Haemophilus Haemophilus Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative coccobacilli, all of whose strains require at least 1 of 2 factors for growth (factor V [NAD] and factor X [heme]); therefore, it is most often isolated on chocolate agar, which can supply both factors. The pathogenic species are H. influenzae and H. ducreyi. Haemophilus es un género de cocobacilos Gram-negativos, cuyas cepas requieren al AL Amyloidosis menos de 1 de 2 factores para su crecimiento ( factor V Factor V Heat- and storage-labile plasma glycoprotein which accelerates the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin in blood coagulation. Factor V accomplishes this by forming a complex with factor Xa, phospholipid, and calcium (prothrombinase complex). Hemostasis [nicotinamida adenina dinucleótido] y factor X Factor X Storage-stable glycoprotein blood coagulation factor that can be activated to factor Xa by both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. A deficiency of factor X, sometimes called stuart-prower factor deficiency, may lead to a systemic coagulation disorder. Hemostasis [hemina]); por lo tanto, con mayor frecuencia se aísla en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum agar chocolate, que puede aportar ambos factores. La especie patógena más común es H. influenzae H. influenzae A species of Haemophilus found on the mucous membranes of humans and a variety of animals. The species is further divided into biotypes I through VIII. Haemophilus, que se transmite a través de gotitas respiratorias y puede causar epiglotitis, meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, otitis media y neumonía. H. ducreyi se transmite por contacto sexual y es la causa del chancroide, un tipo de úlcera genital.
Last updated: Apr 29, 2022
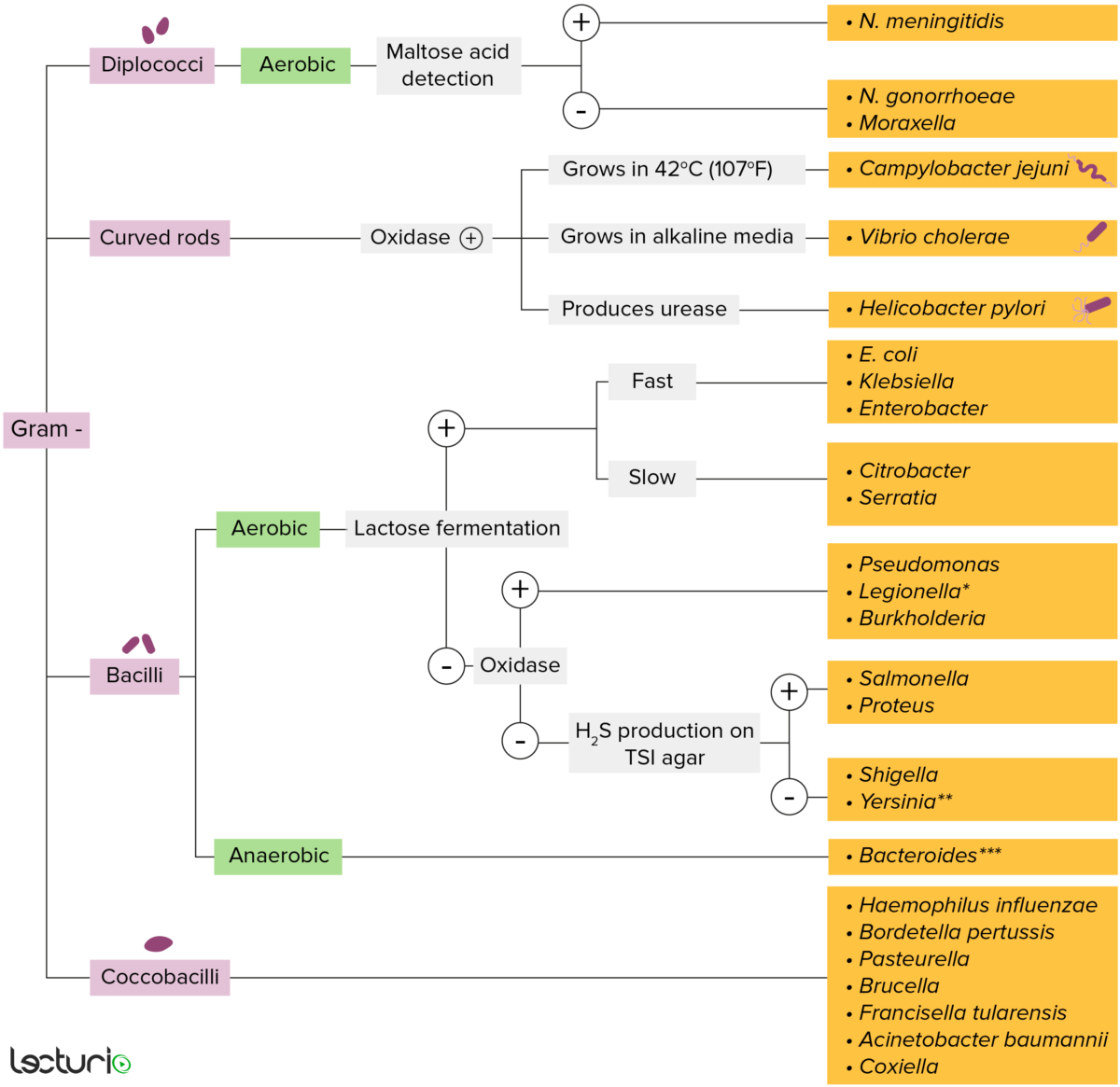
Bacterias Gram-negativas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo con un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa delgada de peptidoglicano no retienen la tinción de cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram. Sin embargo, estas bacterias retienen la contratinción de safranina y, por lo tanto, se tiñe de color rojo rosado, lo que las convierte en gram negativas. Estas bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (diplococos, bastones curvos, bacilos y cocobacilos) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos frente a anaeróbicos). Las bacterias se pueden identificar de manera más estrecha cultivándolas en medios específicos (agar hierro-triple azúcar (TSI, por sus siglas en inglés)) donde se pueden identificar sus enzimas (ureasa, oxidasa) y se puede probar su capacidad para fermentar lactosa.
