Los LOS Neisseria herpesvirus humanos (HHV, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés)-6 y HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 son virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology similares de ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) de doble cadena que pertenecen a la familia Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2. Los LOS Neisseria herpesvirus humanos son ubicuos y las infecciones suelen contraerse durante la infancia. Tanto el HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 como el HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 causan una enfermedad infantil común conocida como roséola infantil (también conocida como roséola o 6ta enfermedad). La roséola es una enfermedad autolimitada que se presenta con fiebre alta, seguida de una erupción maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination difusa de color rosa. El diagnóstico es clínico y el tratamiento es de soporte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
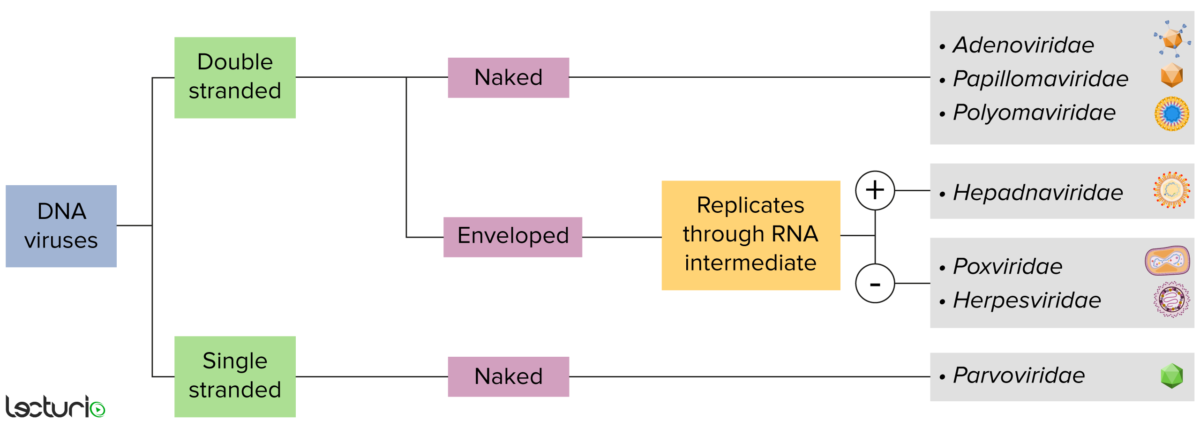
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ácido ribonucleico (ARN). Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como de cadena simple o doble. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que suele tomarse de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
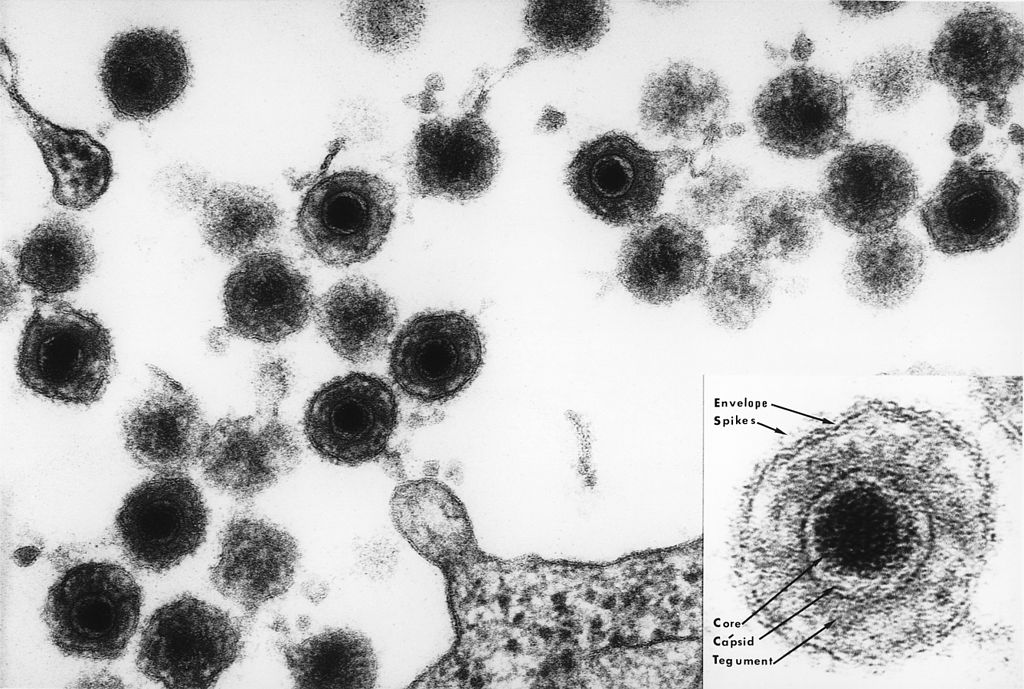
Micrografía electrónica de los viriones del HHV-6
Imagen: “Electron micrograph of one of the HHV6 species” por Bernard Kramarsky. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa relevancia clínica del HHV-6A no se conoce del todo.
