Un émbolo es un material sólido, líquido o gaseoso intravascular que es transportado por la sangre a un sitio distante de su punto de origen. Las embolias de todo tipo justifican una atención médica inmediata. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria émbolos se desprenden de un trombo, formando un tromboembolismo. Otros tipos de émbolos no trombóticos menos comunes son el colesterol, la grasa, el aire, el líquido amniótico y los LOS Neisseria émbolos tumorales. La causa del émbolo depende del tipo, al AL Amyloidosis igual que la presentación clínica, el diagnóstico y el manejo de cada condición embólica. Debido a sus efectos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la circulación, todos los LOS Neisseria émbolos tienen el potencial de provocar falla orgánica y la muerte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La presentación clásica incluye hallazgos cutáneos, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal e insuficiencia renal progresiva tras un procedimiento vascular. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas neurológicos y oculares también son comunes si los LOS Neisseria émbolos se desplazan superiormente.
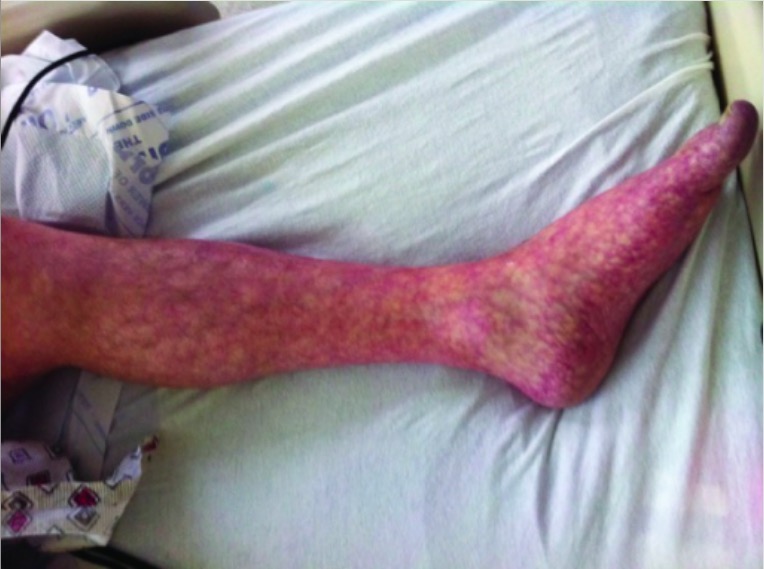
Livedo reticularis de la pierna izquierda
Imagen: “Livedo reticularis of left leg” por Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, TX, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0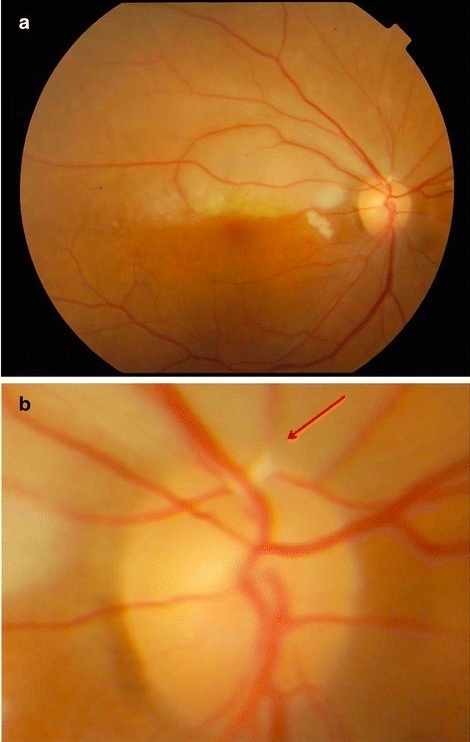
a: foto del fondo de ojo que muestra una retina pálida superiormente
b: vista de cerca del disco óptico de la imagen anterior que muestra una placa de Hollenhorst en el vaso superotemporal (flecha)
El diagnóstico suele ser clínico. El diagnóstico definitivo requiere una biopsia.
