Las infecciones del tracto urinario (ITU) son frecuentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños. Las infecciones de vías urinarias pueden presentarse como cistitis, pielonefritis o bacteriuria Bacteriuria The presence of bacteria in the urine which is normally bacteria-free. These bacteria are from the urinary tract and are not contaminants of the surrounding tissues. Bacteriuria can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. Significant bacteriuria is an indicator of urinary tract infection. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children asintomática, y su presentación clínica puede variar mucho en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la edad del paciente. La E. coli fecal es el patógeno más común. Las vías de infección pueden ser ascendentes (la más frecuente) o hematógenas. La sospecha de ITU se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria síntomas urinarios inferiores (disuria, polaquiuria) o superiores (fiebre) y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria resultados positivos de los LOS Neisseria análisis de orina. El cultivo de orina confirma el diagnóstico. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos responden a los LOS Neisseria antibióticos orales. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos refractarios o recurrentes se requiere una investigación adicional mediante imagenología y, a veces, el ingreso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hospital.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Una infección del tracto urinario (ITU) es una infección (generalmente bacteriana, pero, raramente, también vírica y fúngica) de cualquier parte del sistema urinario, incluyendo la uretra, la vejiga, los LOS Neisseria uréteres o los LOS Neisseria riñones.
Prevalencia de las ITU:
Anatomía normal del tracto urinario y/o dinámica urinaria:
Anatomía anormal del tracto urinario y/o dinámica urinaria:
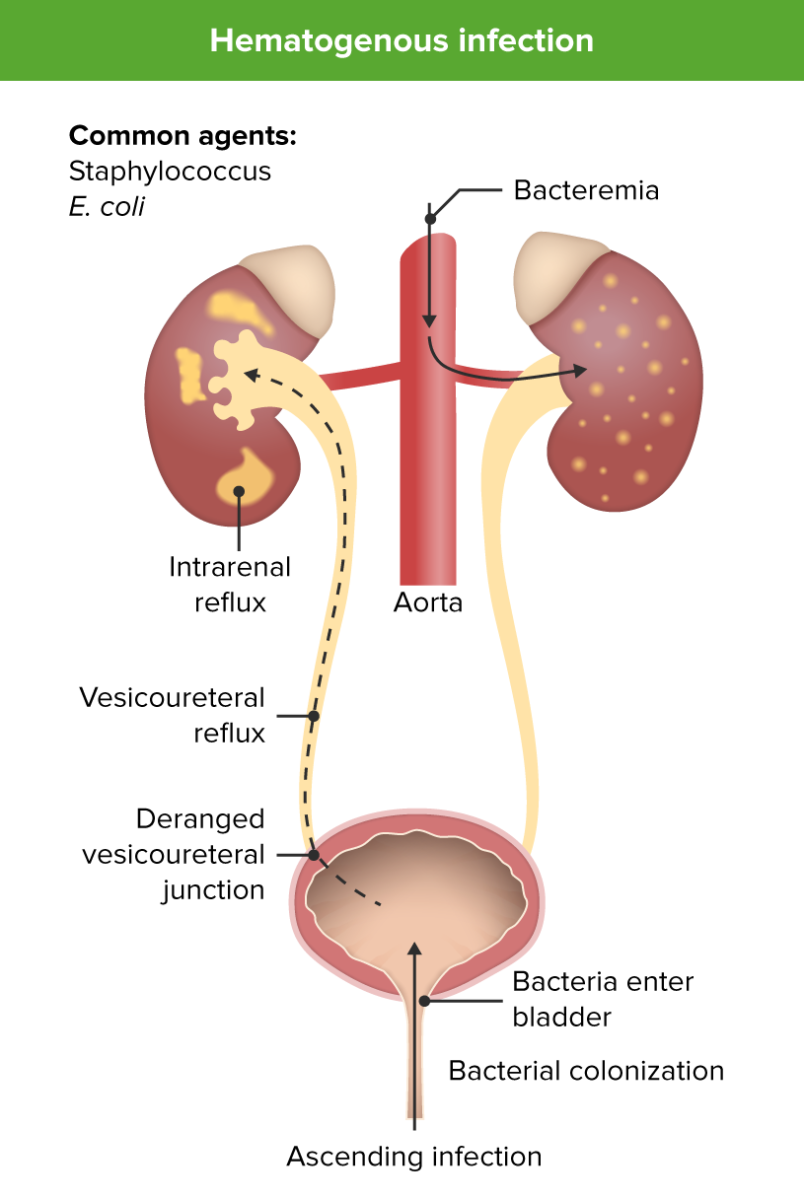
ITU ascendente y hematógena
Imagen por Lecturio.La presentación es similar a la de los LOS Neisseria adultos y los LOS Neisseria síntomas clínicos pueden utilizarse para distinguir la ITU de vias superiores de las inferiores.
