El síndrome nefrítico es una afección renal con signos y síntomas producidos por la inflamación de los LOS Neisseria glomérulos (glomerulonefritis) y el aumento de la permeabilidad de las barreras glomerulares. Las características definitorias incluyen hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children (pero por debajo del rango nefrótico), cilindros de eritrocitos con eritrocitos dismórficos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la microscopía de orina y aumento de la creatinina sérica. Las causas pueden ser genéticas, autoinmunes, idiopáticas o postinfecciosas. La causa más común es la glomerulonefritis aguda post-estreptocócica. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos generales incluyen edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, hipertensión y oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation. El diagnóstico se realiza a partir de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, el examen físico y los LOS Neisseria estudios de laboratorio. A veces es necesaria una biopsia renal para establecer la causa subyacente. Puede haber un cuadro nefrítico-nefrótico combinado, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación crónica. El tratamiento y el pronóstico dependen de la causa y la gravedad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome nefrítico se define como una enfermedad renal causada por la inflamación y la lesión inmunomediada de los LOS Neisseria glomérulos con características clásicas de:
Causas primarias (renales) del síndrome nefrítico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños:
Causas secundarias de síndrome nefrítico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños:

Muestra de orina con hematuria: orina oscura o de color té
Imagen: “hematuria” por omicsonline.org. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Caso grave de vasculitis IgA o púrpura de Henoch-Schönlein:
Se observa púrpura palpable en el pie, la pierna y el brazo del niño.
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes también pueden presentar manifestaciones de enfermedad grave:
Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos son específicos de las causas subyacentes.
Estudios de laboratorio:
Imagenología (ultrasonido renal):
Pruebas específicas dependiendo de la enfermedad:
| Síndrome nefrótico | Síndrome nefrítico | |
|---|---|---|
| Edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema | ++++ | ++ |
| Presión arterial | Normal/elevado | Elevado |
| Proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children | ++++ | ++ |
| Hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma | – o microscópico | +++ |
| Otras características |
|
|
| Síndrome nefrítico | Estudios de laboratorio y adicionales | Resultados de la biopsia renal |
|---|---|---|
| Glomerulonefritis aguda post-estreptocócica |
|
|
| Glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa (un patrón de lesión glomerular, no una enfermedad específica; tiene los LOS Neisseria tipos I-III) | ↓ C3 |
|
| Glomerulonefritis lúpica |
|
|
| Nefropatía por IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | C3 Normal |
|
| Vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus HSP HSP Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), also known as immunoglobulin A vasculitis, is an autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis that typically presents as a tetrad of abdominal pain, arthralgia, hematuria, and purpuric rash. Henoch-Schönlein Purpura/ IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions |
|
|
| Síndrome de Alport (Glomerulonefritis hereditaria) | Biopsia de piel: Ab monoclonal contra la cadena alfa-5 (IV) (la proteína está ausente) | ME: Separación de la membrana basal glomerular, aspecto de tejido de cesta |
| Glomerulonefritis rápidamente progresiva (denota una lesión glomerular grave, pero tiene diferentes etiologías) | Depende de la causa subyacente | Histología más común: formación de semilunas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria glomérulos |
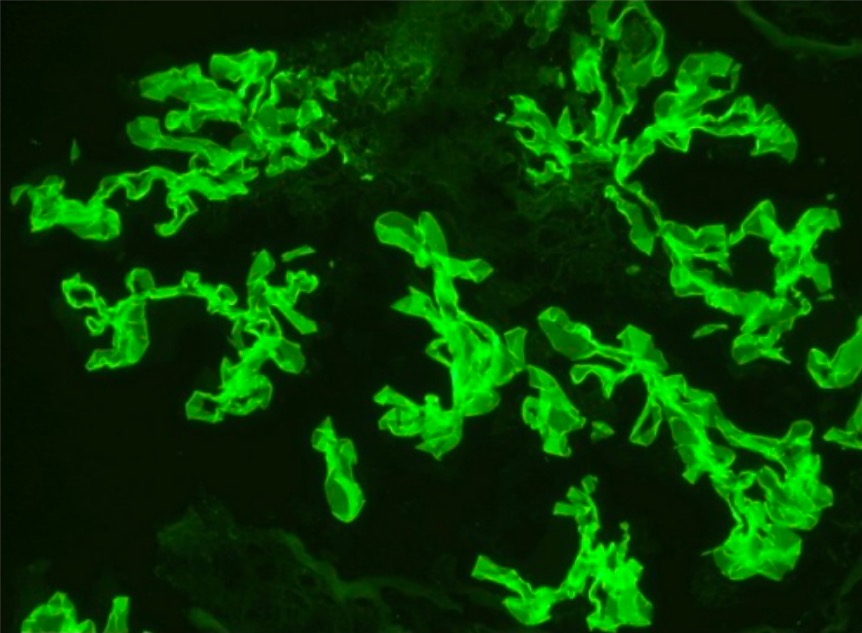
Tinción de inmunofluorescencia que muestra una tinción lineal de MBG para IgG consistente con la membrana de la enfermedad de Goodpasture
Imagen: “Immunofluorescence staining” por Department of Internal Medicine, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK 73117, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Nefropatía IgA: glomérulo con mesangio engrosado e hipercelularidad mesangial segmentaria
Imagen: “Glomerulus” por Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26506, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0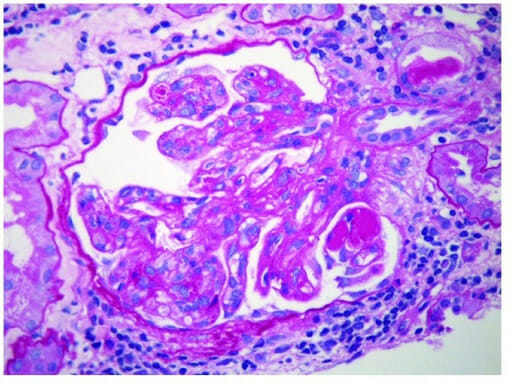
Glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa:
Proliferación endocapilar con extensos depósitos subendoteliales a lo largo de las paredes capilares glomerulares. También hay depósitos mesangiales (microscopía electrónica).
El tratamiento depende de la causa y la gravedad.