El glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme is a high-grade astrocytoma, an aggressive brain tumor arising from astrocytes, with an unknown cause and a poorly understood link to risk factors. There are two main types: primary, a more aggressive form seen more commonly in older patients, and secondary, developing from lower-grade astrocytomas and seen more commonly in younger patients. Glioblastoma Multiforme es un astrocitoma de alto grado, el cual es un tumor Tumor Inflammation cerebral agresivo que surge de los LOS Neisseria astrocitos, con una causa desconocida y una relación poco conocida con los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo. Existen dos tipos principales: el primario, el cual es una forma más agresiva que se observa con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes de edad avanzada y el secundario, que se desarrolla a partir de astrocitomas de bajo grado y se observa con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes más jóvenes. Los LOS Neisseria glioblastomas suelen presentarse con cefalea, convulsiones y déficits neurológicos. La RM es el estándar de oro y la resección quirúrgica combinada con radiación y quimioterapia son el tratamiento de elección. El pronóstico es extremadamente malo, con una supervivencia solamente de 1–5 años en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pacientes que reciben un tratamiento agresivo y de solo 3 meses en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pacientes que no se someten a tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme is a high-grade astrocytoma, an aggressive brain tumor arising from astrocytes, with an unknown cause and a poorly understood link to risk factors. There are two main types: primary, a more aggressive form seen more commonly in older patients, and secondary, developing from lower-grade astrocytomas and seen more commonly in younger patients. Glioblastoma Multiforme es un tipo de tumor Tumor Inflammation cerebral agresivo y rápidamente progresivo que surge de los LOS Neisseria astrocitos:
| Categorías | Tumores específicos |
|---|---|
| Tumores neuroepiteliales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SNC |
|
| Tumores meníngeos |
|
| Tumores de la región selar |
|
| Linfoma primario del SNC | Linfoma primario del SNC |
| Metástasis al AL Amyloidosis cerebro (5 veces más frecuente que los LOS Neisseria tumores cerebrales primarios) | Más comúnmente surgen de: |
| Tumores periféricos |
|
Los LOS Neisseria dos tipos principales de glioblastoma son:
La causa de los LOS Neisseria glioblastomas no está clara y es difícil determinar una única causa. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo que parecen contribuir al AL Amyloidosis glioblastoma incluyen:
Hay varias mutaciones genéticas asociadas a los LOS Neisseria astrocitomas:
Muchos síntomas generalizados se deben al AL Amyloidosis aumento de la PIC. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas pueden incluir:
El diagnóstico de los LOS Neisseria glioblastomas se basa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico por imagen después de la presentación clínica, con una evaluación cuidadosa de antecedentes y del examen físico que hagan sospechar de un tumor Tumor Inflammation cerebral. Se requiere una biopsia para confirmar el diagnóstico. Los LOS Neisseria estudios de laboratorio no son útiles para diagnosticar los LOS Neisseria glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme is a high-grade astrocytoma, an aggressive brain tumor arising from astrocytes, with an unknown cause and a poorly understood link to risk factors. There are two main types: primary, a more aggressive form seen more commonly in older patients, and secondary, developing from lower-grade astrocytomas and seen more commonly in younger patients. Glioblastoma Multiforme.
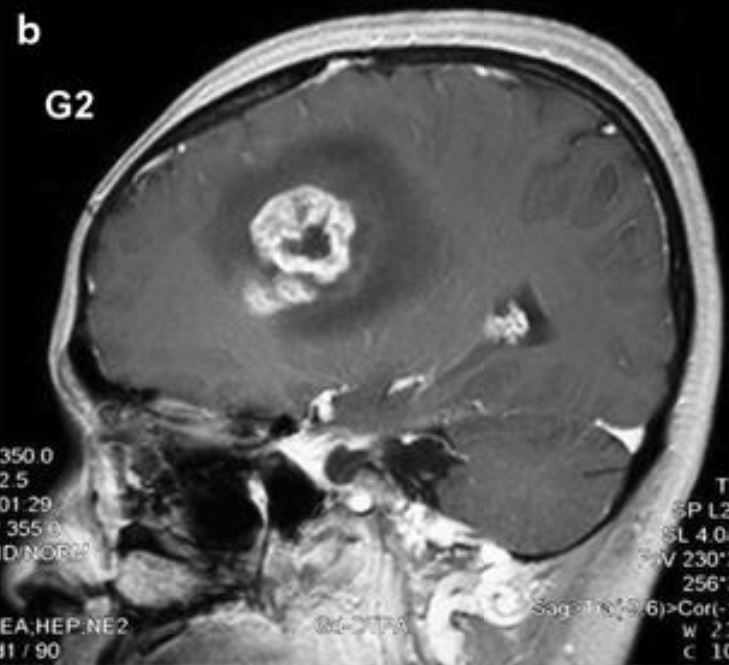
Resonancia magnética de un glioblastoma:
El realce de la lesión con aclaramiento central indica necrosis central.
