La enfermedad hemolítica del feto y del recién nacido, también conocida como eritroblastosis fetal, está causada por la destrucción de los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos del feto por parte de los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos de Inmunoglobulina G ( IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis) maternos. La incompatibilidad del grupo sanguíneo Rhesus (Rh) (frecuentemente provocada por el antígeno D) y la incompatibilidad ABO son causas comunes. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la incompatibilidad Rh, una madre RhD negativa lleva a un bebé RhD positivo; así, se forman anticuerpos contra los LOS Neisseria antígenos cuando los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos del feto pasan a la circulación materna. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la incompatibilidad ABO, comúnmente, una madre con tipo de sangre O tiene anticuerpos existentes contra los LOS Neisseria antígenos A y B. El bebé afectado puede sufrir anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica que le provoque ictericia neonatal grave, hidropesía fetal, complicaciones cardíacas y muerte fetal. Si el embarazo está afectado por incompatibilidad Rh, se realiza vigilancia prenatal para determinar la necesidad de transfusión intrauterina y parto prematuro. El tratamiento postnatal incluye estrecha vigilancia, fototerapia para la ictericia y exanguinotransfusión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos graves. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de las madres RhD negativas, la sensibilización materna puede evitarse utilizando inmunoglobulina anti-D (RhoGAM). El pronóstico es excelente con cuidados prenatales, tamizaje del grupo sanguíneo y disponibilidad de inmunoglobulina RhD.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enfermedad hemolítica del feto y del recién nacido es una anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica del feto o del recién nacido de diversos grados de severidad debida a los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis maternos contra los LOS Neisseria antígenos de superficie de los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos fetales.
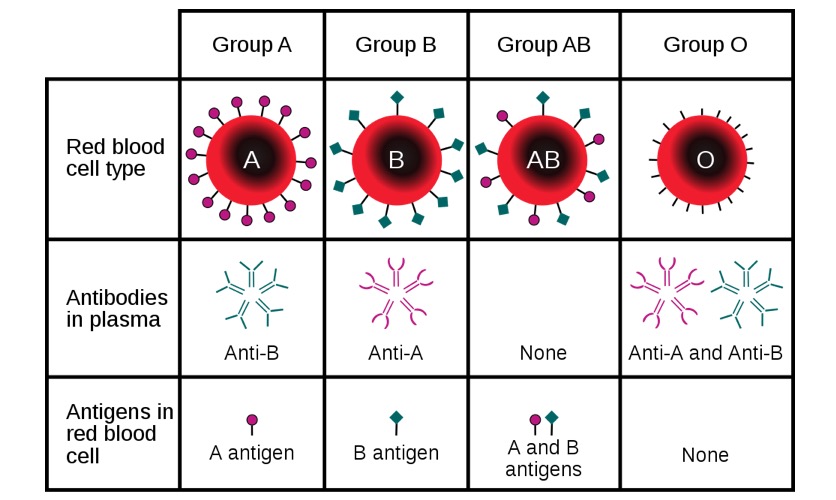
Principales grupos sanguíneos ABO con los respectivos antígenos y anticuerpos según el tipo de sangre
Imagen: “ABO blood type” por InvictaHOG. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoDurante el embarazo, los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos del feto se desplazan a través de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity hacia la circulación materna:
Incompatibilidad ABO:
Incompatibilidad Rhesus:
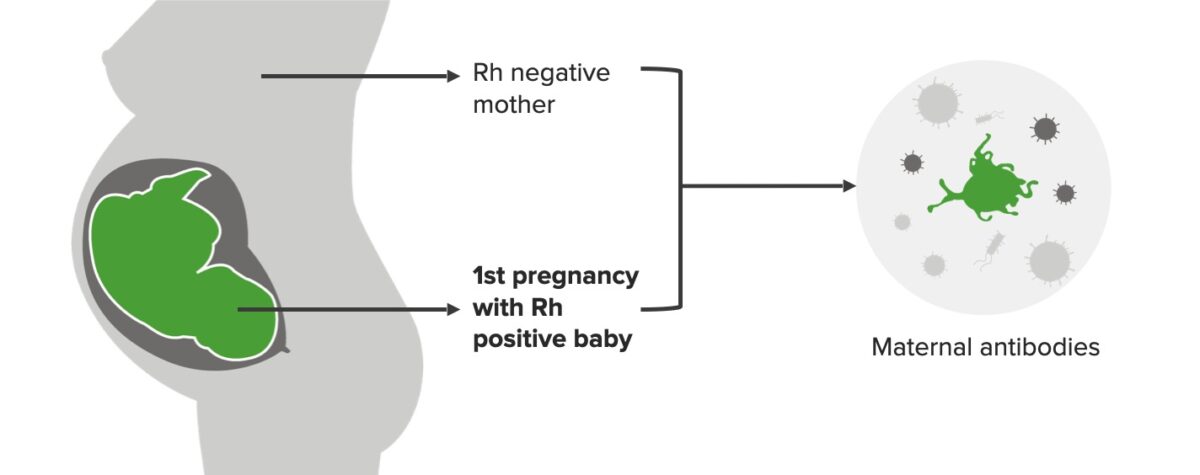
Incompatibilidad Rh, 1er embarazo:
La madre es Rh negativo y el bebé es Rh positivo en el 1er embarazo, lo que desencadena la formación de anticuerpos maternos (IgM). Este escenario no afecta al 1er bebé.
