La enterobiasis Enterobiasis Enterobiasis is a helminth infection caused by Enterobius vermicularis, also known as a pinworm. This infection is typically seen in children and is transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The primary clinical feature is anal pruritus, but patients are often asymptomatic. Enterobius/Enterobiasis es una infección por helmintos causada por Enterobius vermicularis Enterobius Vermicularis Enterobius/Enterobiasis, también conocido como oxiuros. Esta infección se observa típicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños y se transmite por vía fecal-oral. La característica clínica principal es el prurito anal, pero los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen ser asintomáticos. La visualización de los LOS Neisseria huevos o vermes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la prueba de la cinta adhesiva suele ser necesaria para el diagnóstico. Para el tratamiento se utilizan medicamentos antihelmínticos. Para la prevención de la reinfección y de la transmisión se requiere un lavado de manos y corporal frecuente, así como el lavado de la ropa y las sábanas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
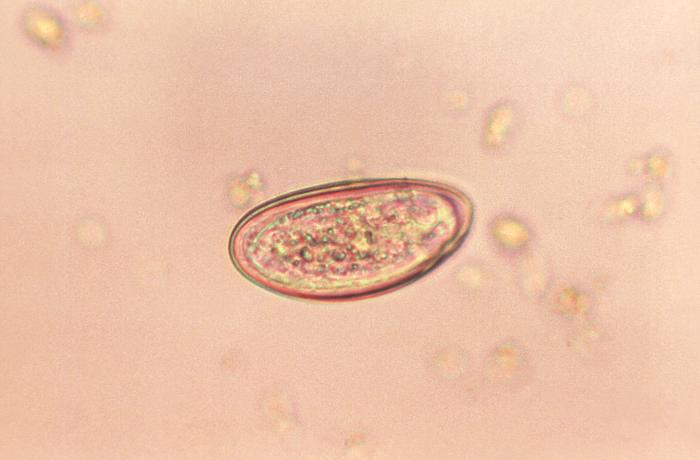
Huevo de Enterobius
Imagen: “Photomicrograph of an Enterobius vermicularis egg” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público
Extremo posterior de un verme adulto de Enterobius vermicularis
Imagen: “Posterior end of an Enterobius vermicularis adult worm” por Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria (DPDM). Licencia: Dominio Público
2 vermes adultos de Enterobius vermicularis
Imagen: “Enterobius vermicularis or pinworm parasite” por Erich. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEnterobius vermicularis Enterobius Vermicularis Enterobius/Enterobiasis, u oxiuros, causante de la enterobiasis Enterobiasis Enterobiasis is a helminth infection caused by Enterobius vermicularis, also known as a pinworm. This infection is typically seen in children and is transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The primary clinical feature is anal pruritus, but patients are often asymptomatic. Enterobius/Enterobiasis.
La enterobiasis Enterobiasis Enterobiasis is a helminth infection caused by Enterobius vermicularis, also known as a pinworm. This infection is typically seen in children and is transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The primary clinical feature is anal pruritus, but patients are often asymptomatic. Enterobius/Enterobiasis es la infección por helmintos más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos y Europa Occidental.
Los LOS Neisseria humanos son los LOS Neisseria principales huéspedes de E. vermicularis.
Todo el ciclo de vida de E. vermicularis tiene lugar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal humano y dura de 2-8 semanas.
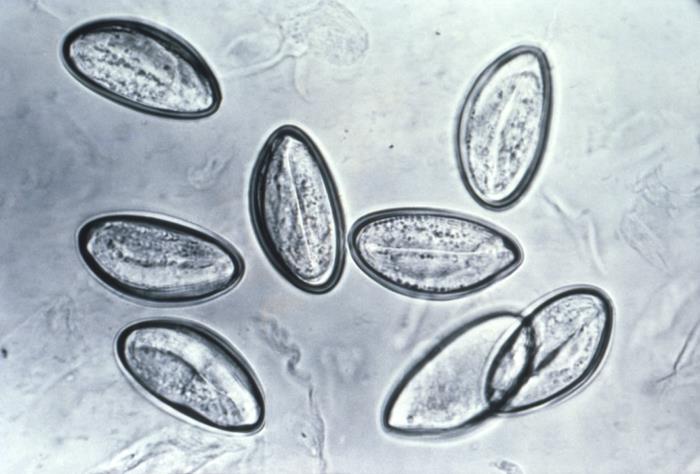
Microfotografía de 8 huevos de Enterobius vermicularis en una cinta de celofán
Imagen: “Photomicrograph depicts eight eggs of the human pinworm, Enterobius vermicularis” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoTerapia médica:
Medidas para reducir la reinfección y la propagación:
| Organismo | Enterobius vermicularis Enterobius Vermicularis Enterobius/Enterobiasis | Toxocara canis Toxocara canis A species of parasitic nematode found in the intestine of dogs. Lesions in the brain, liver, eye, kidney, and lung are caused by migrating larvae. In humans, these larvae do not follow normal patterns and may produce visceral larva migrans (larva migrans, visceral). Toxocariasis | Ascaris Ascaris Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The infection, ascariasis, is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. Transmission occurs primarily via ingestion of water or food contaminated with Ascaris eggs. Most patients with ascariasis are asymptomatic. Ascaris/Ascariasis lumbricoides | Strongyloides stercoralis Strongyloides stercoralis A species of parasitic nematode widely distributed in tropical and subtropical countries. The females and their larvae inhabit the mucosa of the intestinal tract, where they cause ulceration and diarrhea. Strongyloidiasis | Schistosoma Schistosoma Schistosomiasis is an infection caused by Schistosoma, a trematode. Schistosomiasis occurs in developing countries with poor sanitation. Freshwater snails are the intermediate host and are transmitted to humans through skin contact with contaminated fresh water. The clinical