Una quemadura es un tipo de lesión en la piel y tejidos más profundos causada por exposición a calor, electricidad, productos químicos, fricción o a la radiación. Las quemaduras se clasifican según su profundidad en superficiales, de espesor parcial (superficiales o profundas) y de espesor total (términos que han sustituido en gran medida a los "grados" numéricos, aunque el término "cuarto grado" se utiliza de forma variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables para indicar quemaduras de espesor total con afectación de estructuras más profundas). El tratamiento depende en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida de la extensión de la superficie afectada y de la profundidad de las quemaduras. El tratamiento incluye la reanimación con líquidos, la analgesia Analgesia Methods of pain relief that may be used with or in place of analgesics. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts adecuada y el cuidado apropiado de las heridas con el objetivo de prevenir las infecciones oportunistas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las quemaduras son lesiones traumáticas agudas de la piel o del tejido subyacente causadas por la exposición a energía térmica, productos químicos, descargas eléctricas o radiación.
Las quemaduras se describen utilizando dos identificadores: grado y severidad:
| Grado de quemadura | Características | Síntomas | Cicatrización |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quemadura superficial (1er grado) |
|
Prurito a dolor Dolor Inflammation |
|
| Quemaduras parciales superficiales (2do grado) |
|
Dolor Dolor Inflammation severo |
|
| Quemaduras superficiales profundas (2do grado) |
|
Dolor Dolor Inflammation severo | Recuperación parcial con formación de cicatrices |