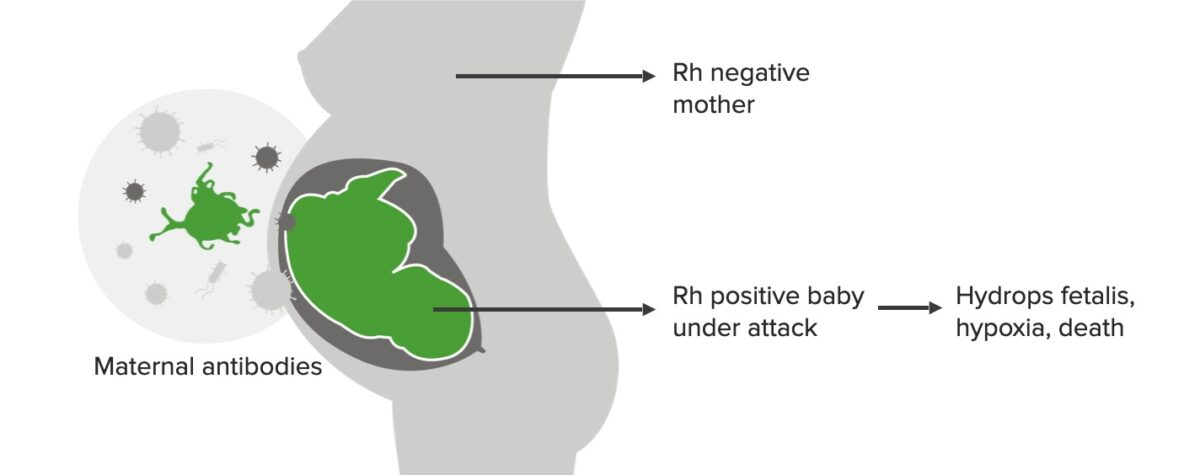
Incompatibilidad Rh, 2do embarazo:
Si bien el 1er bebé no se ve afectado, para entonces se han desarrollado anticuerpos maternos IgG, que atacan al bebé si es Rh positivo. Este escenario puede conducir a hidropesía fetal, hipoxia y muerte.
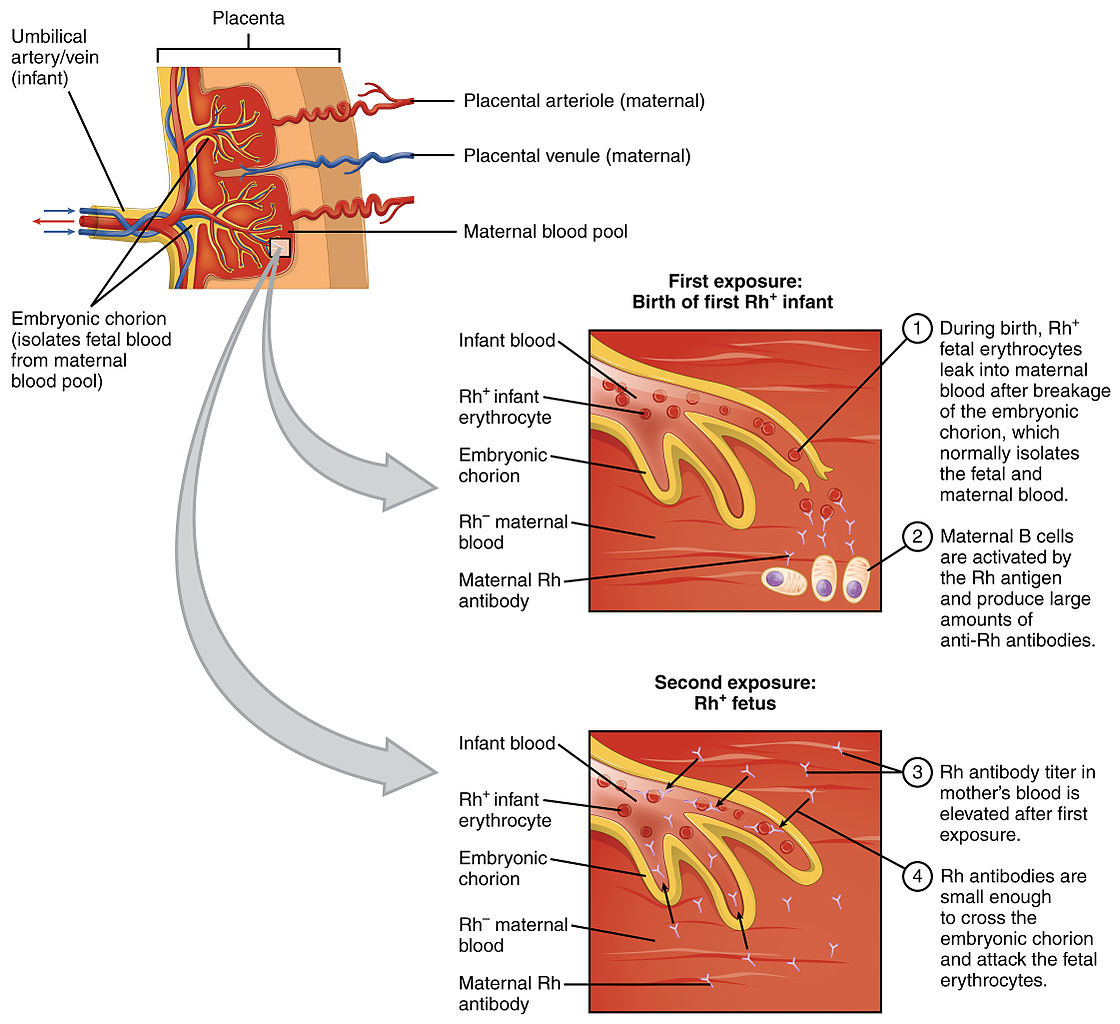
Fisiopatología de la incompatibilidad Rhesus durante los embarazos
Imagen: “Erythroblastosis Fetalis” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0El ultrasonido podría evidenciar hidropesía fetal inmune, una afección potencialmente mortal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que los LOS Neisseria fetos presentan una acumulación anormal de líquido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ultrasonido de la hidropesía fetal inmune pueden incluir:
Enfermedad leve a moderada:
Enfermedad grave:
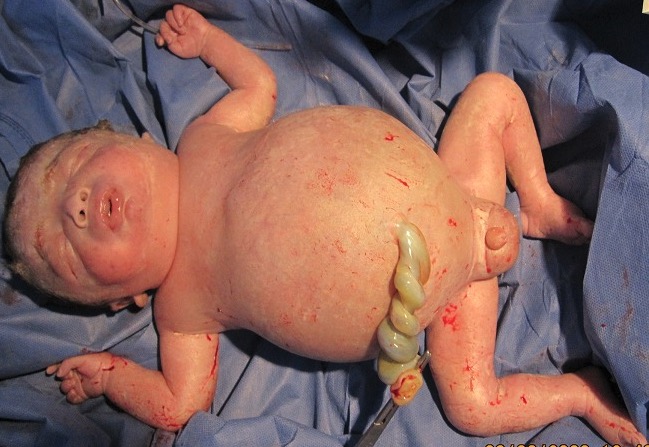
Hidropesía fetal en un recién nacido, de una madre Rhesus negativa sin la debida prevención:
Observe el edema generalizado.