presentation occurs as a result of the host’s immune response to antigens from the eggs. Schistosoma/Schistosomiasis mansoni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características | Nemátodo | Nemátodo | Nemátodo | Nemátodo | Trematodos |
| Reservorio | Humanos | Perros | Humanos |
|
Humanos |
| Transmisión | Fecal-oral | Fecal-oral | Fecal-oral | Contacto de la piel con suelo contaminado | Contacto de la piel con agua contaminada |
| Cuadro clínico |
|
|
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
Análisis de heces |
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
|
|
|
Praziquantel Praziquantel An anthelmintic used in most schistosome and many cestode infestations. Anthelmintic Drugs |
| Prevención | Buena higiene |
|
|
|
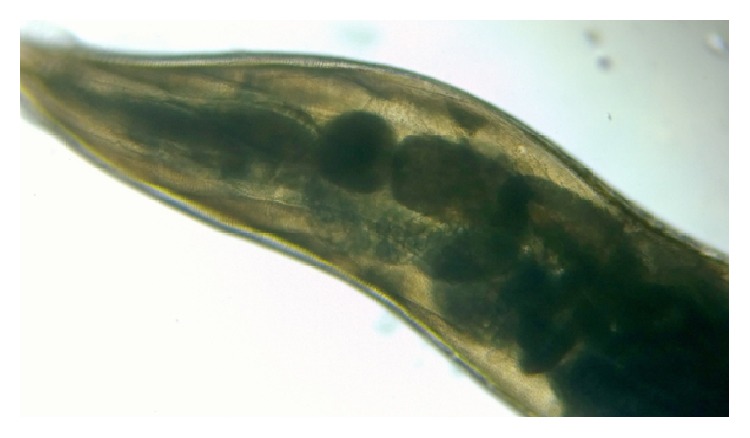
Vista microscópica de bajo poder de Enterobius vermicularis
Imagen: “Double bulb oesophagus of Enterobius vermicularis, under low power” por Kaniyarakkal V et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Verme adulto de Ascaris lumbricoides
Imagen: “An adult Ascaris lumbricoides worm” por CDC Division of Parasitic Diseases. Licencia: Dominio Público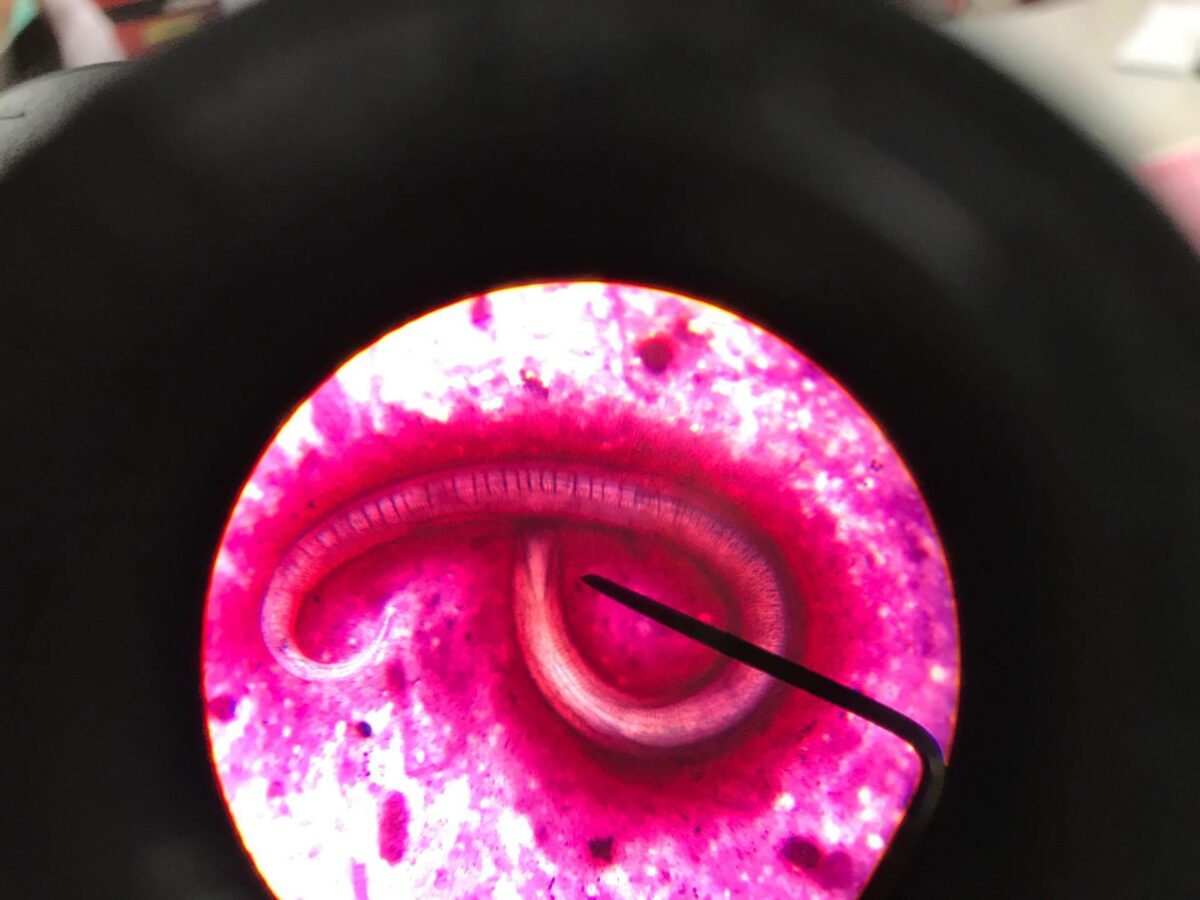
Parásito Strongyloides stercoralis
Imagen: “Strongyloides Stercoralis in sputum” por CDC Division of Parasitic Diseases. Licencia: CC BY 4.0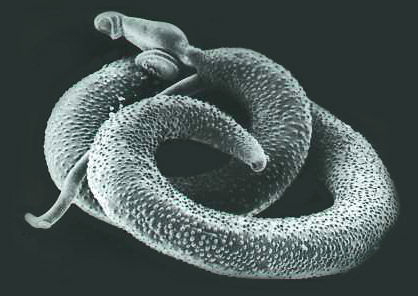
Schistosoma mansoni adulto visto bajo microscopía electrónica
Imagen: “Schistosoma mansoni, adult. SEM [Scanning electron microscopy] of worm, unstained” por Otis Historical Archives of “National Museum of Health & Medicine”. Licencia: CC BY 2.0