La inflamación es un complejo conjunto de respuestas a infecciones y lesiones que involucran a los LOS Neisseria leucocitos como principales mediadores celulares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la defensa del cuerpo contra organismos patógenos. La inflamación también se considera una respuesta a la lesión tisular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el proceso de cicatrización de heridas. Los LOS Neisseria 5 signos cardinales de la inflamación son dolor Dolor Inflammation, calor Calor Inflammation, eritema, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema y pérdida de función. La principal respuesta celular involucra a los LOS Neisseria neutrófilos y macrófagos para fagocitar y lisar el organismo dañino o reparar el tejido necrosado después de la lesión. La inflamación puede ser patológica si se prolonga o cuando los LOS Neisseria procesos normales crean una respuesta excesiva (como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la aterosclerosis). Existen múltiples mediadores de la inflamación que se superponen con la inmunidad innata cuando responden a estímulos nocivos. La inflamación puede volverse crónica, dando como resultado la formación de granulomas Granulomas A relatively small nodular inflammatory lesion containing grouped mononuclear phagocytes, caused by infectious and noninfectious agents. Sarcoidosis, daño tisular y la pérdida de la función de los LOS Neisseria órganos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La inflamación es un conjunto complejo de respuestas a infecciones y lesiones, que involucra a los LOS Neisseria leucocitos como los LOS Neisseria principales mediadores celulares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la defensa del cuerpo contra organismos patógenos. La inflamación también se considera una respuesta a la lesión tisular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el proceso de cicatrización de heridas.
Tipos:
Desencadenantes de la inflamación aguda:
Características de la inflamación aguda:
Características de la inflamación crónica:
Inflamación innata:
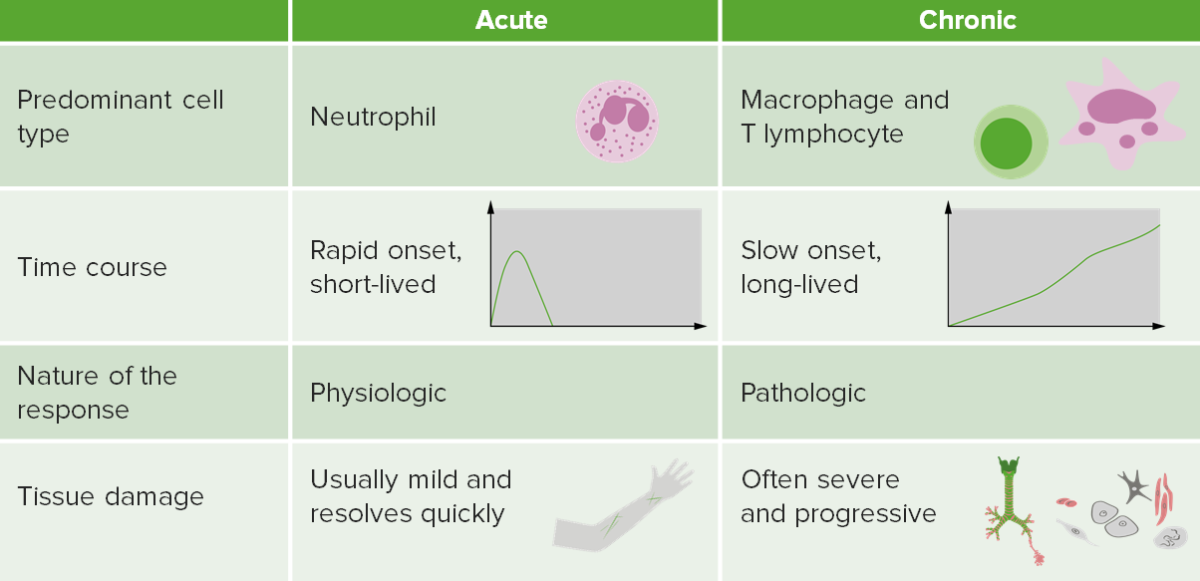
Contraste de inflamación aguda y crónica
Imagen por Lecturio.Existen múltiples mediadores de la inflamación que llevan a las células inflamatorias hacia los LOS Neisseria sitios de lesión y se superponen con la inmunidad innata cuando responden a estímulos dañinos.
