El megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon es una dilatación grave y anormal del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy, y se clasifica como agudo o crónico. Hay muchas etiologías de megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon, incluyendo condiciones neuropáticas y de dismotilidad, infecciones severas, isquemia y enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. El megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon tóxico es una forma aguda de megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon con toxicidad sistémica, y conlleva la mayor morbilidad y mortalidad. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas más comunes son la distensión abdominal, dolor Dolor Inflammation, diarrea sanguinolenta y obstipación. El diagnóstico depende de la causa subyacente y suele establecerse con una combinación de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes del paciente, hallazgos de laboratorio e imagenología. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon crónico pueden necesitar laxantes, enemas y entrenamiento intestinal. El tratamiento del megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon agudo incluye cuidados de soporte, descompresión y posible cirugía.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon es una dilatación severa del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy secundaria a una alteración de la motilidad o a un proceso inflamatorio. La condición se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del tiempo de evolución y la duración:
Estos estudios ayudan a evaluar la gravedad de la enfermedad, las complicaciones y las posibles causas.
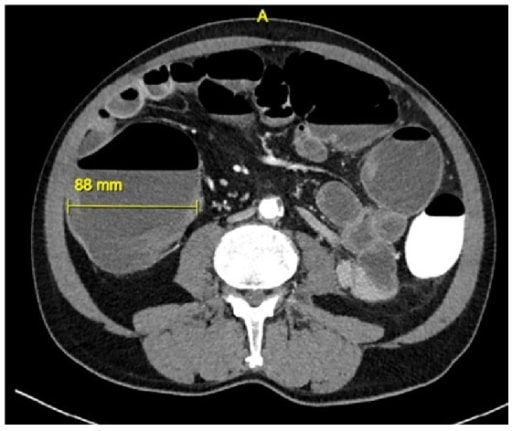
Imagen por tomografía computarizada de megacolon tóxico secundario a infección por C. difficile
Esta TC muestra una distensión colónica de 8,8 cm.
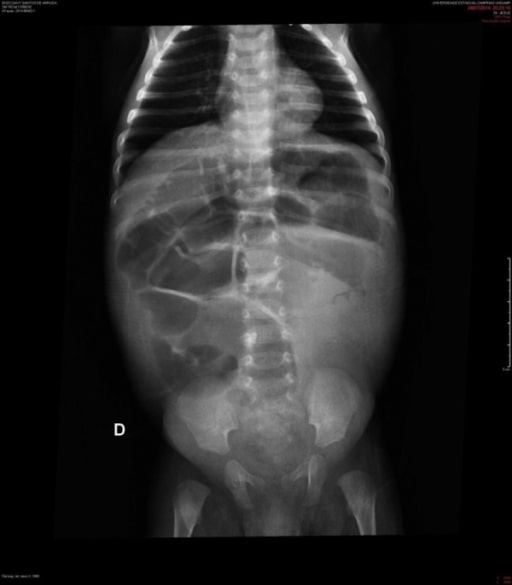
Radiografía abdominal de un paciente de 2 meses con megacolon agangliónico congénito (enfermedad de Hirschsprung)
Esta imagen muestra las asas dilatadas del intestino delgado y del colon.
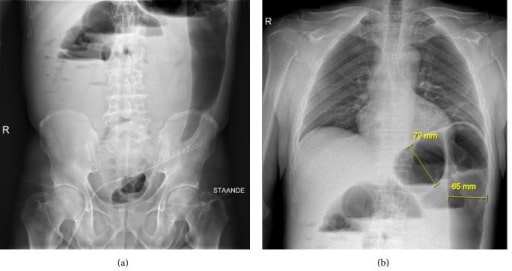
Imagen radiográfica de un paciente con megacolon tóxico
La radiografía se realizó en posición de pie y muestra los niveles de líquido colónico en la región epigástrica y la flexión esplénica.
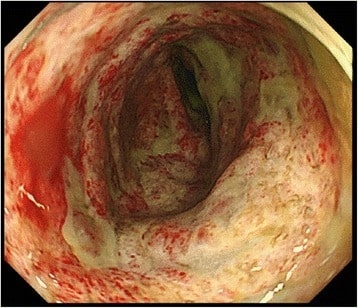
Imagen de colonoscopia que muestra una úlcera grave y una pseudomembrana en el colon descendente en un paciente con megacolon tóxico
Imagen: “Colonoscopy” por Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Clinical Research Institute Cancer Research Division, National Kyushu Medical Center, Fukuoka, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 4.0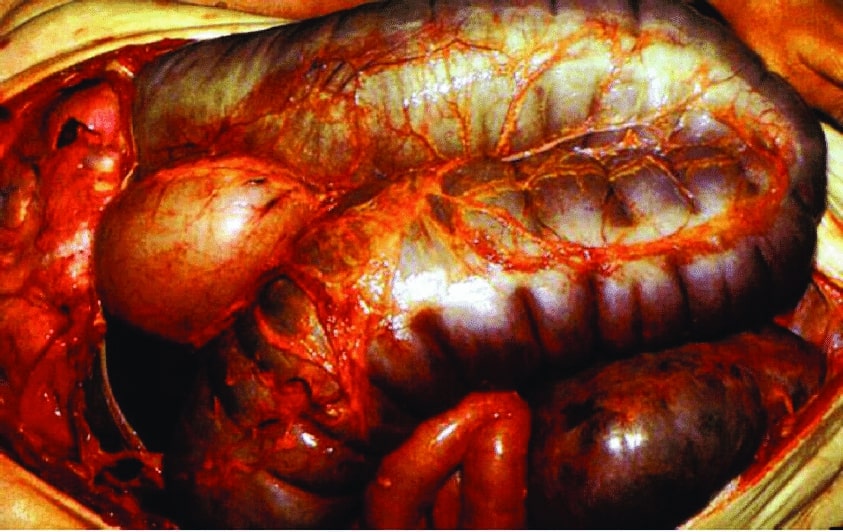
Hallazgos quirúrgicos en el megacolon tóxico relacionado con la colitis por C. difficile
Imagen: “Toxic megacolon” por University of Pittsburgh Department of Pathology. Licencia: CC BY 3.0