| Quemaduras de espesor total (3er grado) |
|
Indolora porque las terminaciones nerviosas han sido destruidas |
|
| Quemaduras de espesor total/escaras (4to grado) | Sin dolor Dolor Inflammation |
|
Para determinar la gravedad de la quemadura, calcule el porcentaje de SCT lesionada:
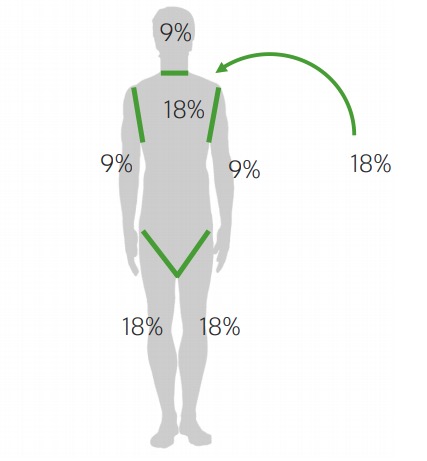
Regla de los 9 en adolescentes y adultos utilizada para determinar la SCT de la quemadura
Imagen por Lecturio.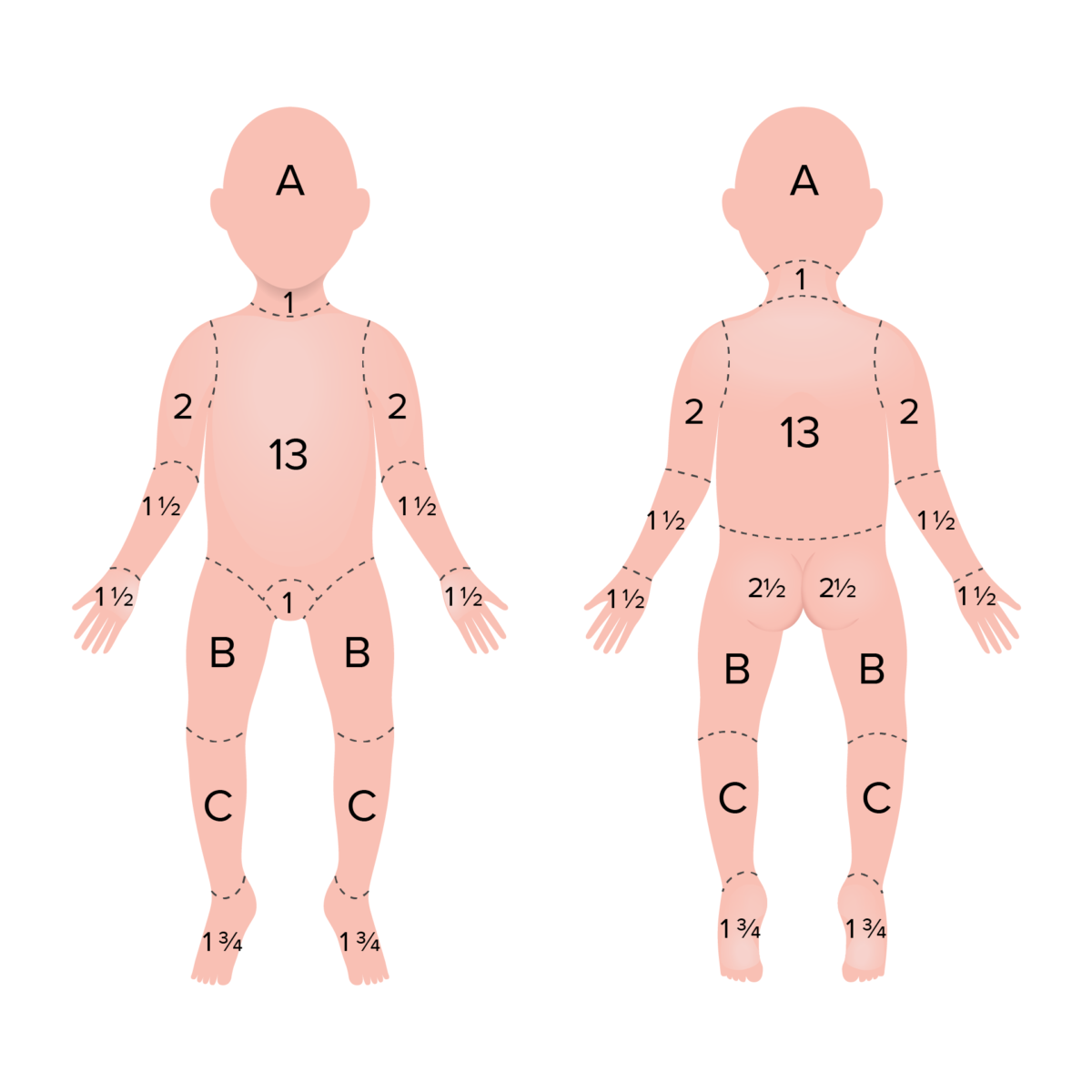
Regla de los 9 en niños utilizada para determinar la SCT de la quemadura
La cabeza y las piernas de los bebés y los niños representan una proporción mayor y menor de la SCT, respectivamente, en comparación con los adultos. A medida que los bebés y los niños crecen, el porcentaje representado por estas áreas cambia para parecerse más a los adultos.
El área A representa el 8,5% de la SCT en un niño de 1 año, el 6,5% en uno de 5 años, el 5,5% en uno de 10 años y el 4,5% en uno de 15 años.
El área B representa el 3,25% de la SCT en un niño de 1 año, el 4,0% en uno de 5 años, el 4,5% en uno de 10 años y el 4,5% en uno de 15 años.
El área C representa el 2,5% de SCT en un niño de 1 año, el 2,75% en uno de 5 años, el 3,0% en uno de 10 años y el 3,25% en uno de 15 años.
| Leve | Moderado | Severo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niños | < 5% SCT | 5%–10% SCT | > 10% SCT |
| Adulto | < 10% SCT | 10%–20% SCT | > 20% SCT |
| Ancianos | < 5% SCT | 5%–10% SCT | > 10% SCT |
| Completo | < 2% espesor completo | 2%–5% espesor completo, alto voltaje, inhalación, circunferencial, comorbilidad | > 5% espesor completo, alto voltaje, inhalación, circunferencial, comorbilidad |
| Disposición | Ambulatorio | Admisión | Unidad de quemados |
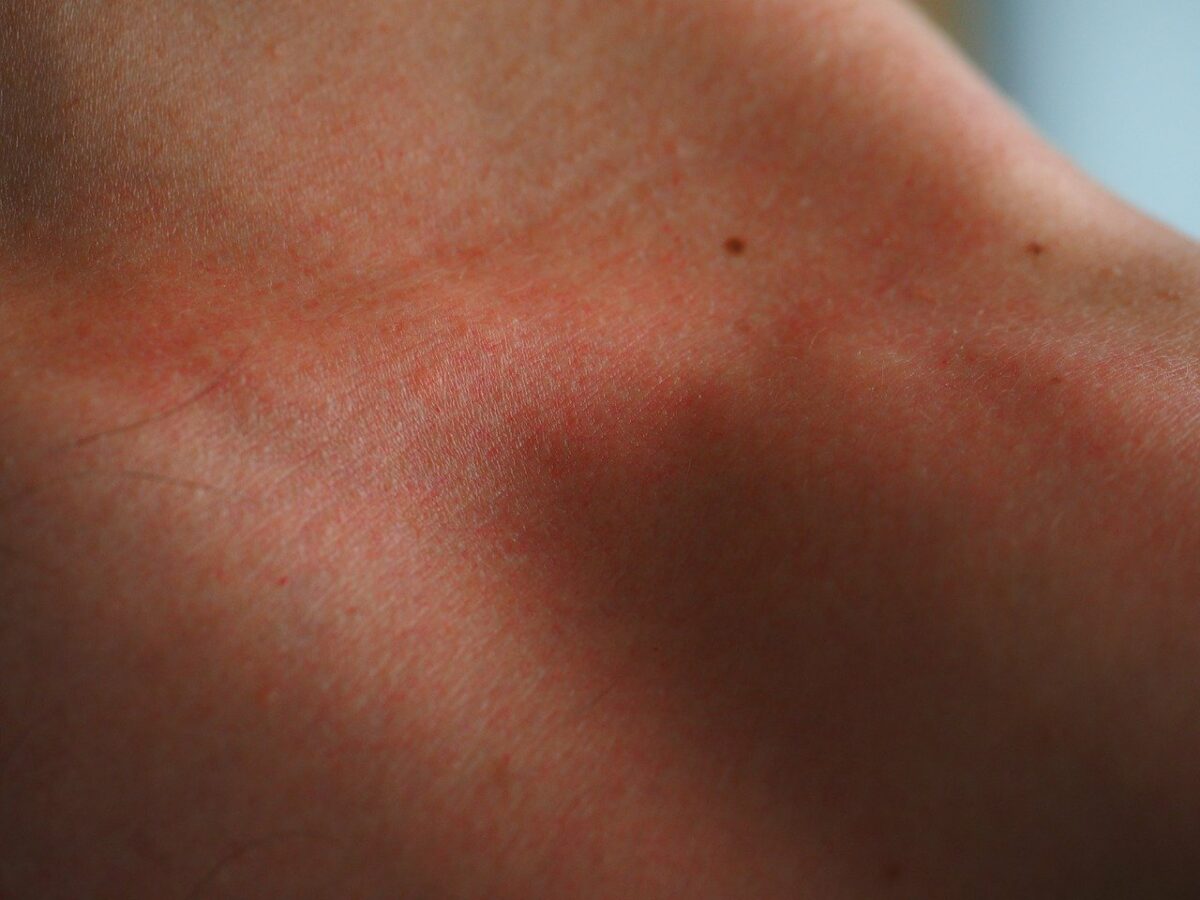
