El hipogonadismo es una condición caracterizada por una producción reducida o nula de hormonas sexuales por parte de los LOS Neisseria testículos o los LOS Neisseria ovarios. El hipogonadismo puede ser consecuencia de una falla primaria (hipergonadotrópica) o secundaria (hipogonadotrópica). El hipogonadismo hipergonadotrópico ocurre cuando las gónadas no producen hormonas sexuales, y el hipogonadismo hipogonadotrópico resulta de fallos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el eje hipotálamo–hipófisis–gónadas. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas incluyen infertilidad, mayor riesgo de osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis, disfunción eréctil, disminución de la libido y regresión (o ausencia) de los LOS Neisseria caracteres sexuales secundarios. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes clínicos, el examen físico, la medición de los LOS Neisseria niveles hormonales y la evaluación de la etiología subyacente. El tratamiento es con terapia de reemplazo hormonal.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El hipogonadismo es una condición en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que hay una disminución de la producción de hormonas sexuales por los LOS Neisseria testículos o los LOS Neisseria ovarios.
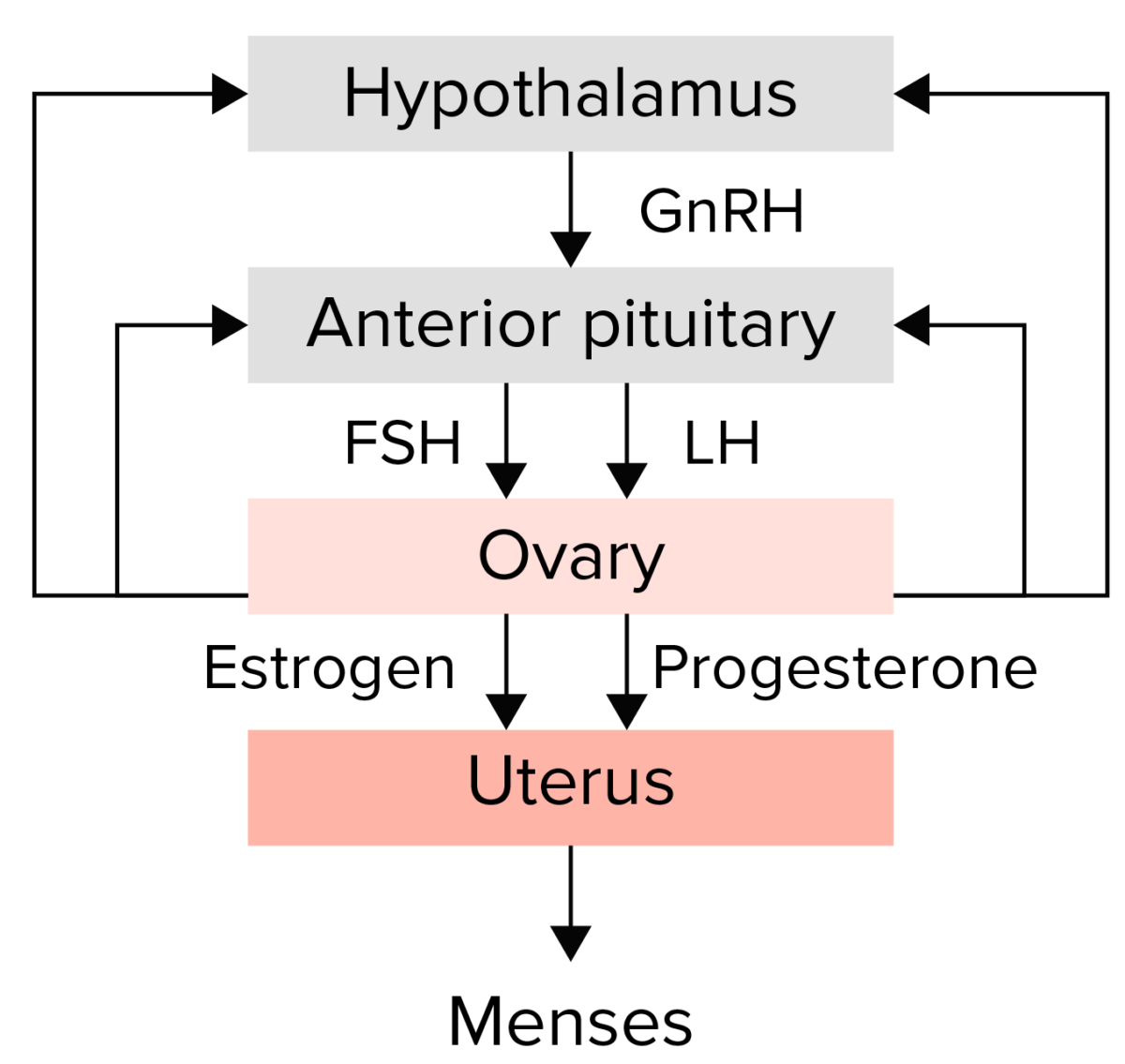
Resumen del eje hipotálamo–hipófisis–ovario:
El hipotálamo secreta la hormona liberadora de gonadotropinas, que estimula a la hipófisis anterior para que libere las hormonas gonadotropinas foliculoestimulante (FSH) y luteinizante (LH). A continuación, las gonadotropinas estimulan al ovario para que produzca estrógenos y progesterona, que a su vez provocan el crecimiento y la maduración del endometrio. Cualquier alteración en esta vía podría conducir a la amenorrea.