Es importante identificar los LOS Neisseria posibles factores de riesgo para una sensibilización desconocida, así como antecedentes previos de enfermedad hemolítica del feto y del recién nacido durante el embarazo. Las posibles incompatibilidades sanguíneas son:
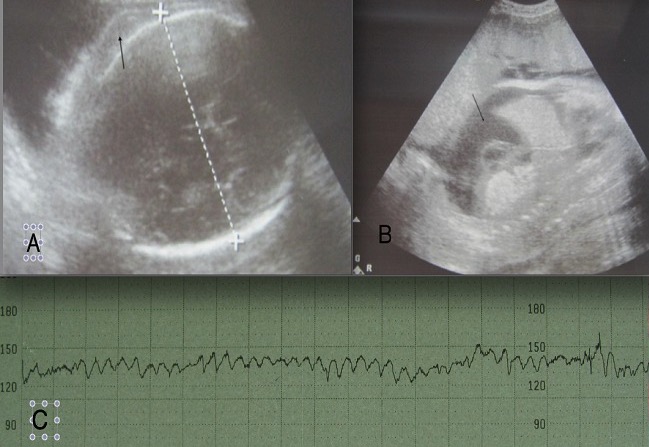
Diagnóstico de la enfermedad hemolítica del feto y del recién nacido
A: ultrasonido de la cabeza del feto que muestra edema del cuero cabelludo (flecha); B: ultrasonido que muestra ascitis (flecha) en un corte sagital del abdomen; C: patrón de frecuencia cardíaca fetal sinusoidal que se observa en pacientes con anemia grave.
Las incompatibilidades RhD son las únicas formas de aloinmunización que se pueden prevenir.
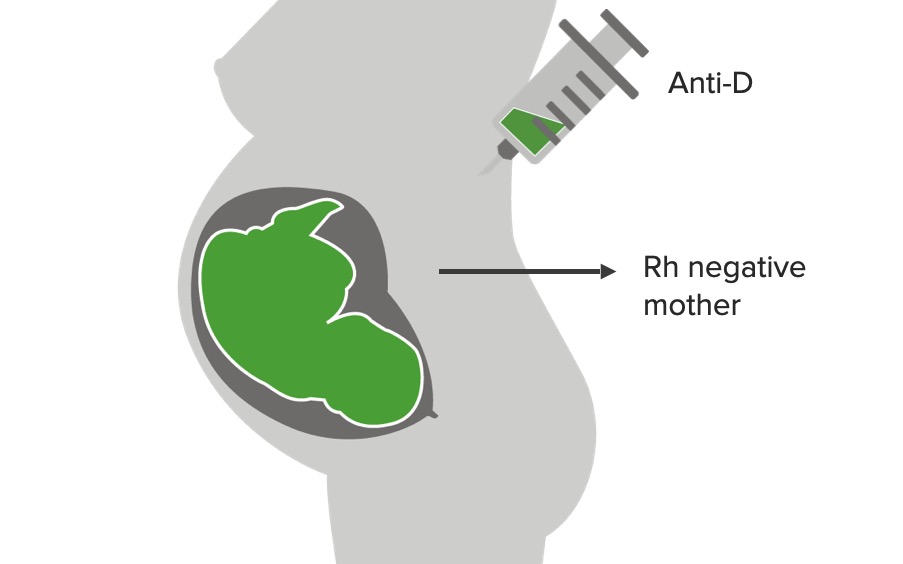
Prevención de la sensibilización mediante inmunoglobulinas anti-D (RhoGAM):
El Anti-D se une a los antígenos Rh negativos en la circulación de la madre para evitar la sensibilización y el desarrollo de una respuesta inmune/formación de anticuerpos frente al Rh negativo.
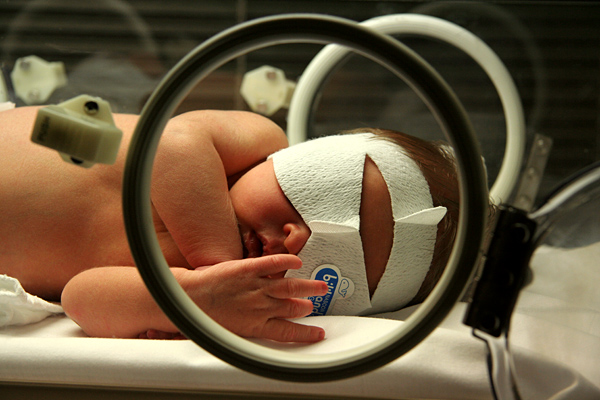
Imagen de ictericia neonatal: recién nacido sometido a fototerapia
Imagen: “Jaundice phototherapy” por Martin Pot. Licencia: CC BY 3.0