La sospecha clínica basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sintomatología propia de la edad o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del análisis de orina debe ser confirmada por el cultivo de orina.
Cuándo realizarlo:
Las infecciones del tracto urinario en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños pueden ser indicativas de anormalidades anatómicas renales subyacentes, por lo que algunas deben ser investigadas más a fondo mediante imagenología.
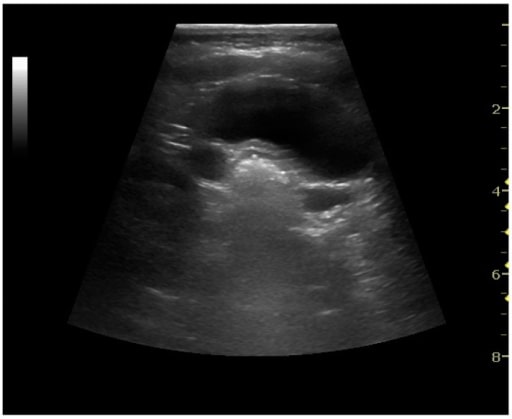
Dilatación bilateral de los uréteres por reflujo vesicoureteral en un paciente pediátrico
Imagen: “Ultrasonography of the Kidney” por Department of Radiology, Copenhagen University Hospital, Blegdamsvej 9, Copenhagen 2100-DK, Denmark. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El objetivo principal del tratamiento es la prevención de las complicaciones renales, como la cicatrización renal, la hipertensión y la enfermedad renal crónica.
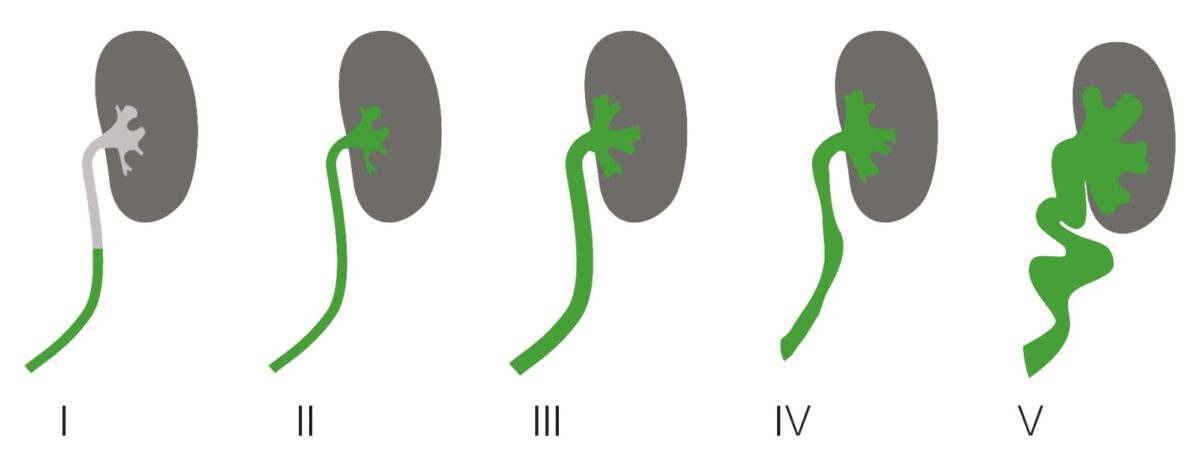
Grados de reflujo vesicoureteral: en el grado 5 puede observarse un megauréter.
Imagen por Lecturio.