Los LOS Neisseria humanos son el reservorio del HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 y del HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7.
El HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 y el HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 se transmiten por contacto con la saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy.
Las infecciones por herpesvirus humano 6 suelen ser leves y se producen durante la infancia. La mayoría de las infecciones por HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 son asintomáticas.
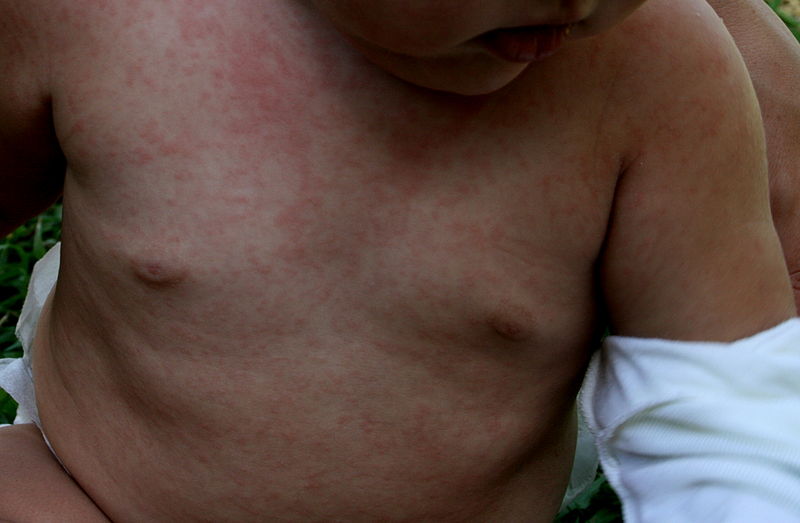
Erupción maculopapular eritematosa observada en la roséola:
Esta erupción es causada más comúnmente por el HHV-6B humano y, en menor medida, por el HHV-7.
El diagnóstico es clínico y rara vez están indicadas pruebas. Se hace HACE Altitude Sickness una excepción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum caso de enfermedad grave en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocomprometidos (e.g., encefalitis, miocarditis).
Por lo general, no es necesario el tratamiento, ya que los LOS Neisseria síntomas son autolimitados. Se puede administrar a los LOS Neisseria pacientes con enfermedad grave:
La siguiente tabla compara los LOS Neisseria 9 herpesvirus considerados endémicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ser humano; en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum total se conocen 115 especies diferentes de herpesvirus, agrupadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 familias:
| HHV | Nombre común | Células diana primarias | Sitio de latencia | Presentación clínica* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (grupo alfa) |
HSV-1 | Células mucoepiteliales | Ganglios de la raíz dorsal |
|
|
2 (grupo alfa) |
HSV-2 |
|
||
|
3 (grupo alfa) |
VZV |
|
||
|
4 (grupo gamma) |
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus |
|
Células B de memoria |
|
|
5 (grupo beta) |
CMV |
|
Células progenitoras hematopoyéticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea |
|
|
6A, 6B (grupo beta) |
HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | Células T | Monocitos | Roséola |
|
7 (grupo beta) |
HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | Células T | ||
|
8 (grupo gamma) |
Herpesvirus asociado al AL Amyloidosis sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |
|
Células B | Sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |
| Número | Otros nombres de la enfermedad | Etiología | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1ra enfermedad |
|
Morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus del sarampión |
|
| 2da enfermedad |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3ra enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rubéola |
|
| 4ta enfermedad |
|
Debido a las cepas de Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess que fabrican la toxina epidermolítica (exfoliativa) |
|
| 5ta enfermedad | Eritema infeccioso | Eritrovirus o parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (eritroparvovirus 1 de los LOS Neisseria primates) |
|
| 6ta enfermedad | Herpesvirus humano 6B o 7 |
|