El hipogonadismo se produce si el eje hipotálamo–hipofisario–gonadal se interrumpe a cualquier nivel.
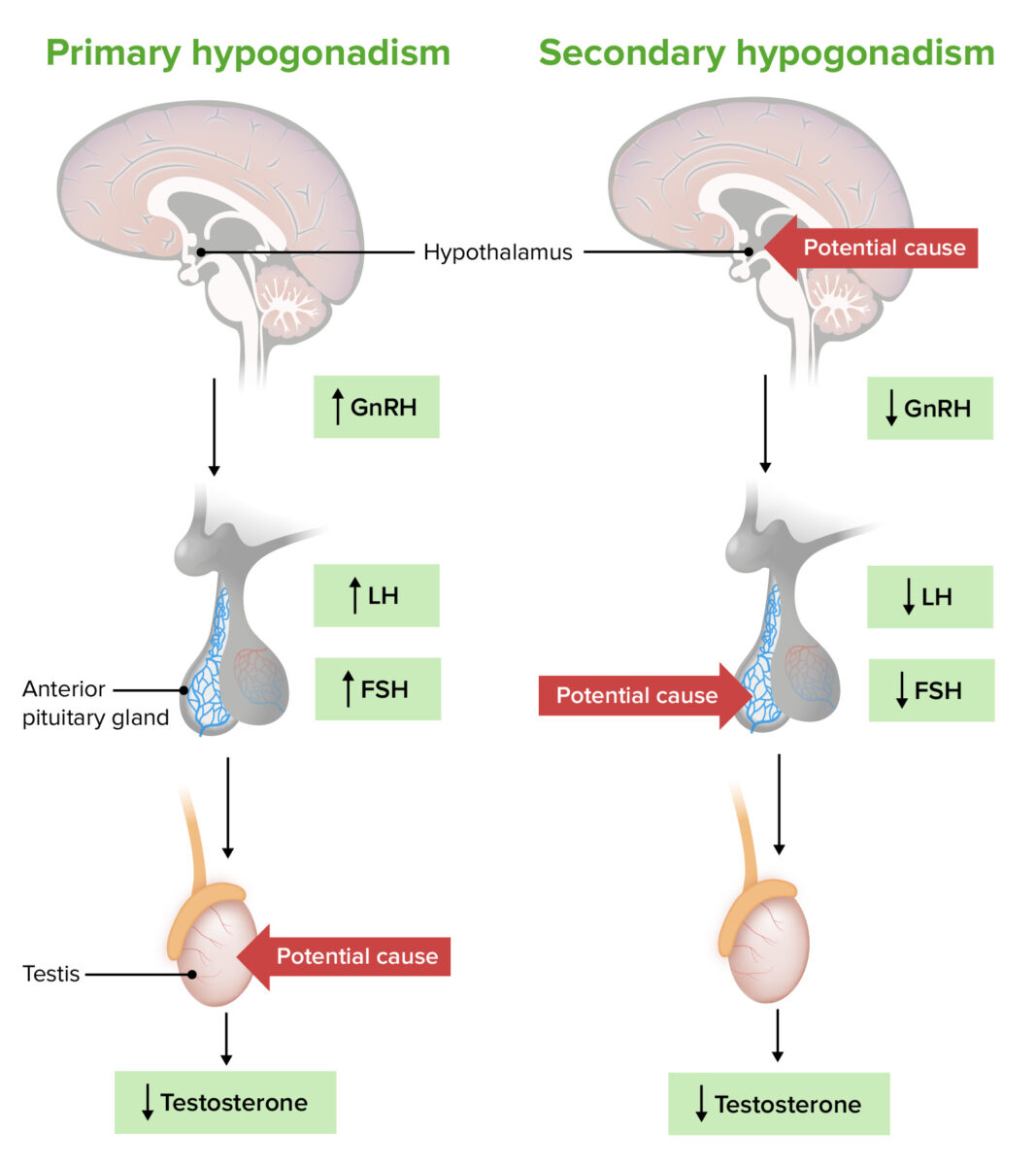
Patogénesis del hipogonadismo primario frente al secundario:
El hipogonadismo primario es el resultado de un problema en los testículos (o en los ovarios), que provoca una disminución de la producción de hormonas sexuales a pesar de los niveles adecuados (o elevados) de la hormona liberadora de gonadotropina, la hormona luteinizante (LH) y la hormona foliculoestimulante (FSH).
En el hipogonadismo secundario, un problema en el hipotálamo o la hipófisis provoca una disminución de la hormona liberadora de gonadotropina, la LH y la FSH, lo que da lugar a una menor producción de hormonas sexuales (a pesar de que los testículos o los ovarios sean normales).
La presentación clínica varía según la edad de inicio y el sexo.
Hombres:
Mujeres: