La criptococosis es una infección fúngica oportunista causada por especies de Cryptococcus Cryptococcus Cryptococcosis is an opportunistic, fungal infection caused by the Cryptococcus species. The principal pathogens in humans are C. neoformans (primary) and C. gattii. Cryptococcus neoformans is typically found in pigeon droppings and acquired by inhaling dust from contaminated soil. The majority of affected patients are immunocompromised. Cryptococcus/Cryptococcosis. Los LOS Neisseria principales patógenos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos son C. neoformans C. neoformans A species of the fungus cryptococcus. Its teleomorph is filobasidiella neoformans. Cryptococcus/Cryptococcosis (principalmente) y C. gattii C. gattii A species of the fungus cryptococcus. Its teleomorph is filobasidiella bacillispora. Cryptococcus/Cryptococcosis. Cryptococcus Cryptococcus Cryptococcosis is an opportunistic, fungal infection caused by the Cryptococcus species. The principal pathogens in humans are C. neoformans (primary) and C. gattii. Cryptococcus neoformans is typically found in pigeon droppings and acquired by inhaling dust from contaminated soil. The majority of affected patients are immunocompromised. Cryptococcus/Cryptococcosis neoformans se encuentra normalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria excrementos de las palomas y se adquiere al AL Amyloidosis inhalar el polvo del suelo contaminado. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes que se ven afectados están inmunocomprometidos. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con SIDA, uso crónico de esteroides y trasplante de órgano se ven especialmente afectados. El principal factor de virulencia es la presencia de la cápsula antifagocítica, formada por repetidos antígenos polisacáridos capsulares. La infección suele afectar a los LOS Neisseria pulmones y se presenta como una lesión primaria o neumonía. Si la diseminación ocurre puede afectar al AL Amyloidosis cerebro y las meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy, la piel, los LOS Neisseria huesos y los LOS Neisseria órganos viscerales. El tratamiento de la meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis criptocócica suele consistir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum anfotericina B y flucitosina, seguido de fluconazol. La criptococosis es una enfermedad definitoria del SIDA y se asocia típicamente a un recuento de CD4 < 100 células/μL.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El factor de riesgo más importante para la infección es el estado de inmunidad. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum frecuencia decreciente, las siguientes condiciones son las más frecuentemente asociadas a la infección:
La presentación clínica varía según la zona afectada y el estado inmunitario del huésped:
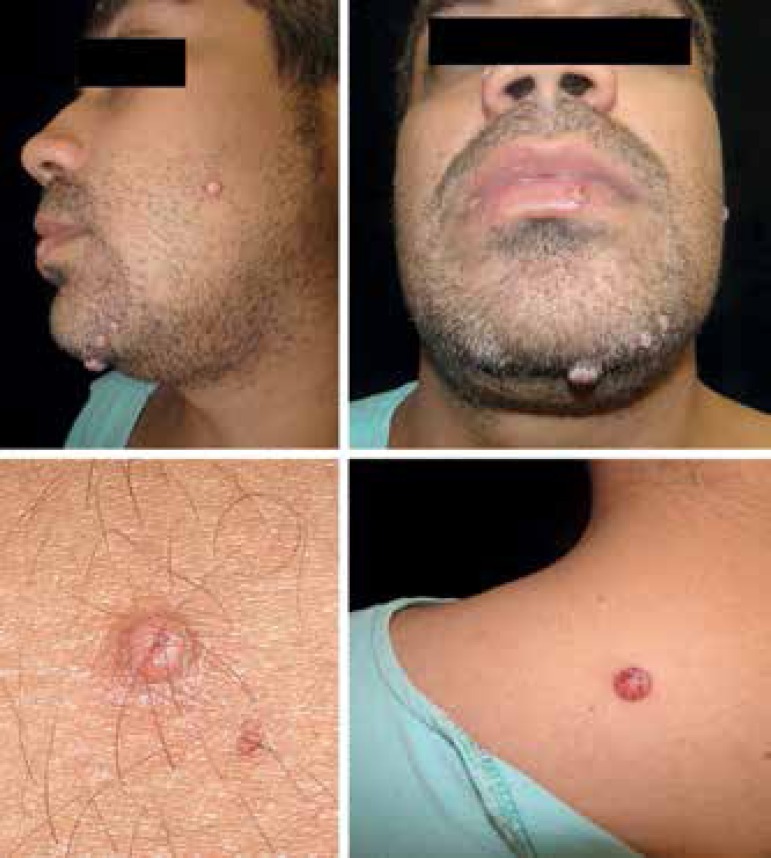
Criptococosis cutánea: Las lesiones papulonodulares (algunas muestran costras y centro umbilicado) están en la cara y el dorso superior. La infección por Cryptococcus se confirma en las lesiones cutáneas.
