El liquen plano es una enfermedad cutánea inflamatoria idiopática mediada por células. Se caracteriza por lesiones cutáneas pruriginosas, planas, papulares y de color púrpura, que suelen aparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las superficies flexoras de las extremidades. Otras zonas afectadas son los LOS Neisseria genitales, las uñas, el cuero cabelludo y las mucosas. Se desconoce la etiología exacta, pero se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia descubierto que está asociada a la infección por hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus, a otras enfermedades y a múltiples medicamentos. Para confirmar el diagnóstico se utiliza una biopsia de la lesión más prominente. El liquen plano cutáneo suele resolverse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 1–2 años. Otras formas, sin embargo, son crónicas y persistentes. Los LOS Neisseria corticoides tópicos son el tratamiento de elección.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
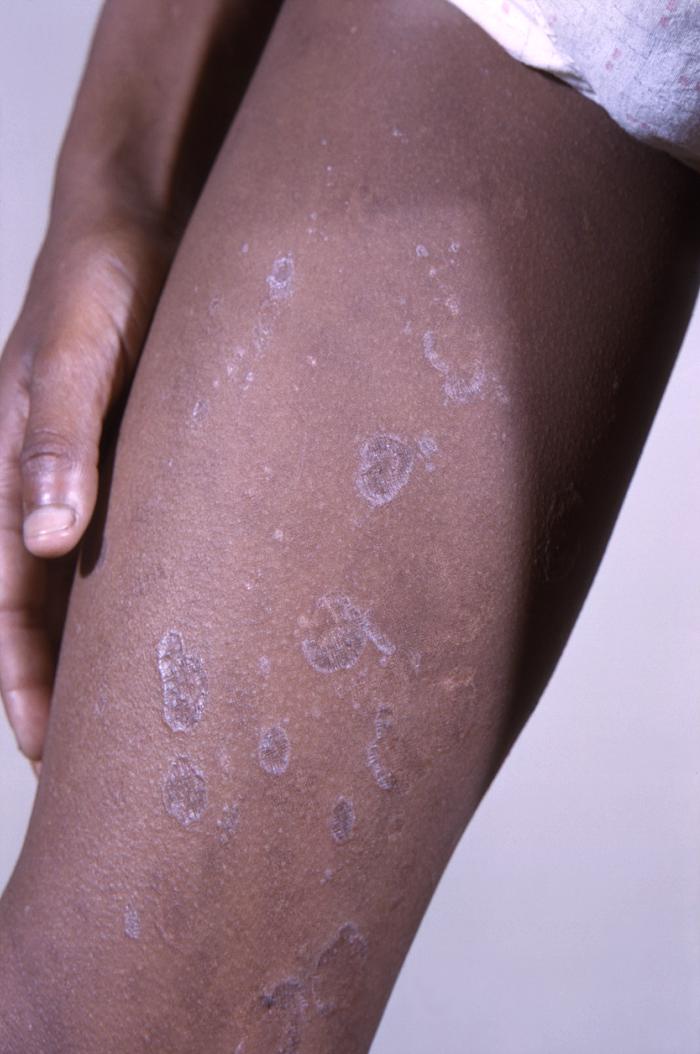
