Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome son un grupo de medicamentos diuréticos que se utilizan principalmente para tratar la sobrecarga de volumen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum condiciones edematosas como la insuficiencia cardíaca y la cirrosis. Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome también tratan la hipertensión, pero no como agente de 1ra línea. El medicamento inhibe la reabsorción de sodio a través del cotransportador NKCC2 NKCC2 Renal Potassium Regulation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rama ascendente gruesa del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome de Henle, provocando una diuresis importante. Es importante un monitoreo cuidadoso porque los LOS Neisseria diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome provocan un aumento de la excreción de sodio, potasio, cloro, calcio, magnesio y agua. Además de las anomalías de electrolitos y líquidos, los LOS Neisseria diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome pueden provocar nefrotoxicidad y ototoxicidad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome son un grupo de medicamentos utilizados principalmente para tratar el edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema (y a veces la hipertensión) mediante la inhibición de la reabsorción de sodio a través del cotransportador NKCC2 NKCC2 Renal Potassium Regulation (también conocido como cotransportador de Na+-K+-Cl–) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rama ascendente gruesa del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome de Henle ( TAL TAL Renal Sodium and Water Regulation), lo que provoca una diuresis significativa.
| Sitio de acción | Clase | Subclases |
|---|---|---|
| Medicamentos renales | Medicamentos que afectan al AL Amyloidosis SRAA | |
| Diuréticos |
|
|
| Medicamentos extrarrenales | Vasodilatadores directos | |
| Agentes que actúan a través del sistema nervioso simpático |
|
Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos incluyen:
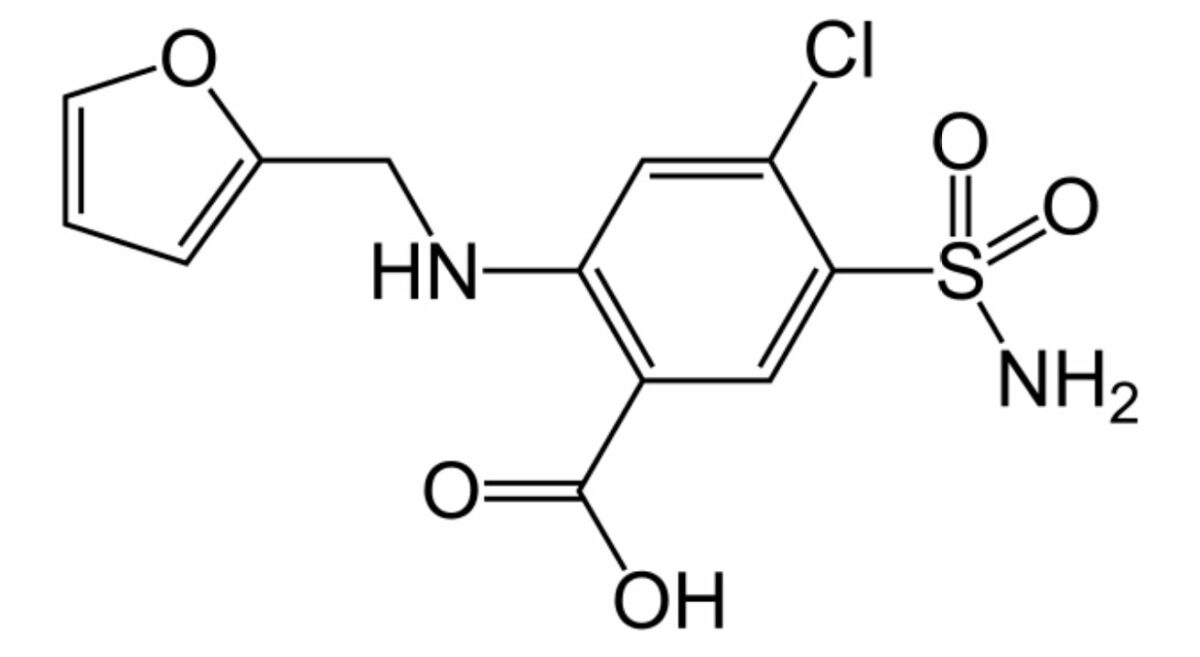
Estructura química de la furosemida
Imagen: “Furosemida” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público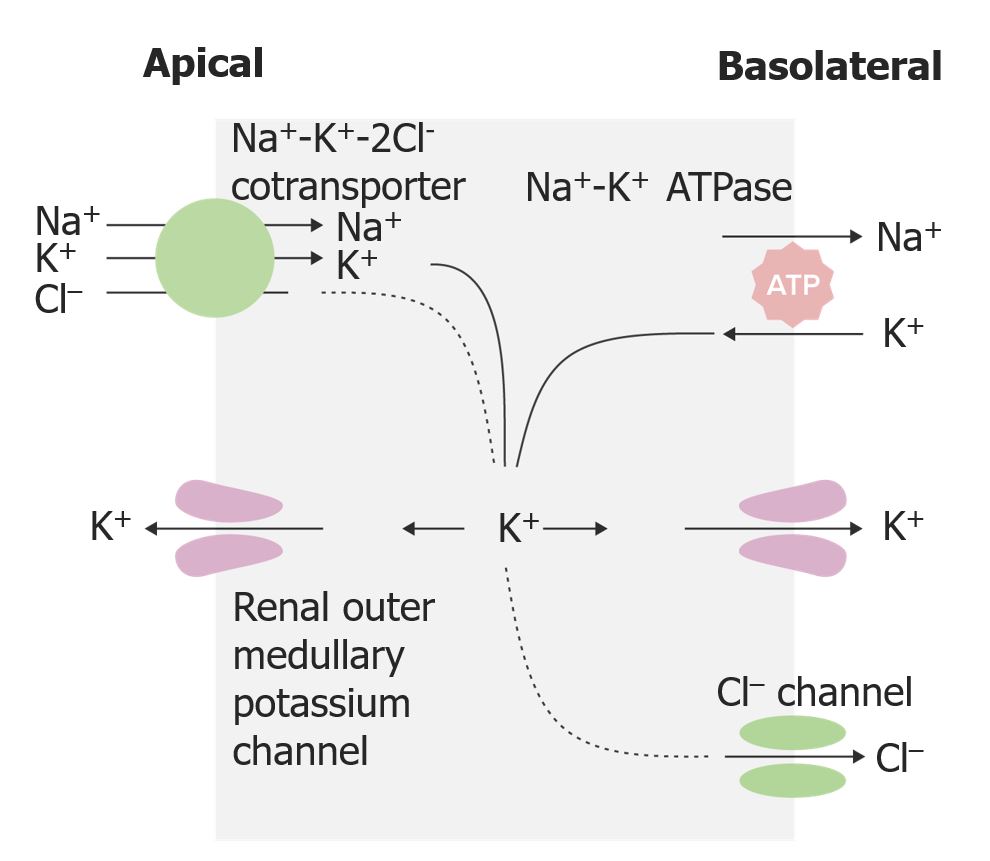
Acción de los diuréticos de asa en la rama ascendente gruesa del asa de Henle