Imagen: “Disseminated cryptococcosis with cutaneous involvement in an immunocompetent patient” por Gabriely Lessa Sacht et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0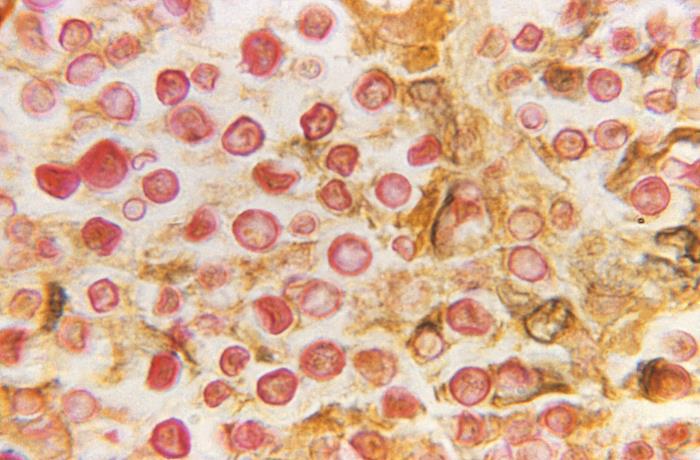
Microfotografía de Cryptococcus neoformans procesada mediante la tinción de mucicarmín:
El polisacárido de la cápsula de C. neoformans crea una mancha roja prominente.
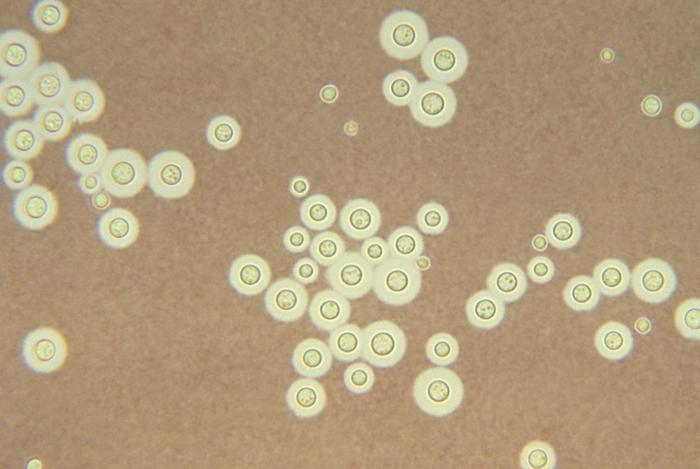
Imagen histológica que muestra Cryptococcus neoformans teñido con tinta china: La aparición de un halo alrededor de cada célula de levadura representa la cápsula observable. Imagen: “Cryptococcus neoformans” por CDC/ Dr. Leanor Haley. Licencia: Dominio Público
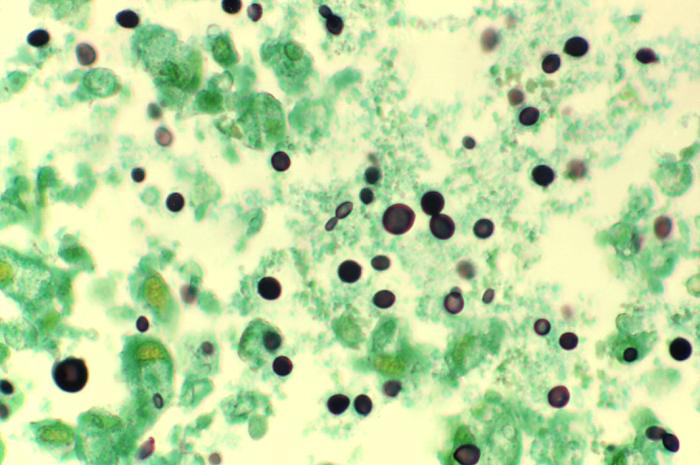
Microfotografía de una muestra de tejido pulmonar teñida con metenamina, obtenida de un paciente con síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida (SIDA) infectado por Cryptococcus:
La histopatología revela numerosos organismos extracelulares de C. neoformans en forma de levadura dentro del espacio alveolar. Algunos de las levaduras muestran una gemación con base estrecha y una variación de tamaño característica.