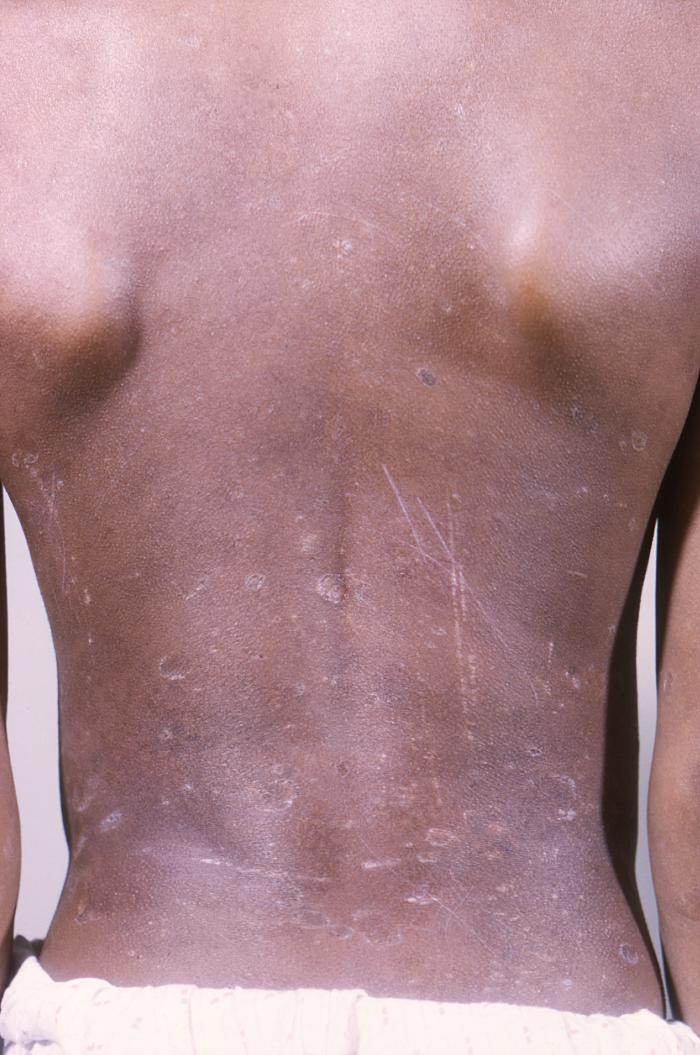
Liquen plano en la espalda de un niño afroamericano de 11 años con un antecedente de 6 años de liquen plano generalizado. Obsérvese la presencia del fenómeno de Koebner: la propagación de las lesiones de liquen plano a lo largo de las zonas de traumatismo, incluidos los arañazos en la piel.
Imagen: “12186” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público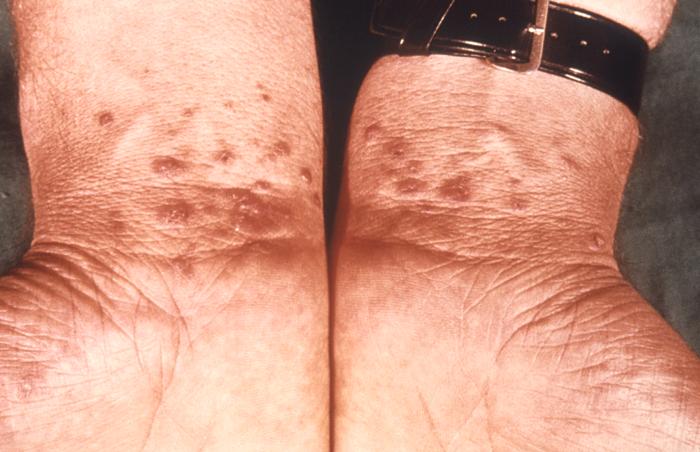
Liquen plano bilateral en las muñecas
Imagen: “6545” por CDC/ Susan Lindsley. Licencia: Dominio Público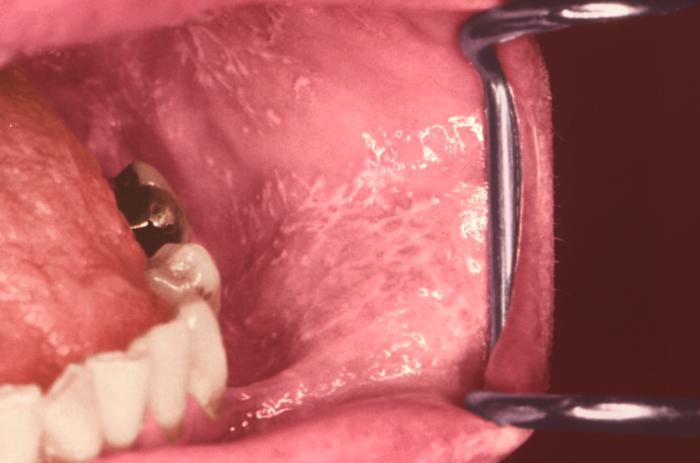
Liquen plano que se presenta como estrías de Wickham en la mucosa oral
Imagen: “12632” por CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter. Licencia: Dominio Público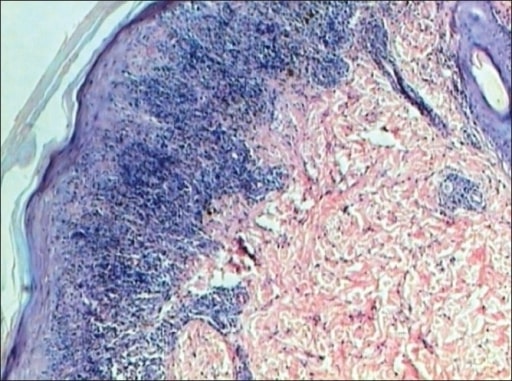
Liquen plano: la epidermis presenta hiperqueratosis, hipergranulosis, acantosis y crestas de Rete en dientes de sierra. La dermis muestra un infiltrado linfocítico en banda que toca la epidermis (tinción H&E, ×40).