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0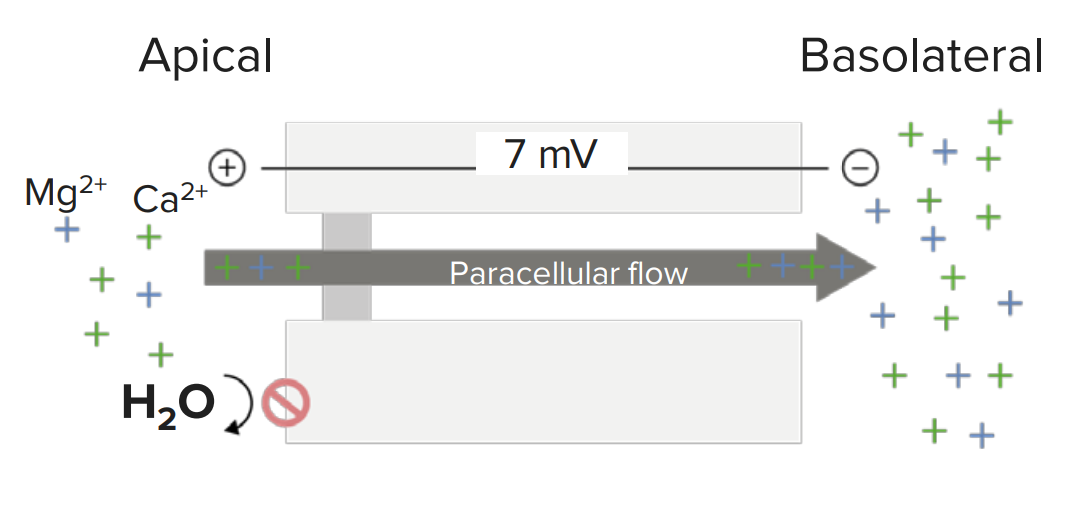
Reabsorción paracelular pasiva de magnesio y calcio en la rama ascendente gruesa del asa de Henle: impulsada por el gradiente de voltaje entre el lumen tubular (región apical) y el líquido intersticial (región basolateral)
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Medicamento | Absorción | Distribución | Metabolismo | Excreción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furosemida ( Lasix Lasix A benzoic-sulfonamide-furan. It is a diuretic with fast onset and short duration that is used for edema and chronic renal insufficiency. Loop Diuretics®) |
|
Unión a proteínas: 95% | Metabolismo hepático mínimo |
|
| Bumetanida ( Bumex Bumex A sulfamyl diuretic. Loop Diuretics®) |
|
|
Metabolismo hepático parcial |
|
| Torasemida ( Demadex Demadex A pyridine and sulfonamide derivative that acts as a sodium-potassium chloride symporter inhibitor (loop diuretic). It is used for the treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure; chronic renal insufficiency; and liver diseases. It is also used for the management of hypertension. Loop Diuretics®) |
|
|
Hepático (80%) vía CYP2C9 CYP2C9 A cytochrome p-450 subtype that has specificity for acidic xenobiotics. It oxidizes a broad range of important clinical drugs that fall under the categories of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents; hypoglycemic agents; anticoagulants; and diuretics. Anticoagulants |
|
| Ácido etacrínico ( Edecrin Edecrin A compound that inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. This compound has been classified as a loop or high ceiling diuretic. Loop Diuretics®) | Efecto máximo:
|
Unión a proteínas: > 90% | Hepático (40%) a través de la vía cisteína conjugada activada |
|
Mnemotecnia:
Para no olvidar los LOS Neisseria efectos adversos de los LOS Neisseria diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome, recordar “Ohh Daang” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome deben utilizarse con precaución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las siguientes situaciones:
Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos tiazídicos, los LOS Neisseria diuréticos ahorradores de potasio, los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica y los LOS Neisseria diuréticos osmóticos también son diuréticos comunes.
| Medicamento | Mecanismo | Efecto fisiológico | Indicación |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diurético tiazídico: Hidroclorotiazida | ↓ Reabsorción de NaCl en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el túbulo contorneado distal a través de la inhibición del cotransportador de Na+/Cl–. |
|
|
| Diurético de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome: Furosemida | Inhibe el cotransportador luminal de Na+/K+/Cl– en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rama ascendente gruesa del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome de Henle |
|
|
| Diurético ahorrador de potasio: Espironolactona |
|
|
|
| Inhibidor de la anhidrasa carbónica: Acetazolamida | Inhibe tanto la hidratación del CO2 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células epiteliales del túbulo contorneado proximal como la deshidratación del H2CO3 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lumen del túbulo contorneado proximal; provoca una excreción ↑ HCO3– y Na+. |
|
|
| Diuréticos osmóticos: Manitol | ↑ Presión osmótica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el filtrado glomerular → ↑ líquido tubular e impide la reabsorción de agua. |
|
|
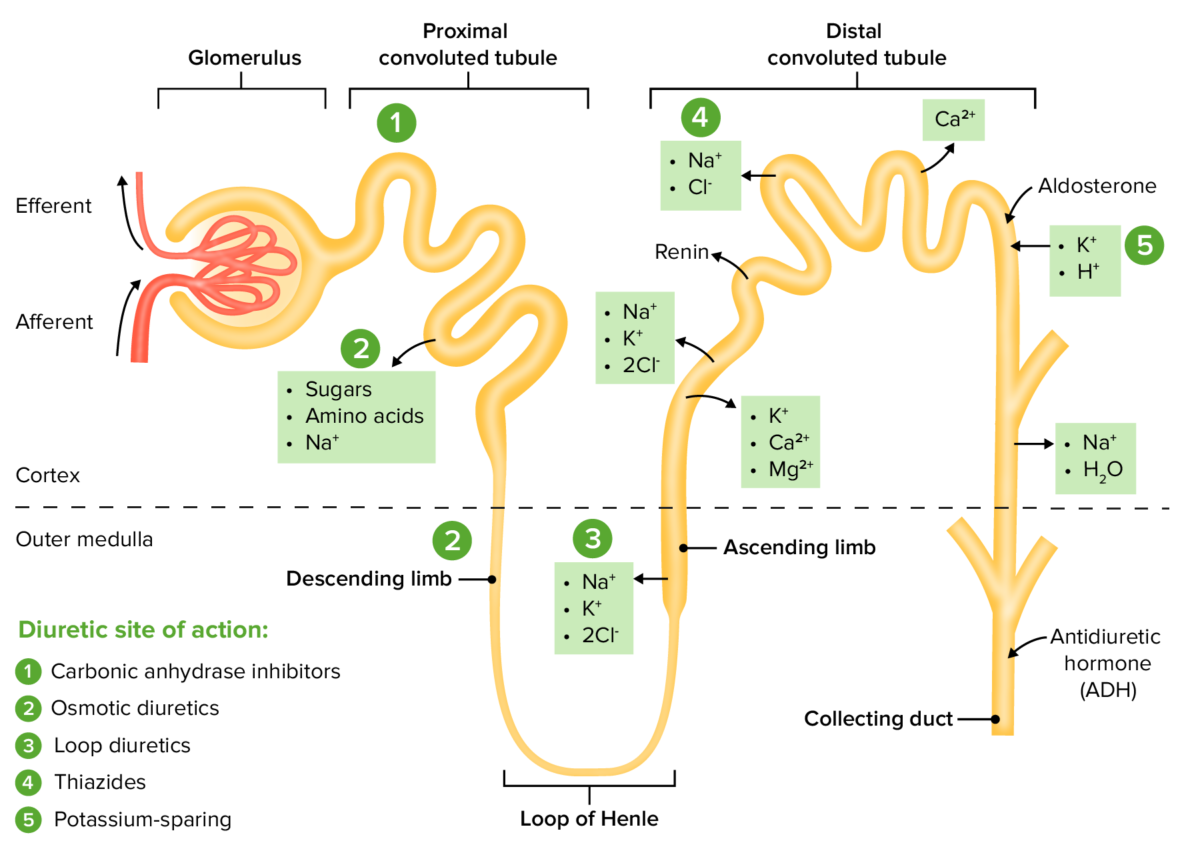
Sitios de acción, dentro de la nefrona, para las clases de medicamentos diuréticos
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0