El síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico es una enfermedad aguda multisistémica causada por las bacterias productoras de toxinas, Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess y Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes. El síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico estafilocócico es más frecuente y se asocia a los LOS Neisseria tampones y al AL Amyloidosis taponamiento nasal. El síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico estreptocócico suele deberse a infecciones invasivas por estreptococos del grupo A, como la bacteriemia y la fascitis necrosante, y tiene una tasa de mortalidad más elevada. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes se presentan con fiebre, taquicardia, hipotensión, una erupción eritematosa y evidencia de disfunción orgánica multisistémica. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria datos clínicos, de laboratorio y de cultivos. El tratamiento implica la reanimación con líquidos intravenosos, antibióticos, soporte vasopresor e identificación y tratamiento del posible foco infeccioso.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico es una enfermedad aguda y multisistémica causada por bacterias productoras de toxinas:
Factores de riesgo:
Tanto el síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico estafilocócico como el estreptocócico se presentan de forma similar, con una rápida aparición de signos y síntomas ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuestión de horas).
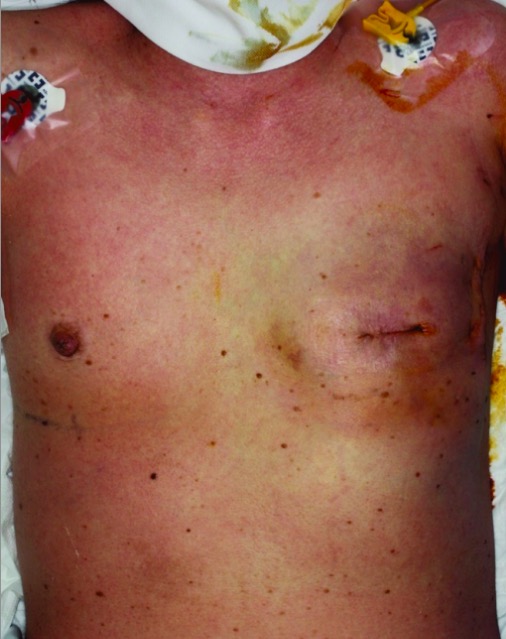
Erupción eritematosa difusa en un paciente con síndrome de shock tóxico estafilocócico
Imagen: “Case 2 on the first day of onset” por Department of Plastic Surgery, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.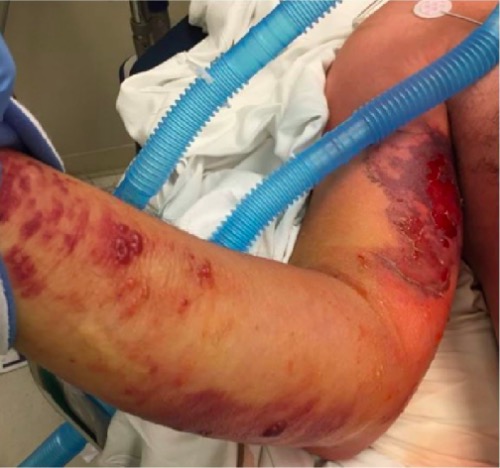
Hallazgos cutáneos en un paciente con fascitis necrosante y síndrome de shock tóxico estreptocócico
Obsérvese el edema difuso, la equimosis, el eritema y las ampollas
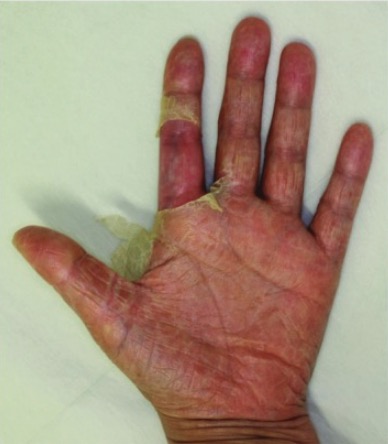
Erupción descamativa en las palmas debida a un síndrome de shock tóxico estafilocócico
Imagen: “The hands of case 1” por Department of Plastic Surgery, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editada por Lecturio.Según el Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, se utilizan los LOS Neisseria siguientes criterios para definir el síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico:
Síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico estafilocócico:
Síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico estreptocócico