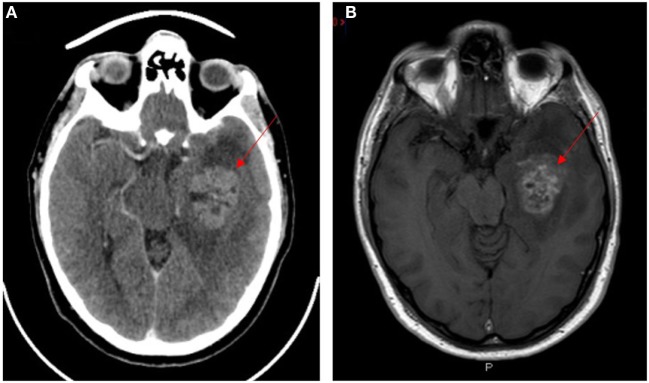
Neuroimagen del glioblastoma multiforme (lesiones indicadas con flechas rojas):
A: TC con contraste
B: RM con contraste ponderado en T1
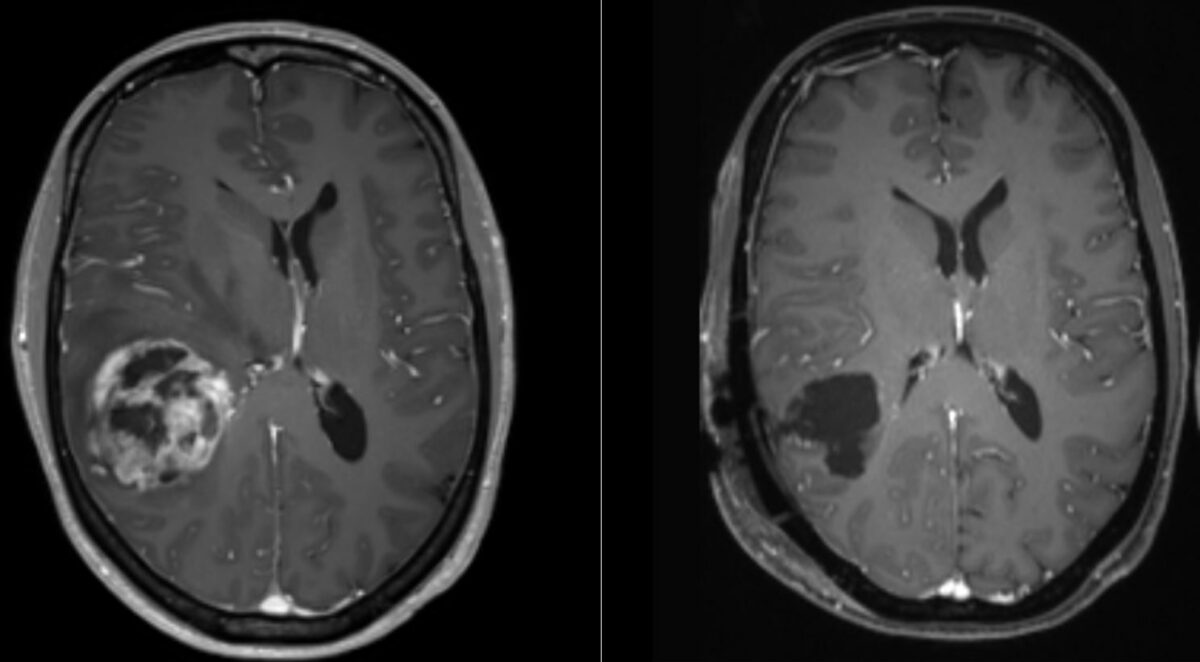
RM del glioblastoma:
La imagen representa el tumor visto antes de la operación (izquierda) y después de la misma (derecha). La imagen de la izquierda muestra una zona central de necrosis rodeada por una región realzada y un desplazamiento de la línea media.
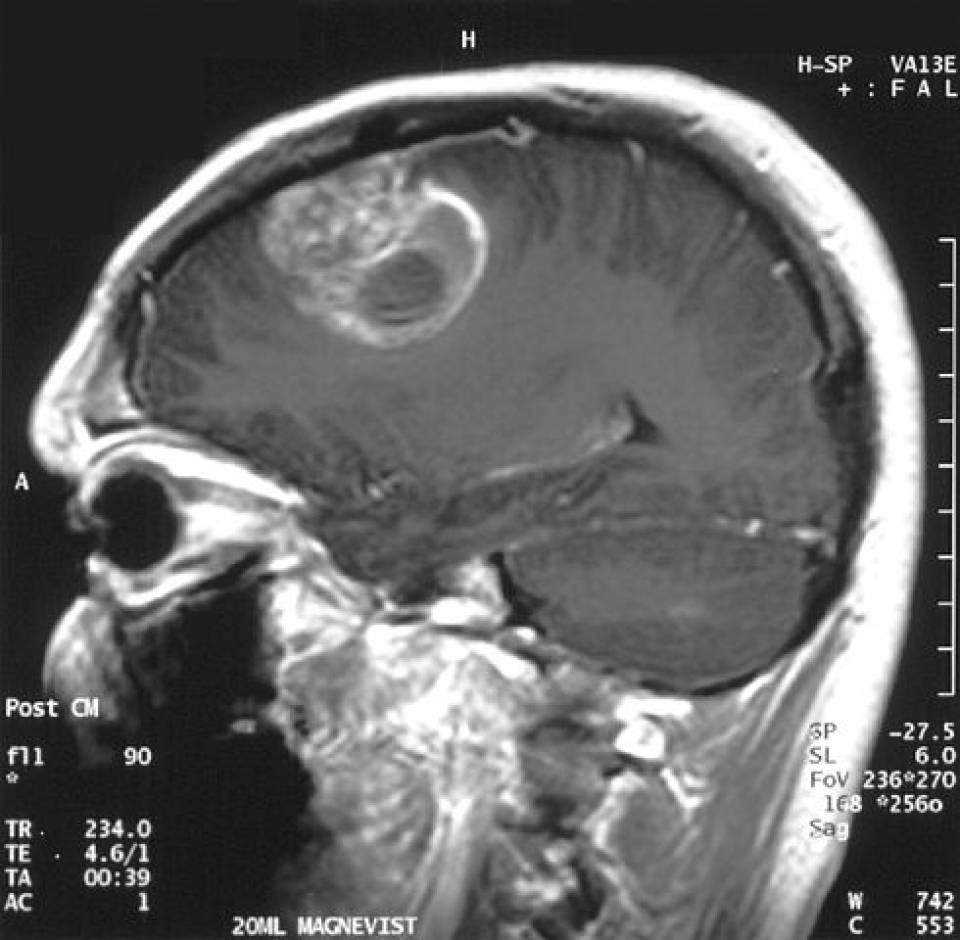
Resonancia magnética sagital que muestra una masa en el cerebro diagnosticada como glioblastoma:
La lesión está rodeada por una zona de realce y una zona central de necrosis.
Se requiere una muestra histopatológica obtenida mediante biopsia para el diagnóstico definitivo. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos incluyen:
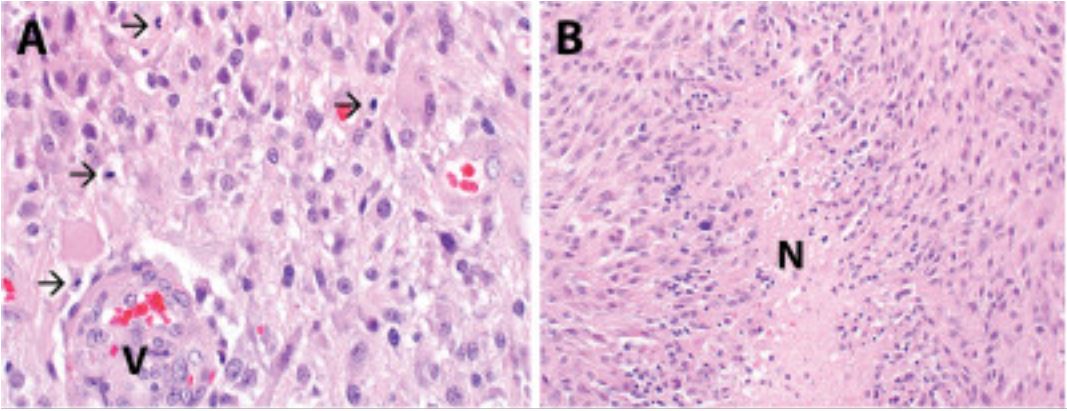
Glioblastoma multiforme (astrocitoma de grado IV de la OMS):
La evaluación histopatológica revela una neoplasia astrocítica hipercelular que infiltra el parénquima cerebral circundante.
B: Se observa necrosis en la muestra, incluida la necrosis pseudopalisante (designada N).
Imagen: “Complete clinical regression of a BRAF V600E-mutant pediatric glioblastoma multiforme after BRAF inhibitor therapy” por Robinson GW, Orr BA, Gajjar A. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, recortada por Lecturio.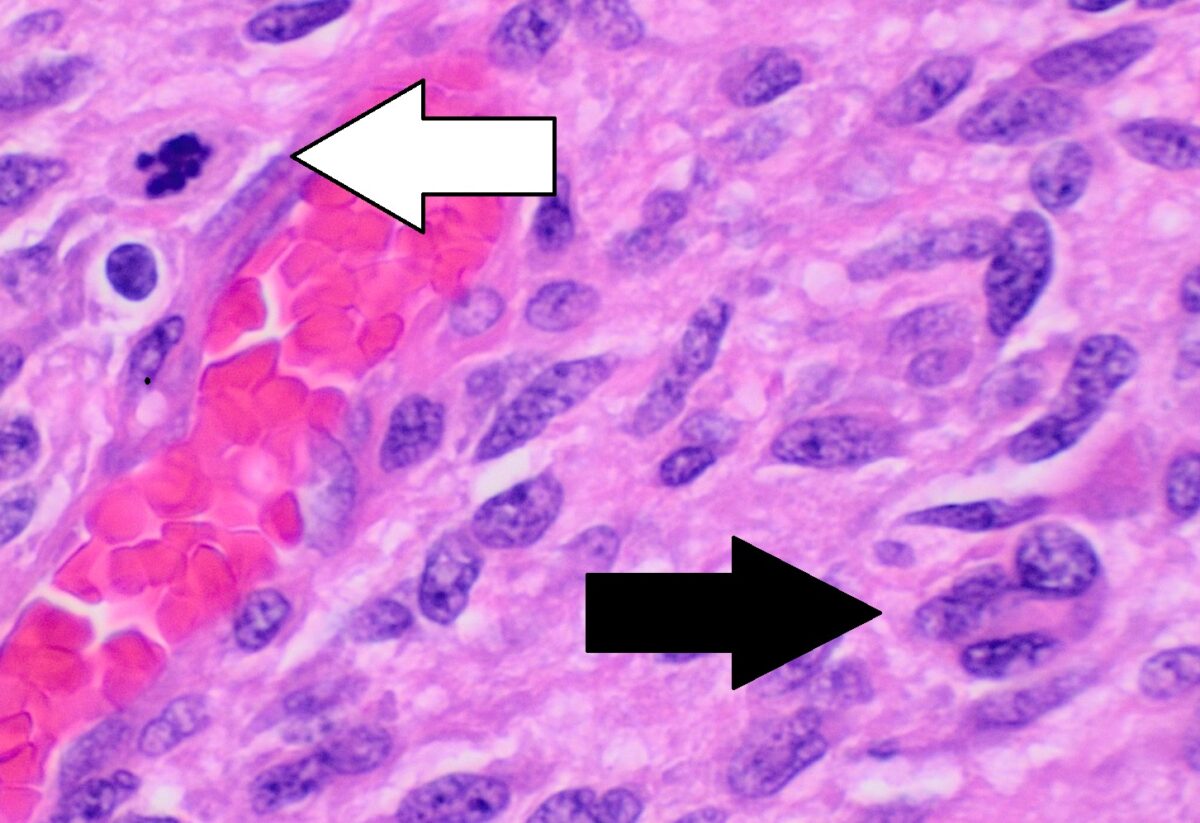
Histopatología de un glioblastoma que muestra pleomorfismo nuclear, múltiples figuras mitóticas (flecha blanca) y células multinucleadas (flecha negra)
La disposición celular no tiene algún patrón.
El enfoque principal del tratamiento es la intervención quirúrgica, seguida de radioterapia y quimioterapia. Ningún tratamiento es curativo y el pronóstico sigue siendo malo, incluso con un tratamiento agresivo.
Los LOS Neisseria retos que dificultan el tratamiento de los LOS Neisseria glioblastomas son:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de los LOS Neisseria pacientes que presentan hallazgos neurológicos, deben considerarse las siguientes afecciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico diferencial del glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme Glioblastoma multiforme is a high-grade astrocytoma, an aggressive brain tumor arising from astrocytes, with an unknown cause and a poorly understood link to risk factors. There are two main types: primary, a more aggressive form seen more commonly in older patients, and secondary, developing from lower-grade astrocytomas and seen more commonly in younger patients. Glioblastoma Multiforme.