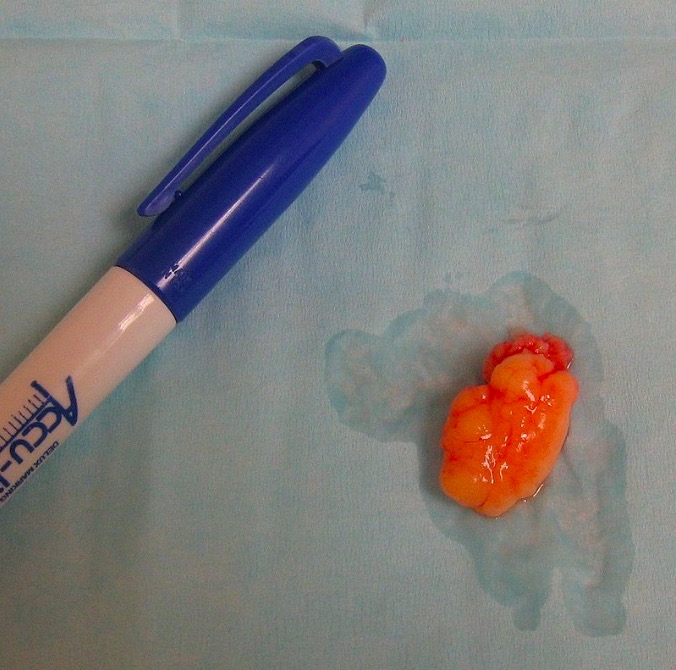
Lipoma:
Un pequeño lipoma subcutáneo, extirpado intacto, se muestra aquí en su estado fresco, con una fina cápsula que lo cubre. Obsérvese el color amarillo pálido (en comparación con la grasa normal no neoplásica).