| Reactante | Función |
|---|---|
| PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) |
|
| VES |
|
| Haptoglobina |
|
| SAA | Provoca el reclutamiento de células inmunitarias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sitio de la inflamación. |
Vasodilatación:
Mayor permeabilidad:
La liberación celular de sustancias químicas provoca:
Reclutamiento de neutrófilos:
Fagocitosis y eliminación:
Liberación de mediadores:
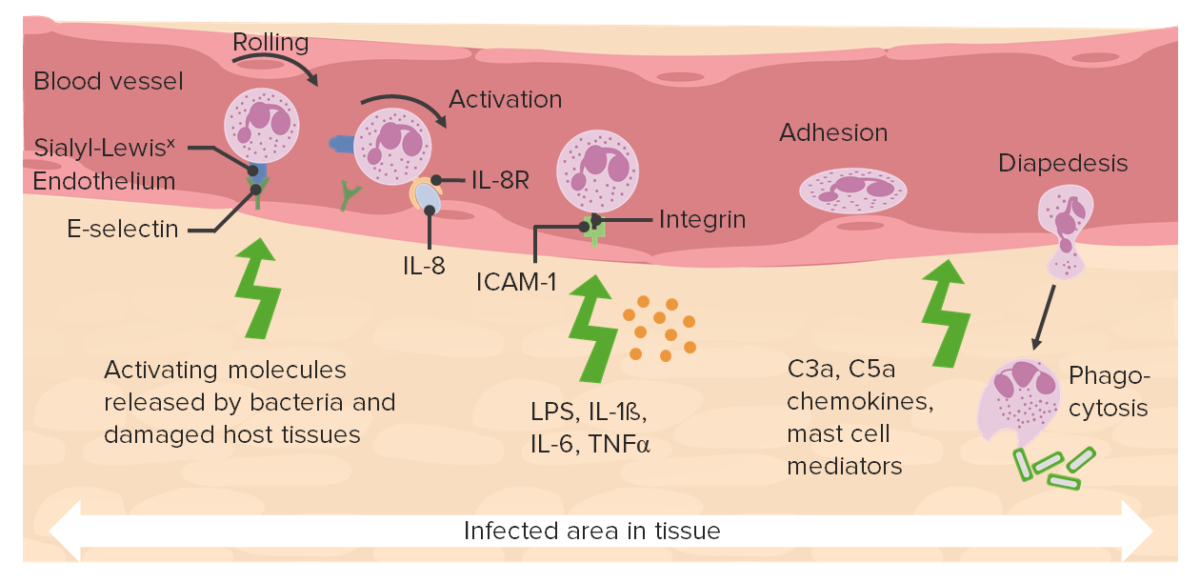
Interacción de varias quimioquinas:
Varios ligandos y receptores se unen y promueven la extravasación de neutrófilos.
C3a y C5a: complemento
ICAM-1: molécula de adhesión intercelular 1 (en inglés)
LPS: lipopolisacáridos
TNF-α: factor de necrosis tumoral alfa (en inglés)
La inflamación puede resolverse, formar abscesos o volverse crónica.
La inflamación aguda con lesiones persistentes puede conducir a inflamación crónica. La inflamación crónica también se puede observar con infecciones virales y trastornos autoinmunes.
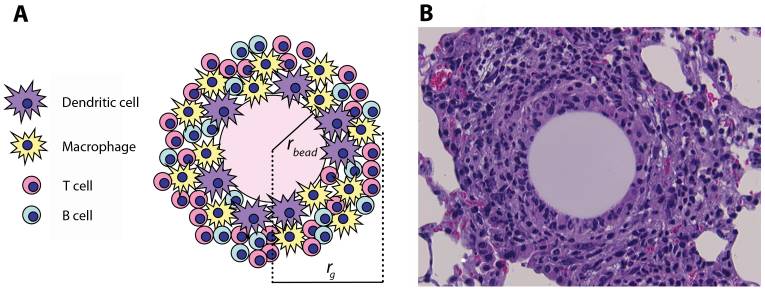
(A) Representación esquemática y (B) apariencia histológica de un granuloma pulmonar artificial inducido en un ratón 4 días después de la inyección de microesferas recubiertas de derivado proteico purificado (PPD, por sus siglas en inglés) (tinción H&E; aumento: ×800)
rbead: radio de la esfera
rg: radio del granuloma
Ejemplos de inflamación que se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una respuesta patológica:
Trastornos por deficiencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos mediadores de la respuesta inflamatoria: