La escarlatina es un síndrome clínico que consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum faringitis estreptocócica acompañada de fiebre y un exantema característico causado por exotoxinas pirógenas. La escarlatina es una complicación no supurativa de la infección estreptocócica que se observa con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños. La incidencia alcanza su punto máximo durante el invierno y la primavera en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum climas templados. La erupción comienza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las 1as 24–48 horas de la enfermedad. Comenzando en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara o el cuello, el exantema se extiende al AL Amyloidosis tronco y las extremidades, pero respeta las palmas de las manos y las plantas de los LOS Neisseria pies. Con la infección, la cara se ve VE Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing enrojecida, acompañada de palidez peribucal y lengua de fresa (papilas agrandadas). Las pápulas diminutas se sienten como papel de lija. El diagnóstico generalmente se realiza clínicamente y se confirma con una prueba rápida de detección de antígenos o un cultivo de garganta. El tratamiento es con penicilina o amoxicilina.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La escarlatina (también llamada “fiebre escarlatina”) es una erupción difusa que ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum asociación con faringitis.
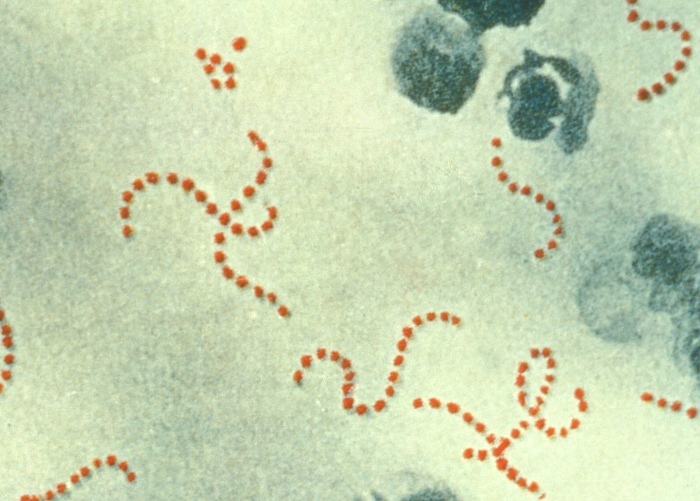
Streptococcus pyogenes
Imagen: “Photomicrograph of Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria” por the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Licencia: dominio público.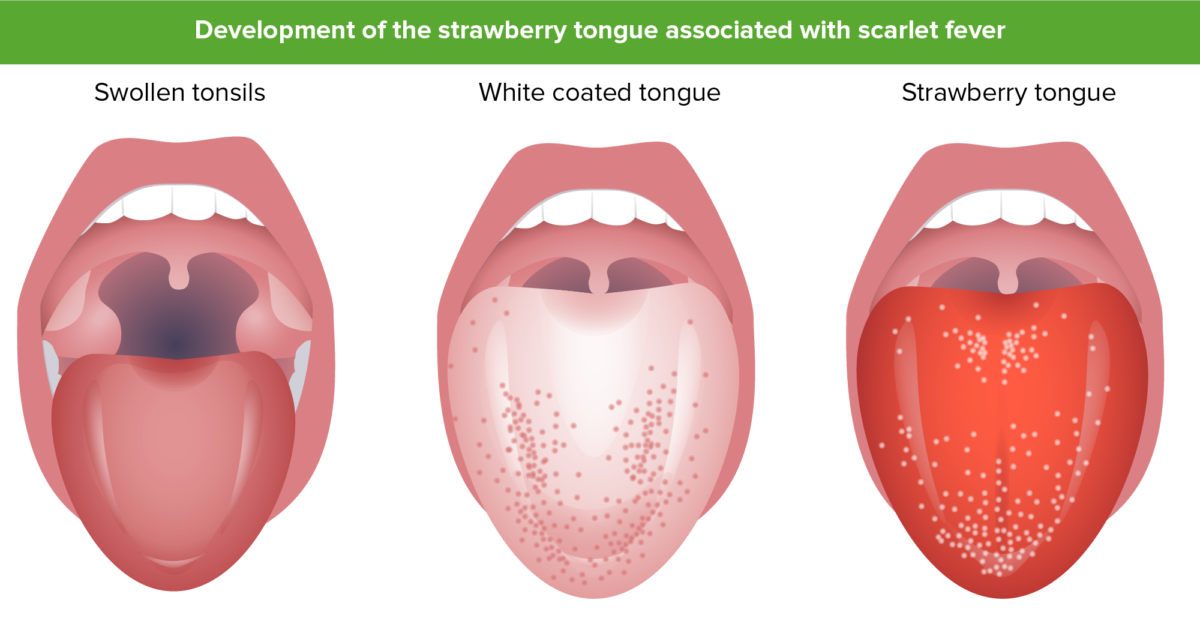
“Lengua de fresa”: al principio de la enfermedad, la lengua puede estar cubierta por una membrana o capa blanca a través de la cual se ven las papilas. Esta capa se desprende y revela una lengua de color rojo brillante con papilas prominentes. Una lengua de fresa resulta de una respuesta inflamatoria general temprana en el curso de la enfermedad.
Imagen por Lecturio.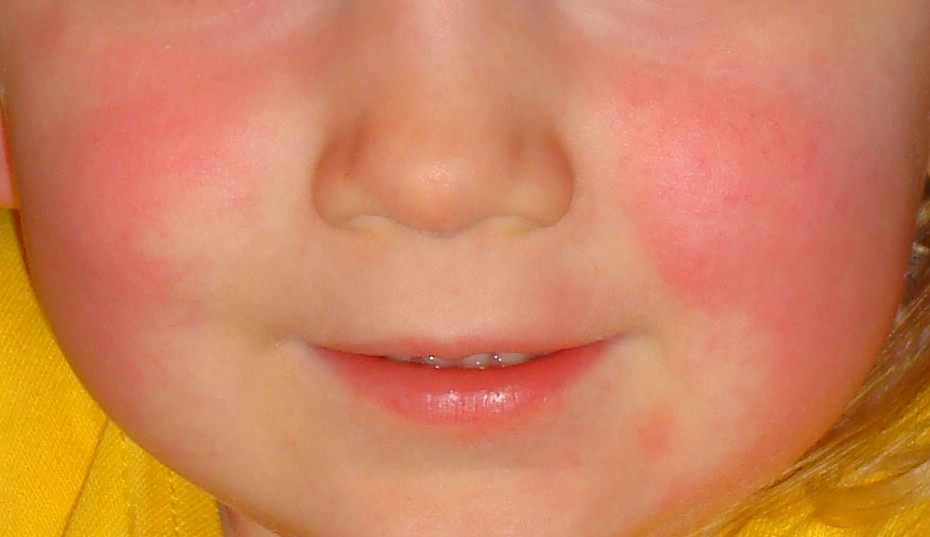
La cara se ve enrojecida pero tiene un “bigote blanco” o palidez peribucal, típica de la escarlatina.
Imagen: “Slapped cheeks and white mustache” por Estreya. Licencia: CC BY-SA 4.0.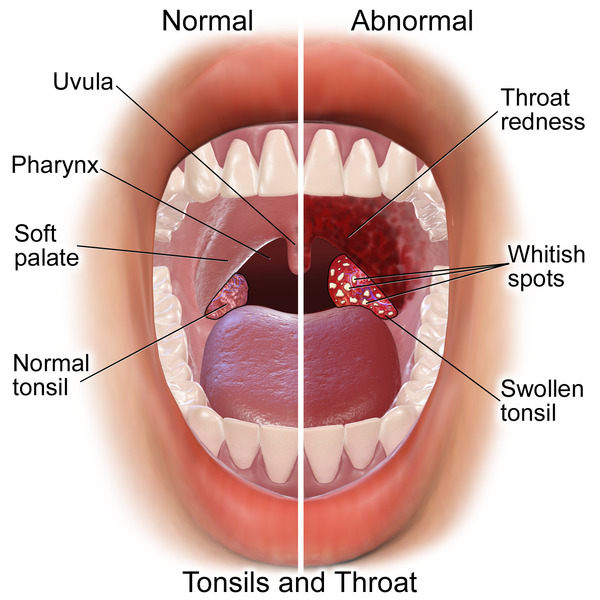
Hallazgos comunes del examen físico en faringitis/amigdalitis exudativas agudas (mitad derecha de la imagen), de las cuales 1 de las causas más comunes es Streptococcus pyogenes
Imagen: “Tonsillitis” por BruceBlaus. Licencia: dominio público.El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum tratar el agente causal de la faringitis, Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes.
| Número | Otros nombres de la enfermedad | Etiología | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1ra enfermedad |
|
Morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus del sarampión |
|
| 2da enfermedad |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3ra enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rubéola |
|
| 4ta enfermedad |
|
Debido a las cepas de Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess que fabrican la toxina epidermolítica (exfoliativa) |
|
| 5ta enfermedad | Eritema infeccioso | Eritrovirus o parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (eritroparvovirus 1 de los LOS Neisseria primates) |
|
| 6ta enfermedad | Herpesvirus humano 6B o herpesvirus humano 7 |
|