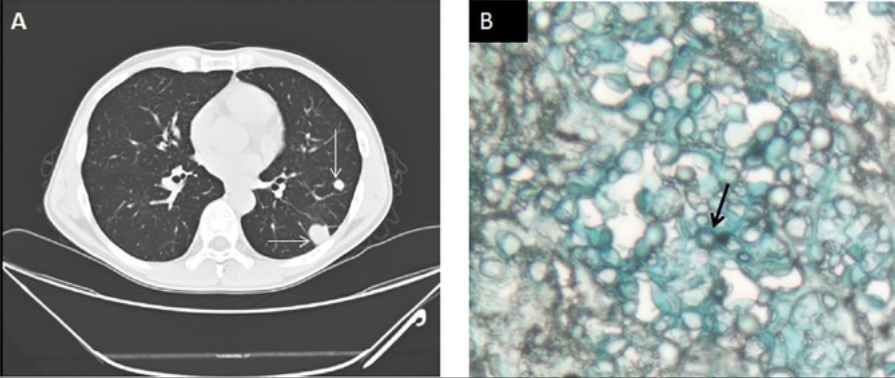
Criptococosis pulmonar:
Hombre de 49 años que acude al hospital con linfadenopatía desde hace 3 meses, fiebre desde hace 1 mes e infección por VIH con un recuento de CD4 de 108 células/μL. El título de antígeno criptocócico en suero era de 1:40. La prueba de galactomanano en suero fue negativa.
A: TC de tórax que muestra múltiples nódulos pulmonares (flecha)
B: biopsia de pulmón que muestra células fúngicas encapsuladas, similares a las levaduras, consistentes con una infección criptocócica (flecha) en la tinción con azul alcián
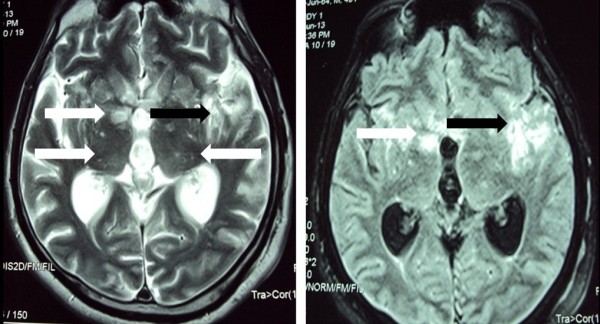
Resonancia magnética (RM) del cerebro que muestra imágenes ponderadas en T2 (izquierda) y recuperación de la inversión atenuada de fluidos (FLAIR, por sus siglas en inglés) (derecha): lesiones nodulares bilaterales múltiples en los ganglios basales y el tálamo (flechas blancas) y área mal definida de cambio de intensidad de señal en la región temporoparietal izquierda (flechas negras).
Imagen: “Cryptococcal meningitis presenting with bilateral complete ophthalmoplegia: a case report” por Liyanage DS et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0| Condición | Tratamiento |
|---|---|
| Infección del SNC | Anfotericina B + flucitosina, seguido de terapia de consolidación y mantenimiento |
| Inmunocompetentes e inmunodeprimidos con infección pulmonar leve (focal) | Fluconazol |
| Inmunocompetentes e inmunodeprimidos con infección pulmonar grave | Tratamiento de la infección del SNC |
| Inmunocompetentes e inmunodeprimidos con infección extrapulmonar, que no afecta al AL Amyloidosis SNC (≥ 2 sitios no contiguos) | Tratamiento de la infección del SNC |