Quemadura superficial
Imagen: “Sunburn Skin Red Flushed Dermatology Burned” por Hans Braxmeier. Licencia: Dominio público.
Quemaduras faciales superficiales de espesor parcial causadas por el paso rápido de una bola de fuego tras una explosión de gasolina en un espacio cerrado
Imagen: “Burn injury and explosions: an Australian perspective” por Greenwood JE. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.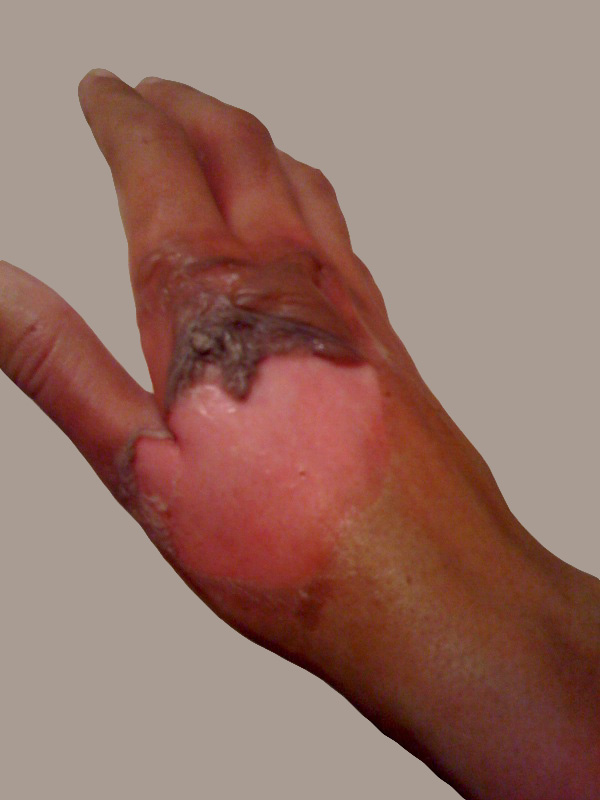
Quemadura profunda de espesor parcial
Imagen: “Major-2nd-degree-burn” por Westchaser. Licencia: Dominio público.
Quemaduras de espesor total
Imagen: “Burn injury and explosions: an Australian perspective” por Greenwood JE. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.Las quemaduras se producen por el contacto directo con:
La piel tiene una baja conductividad térmica, por lo que la mayoría de las quemaduras térmicas sólo afectan a la epidermis Epidermis The external, nonvascular layer of the skin. It is made up, from within outward, of five layers of epithelium: (1) basal layer (stratum basale epidermidis); (2) spinous layer (stratum spinosum epidermidis); (3) granular layer (stratum granulosum epidermidis); (4) clear layer (stratum lucidum epidermidis); and (5) horny layer (stratum corneum epidermidis). Skin: Structure and Functions.
Las áreas lesionadas pueden subdividirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 zonas, como una diana:
Tratamiento de quemaduras superficiales
El tratamiento de las quemaduras superficiales consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la administración de antiinflamatorios no esteroideos (AINE) y compresas frías para el dolor Dolor Inflammation.
Tratamiento de quemaduras de espesor parcial:
Manejo de quemaduras de espesor total: