Los LOS Neisseria ependimomas son tumores de las células gliales que surgen de las células ependimarias productoras del LCR las cuales recubren el sistema ventricular. Los LOS Neisseria ependimomas suelen aparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fosa posterior, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum contacto con el 4to ventrículo o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula espinal intramedular. La presentación clínica de los LOS Neisseria ependimomas varía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la localización del tumor Tumor Inflammation. La resonancia magnética es la imagenología de elección, pero se requiere la confirmación histológica para el diagnóstico. La base del tratamiento del ependimoma intracraneal es la resección quirúrgica y la radioterapia adyuvante; los LOS Neisseria pacientes jóvenes reciben en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cambio quimioterapia. Los LOS Neisseria ependimomas de la médula espinal se tratan con una resección quirúrgica máxima.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria ependimomas son tumores de las células gliales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SNC que surgen de las células ependimarias.
| Categorías | Tumores específicos |
|---|---|
| Tumores neuroepiteliales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SNC |
|
| Tumores meníngeos |
|
| Tumores de la región selar |
|
| Linfoma primario del SNC | Linfoma primario del SNC |
| Metástasis al AL Amyloidosis cerebro (5 veces más común que los LOS Neisseria tumores cerebrales primarios) | Más comúnmente surgen de: |
| Tumores periféricos |
|
Ependimoma intracraneal:
Ependimoma espinal:
La presentación clínica depende de la localización del ependimoma y de la edad del paciente. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes tienen síntomas aproximadamente 3–6 meses antes del diagnóstico.
La imagenología se obtienen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 1er lugar como parte del trabajo de diagnóstico, pero la evaluación histológica es necesaria para confirmar el diagnóstico. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagenología pueden sugerir un ependimoma y así guiar la cirugía.
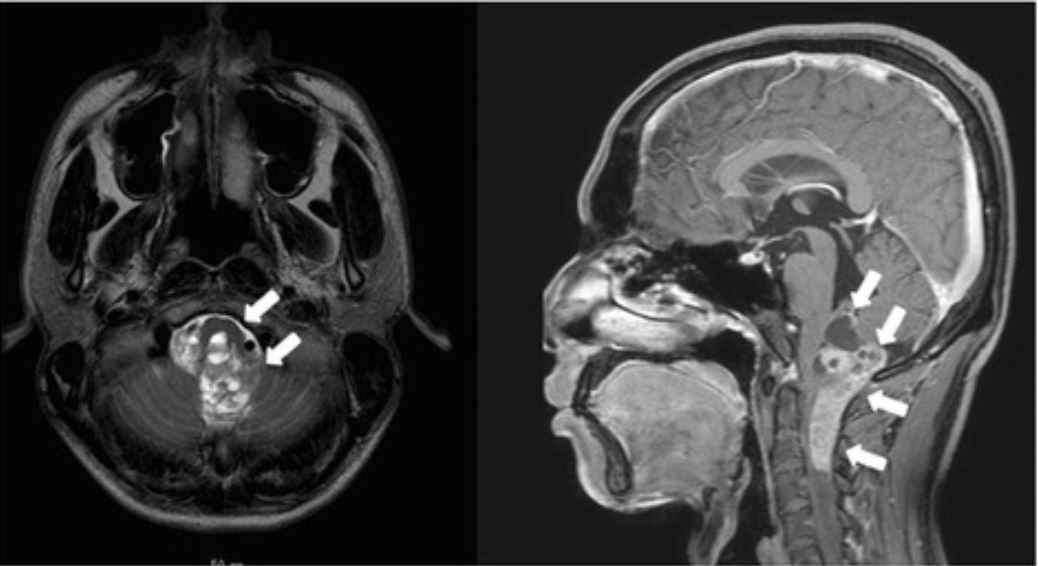
La resonancia magnética revela un ependimoma anaplásico que se extiende desde el tronco encefálico hasta el 4to ventrículo.
Imagen: “Giant duodenal ulcers after neurosurgery for brainstem tumors that required reoperation for gastric disconnection: a report of two cases” por BMC Surgery. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El ependimoma se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un diagnóstico histológico; por lo tanto, el estándar de oro para el diagnóstico es la evaluación patológica de una muestra de tejido. Los LOS Neisseria ependimomas se clasifican por grados histológicos según la OMS.
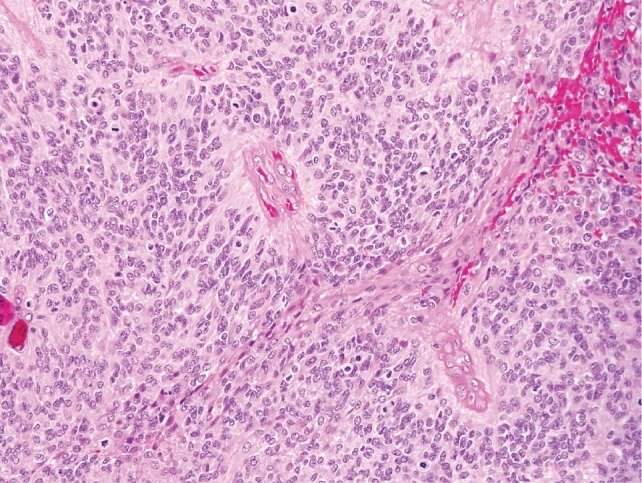
Ependimoma intracraneal grado III de la Organización Mundial de la Salud:
Se observan pseudorosetas perivasculares, así como una actividad mitótica rápida, lo que clasifica el tumor como un ependimoma anaplásico.