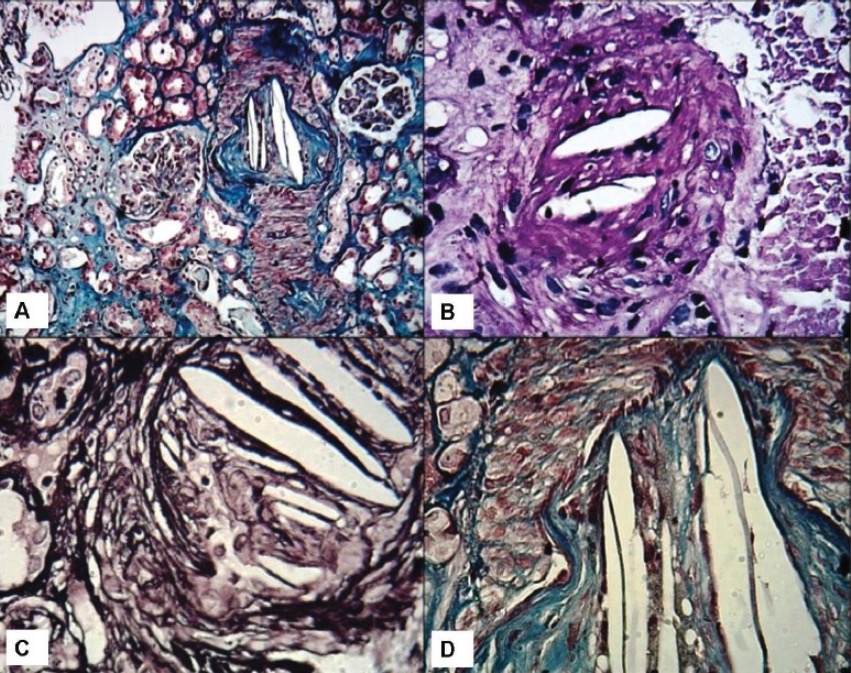
Biopsias renales que muestran hendiduras de colesterol:
A: Vista de bajo poder que muestra una arteria interlobulillar con oclusión luminal y cristales en forma de aguja en el lumen. Se observan dos glomérulos en la vecindad con cambios menores en la microscopía de luz. Se observa una leve atrofia tubular en parches (tinción de tricrómico de Masson, ×100).
B: Vista a medio poder que muestra una pequeña arteria con hendiduras luminales de colesterol que causan oclusión luminal (tinción de ácido periódico-Schiff, ×200).
C: Vista de alto poder que muestra las típicas hendiduras de colesterol de aspecto vacío y en forma de aguja en las luces (tinción de plata con metenamina de Jones, ×400).
D: Vista de alto poder que muestra hendiduras luminales de colesterol y fibrosis de la íntima. Los medios aparecen rojos en esta tinción (tinción de tricrómico de Masson, ×400).
La patogénesis puede ser por 1 o ambos de los LOS Neisseria siguientes mecanismos:
Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas suelen desarrollarse entre 24–72 horas después del suceso desencadenante.
La embolia grasa suele ser un diagnóstico clínico tras excluir otras posibilidades.
Una embolia de aire se produce cuando las burbujas de gas entran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la circulación y bloquean el flujo sanguíneo.
| Etiología | Ejemplos |
|---|---|
| Procedimientos quirúrgicos |
|
| Cateterismo intravenoso |
|
| Trauma |
|
| Barotrauma Barotrauma Injury following pressure changes; includes injury to the eustachian tube, ear drum, lung and stomach. Invasive Mechanical Ventilation pulmonar |
|
La presentación depende del lugar y del tamaño de la embolia.
Embolia aérea venosa → aire viaja al AL Amyloidosis ventrículo derecho → circulación pulmonar:
Embolia aérea arterial → aire viaja a los LOS Neisseria órganos diana → isquemia:
El diagnóstico se realiza mediante la determinación de aire en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio intravascular o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria órganos de un paciente con factores de riesgo conocidos. Sin embargo, el aire suele reabsorberse rápidamente y dejar de estar presente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el momento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum que el paciente se somete a las pruebas de diagnóstico; por lo tanto, el diagnóstico suele hacerse clínicamente.
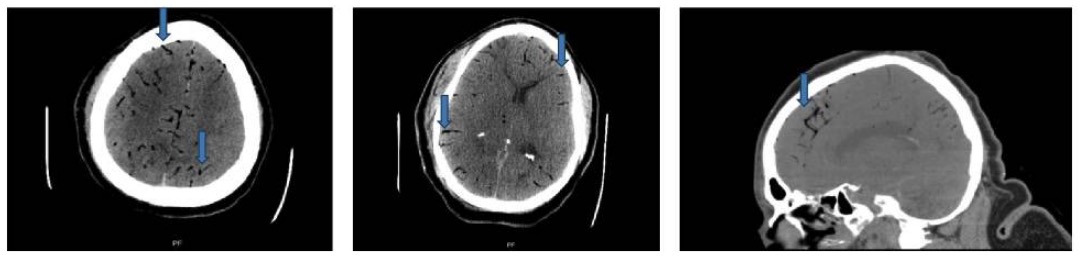
TC de la cabeza: cortes axiales y sagitales que muestran focos de gas en las arterias cerebrales de forma bilateral (flechas azules)
Imagen: “Case 2 CT scan of head” por Rashmi Mishra et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Estabilizar al AL Amyloidosis paciente:
Reposicionamiento:
Terapias definitivas:

Cámara de oxigenoterapia hiperbárica
Imagen: “Hyperbaric oxygen therapy chamber” por Mark Murphy. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa embolia de líquido amniótico es una complicación durante el parto y el posparto inmediato.
La embolia de líquido amniótico suele presentarse de forma dramática, como un colapso cardiopulmonar de inicio súbito que se produce durante el parto o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria 30 minutos posteriores al AL Amyloidosis mismo.
La embolia de líquido amniótico es un diagnóstico clínico basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación.
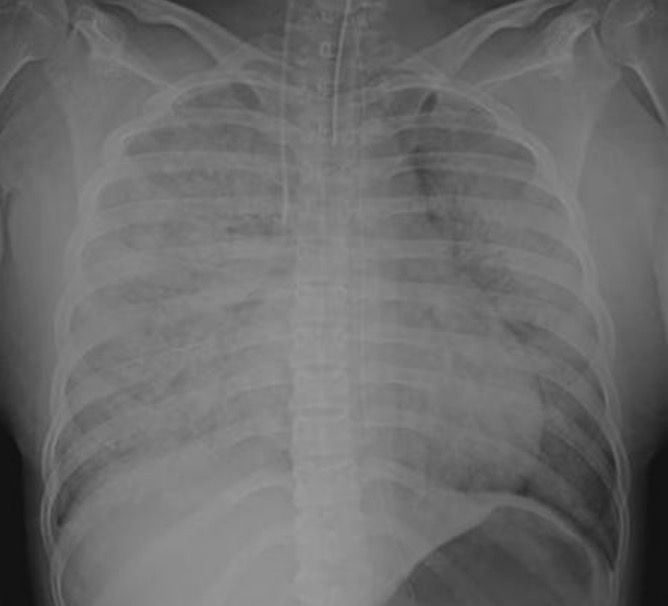
Radiografía de tórax de una paciente con embolia de líquido amniótico:
Se observa una infiltración difusa en todos los pulmones.
La supervivencia depende de un diagnóstico rápido y una reanimación eficaz.
| Tipo de embolia | Presentaciones clínicas más comunes | Tratamiento |
|---|---|---|
| Embolia de colesterol | Origen torácico:
|
Se enfoca
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum la reducción de riesgos
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum la enfermedad aterosclerótica:
|
| Embolia grasa | Por un traumatismo ortopédico:
|
Cuidados de soporte |
| Embolia de aire | Por:
|
|
| Embolia de líquido amniótico | Durante el parto o dentro de
los
LOS
Neisseria 30 minutos posteriores
al
AL
Amyloidosis mismo:
|
|
| Embolia tumoral | De cualquier malignidad
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum fase terminal:
|
|