Imagen: “Lichen planus” por Department of Pathology, JJ Hospital, Mumbai, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0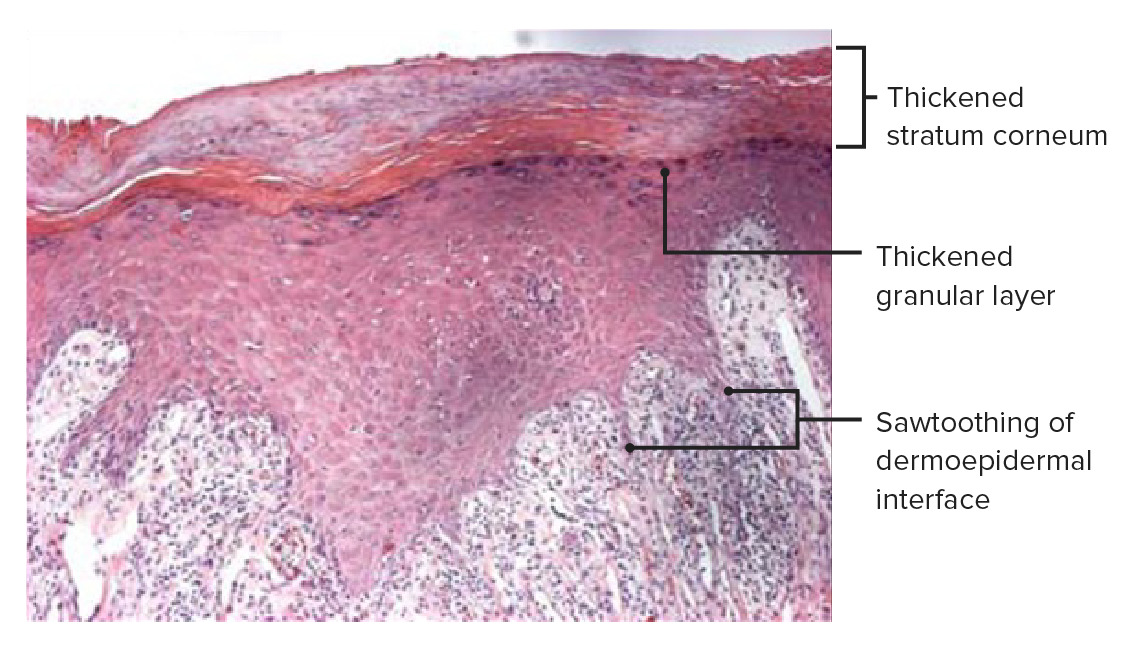
Histopatología de una biopsia de piel de una placa de liquen plano que muestra densos infiltrados inflamatorios liquenoides debajo de la lámina propia. Obsérvese la inflamación en la unión dérmico-epidérmica y un contorno inferior angulado en zigzag, que le da el aspecto de diente de sierra característico del liquen plano. Obsérvese también el engrosamiento de la capa de células granulares (hipergranulosis) y del estrato córneo (hiperqueratosis), que son más pronunciados en las líneas blancas de las estrías de Wickham.
Imagen: “Histopathology of lichen planus” por Shi G, Sohn KC et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editada por Lecturio.