* Se tiñe pobremente en la tinción de Gram
** Bastón/cocobacilo pleomórfico
*** Requiere medios de transporte especiales
Características generales de las especies de Haemophilus Haemophilus Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative coccobacilli, all of whose strains require at least 1 of 2 factors for growth (factor V [NAD] and factor X [heme]); therefore, it is most often isolated on chocolate agar, which can supply both factors. The pathogenic species are H. influenzae and H. ducreyi. Haemophilus:
Factores de virulencia de las especies de Haemophilus Haemophilus Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative coccobacilli, all of whose strains require at least 1 of 2 factors for growth (factor V [NAD] and factor X [heme]); therefore, it is most often isolated on chocolate agar, which can supply both factors. The pathogenic species are H. influenzae and H. ducreyi. Haemophilus:
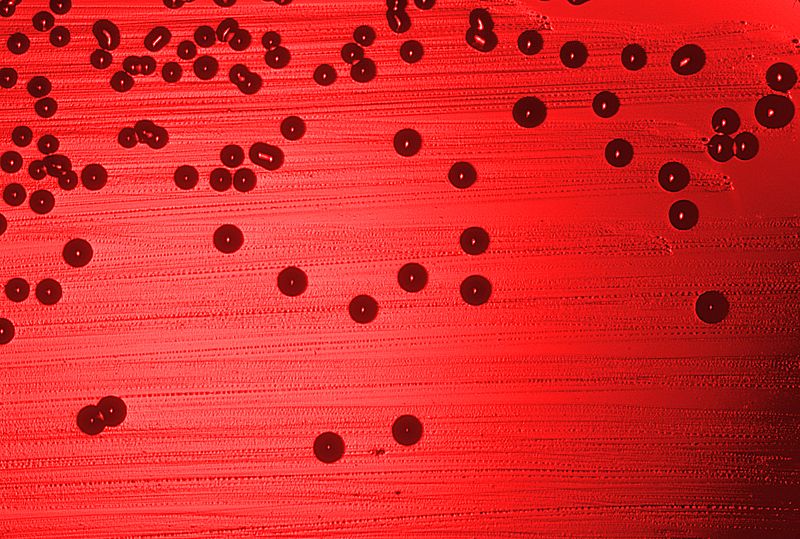
Bacteria Haemophilus influenzae cultivada en una placa de agar sangre.
Imagen: “Haemophilus influenzae 01” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público| Patógeno | Población en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum riesgo | Síntomas | |
|---|---|---|---|
| H influenzae | Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis |
|
Predominantemente causada por cepas con cápsula tipo B |
| Otitis media | Niños y adultos |
|
|
| Epiglotitis | Niños de 2–7 años |
|
|
| Neumonía | Ancianos, pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) | Presentación típica: esputo teñido de sangre |
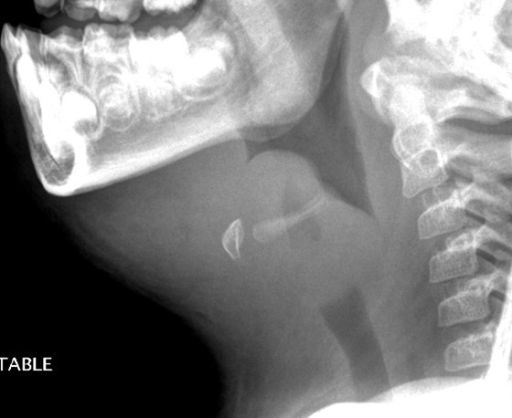
Radiografía lateral del cuello que muestra epiglotitis y obstrucción completa de las vías respiratorias en una niña de 5 años. Esta afección suele estar causada por la bacteria Haemophilus influenzae.
Imagen: “Acute epiglottitis as the initial presentation of pediatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus” por Charuvanij S et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Para ayudar a recordar las manifestaciones clínicas comunes de H. influenzae H. influenzae A species of Haemophilus found on the mucous membranes of humans and a variety of animals. The species is further divided into biotypes I through VIII. Haemophilus, usar la siguiente regla mnemotecnia:
Bacteria Haemophilus ducreyi, agente causal del chancroide, teñida con violeta de genciana.