La celulitis es una infección común causada por bacterias que afecta a la dermis y al tejido subcutáneo de la piel. Con frecuencia es causada por Staphylococcus aureus y Streptococcus pyogenes. La infección de la piel se presenta como un área eritematosa y edematosa con calor y dolor a la palpación. Las fronteras no están claramente delimitadas. Las extremidades inferiores son el sitio de infección más frecuente, pero la celulitis puede ocurrir en cualquier parte del cuerpo. El diagnóstico suele ser clínico y el tratamiento incluye antibióticos orales y/o parenterales. Se puede agregar cobertura para staphylococcus aureus resistente a la meticilina ( MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), dependiendo de la presencia de factores de riesgo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La celulitis es una inflamación de la piel y los LOS Neisseria tejidos subcutáneos. A menudo se debe a una infección.
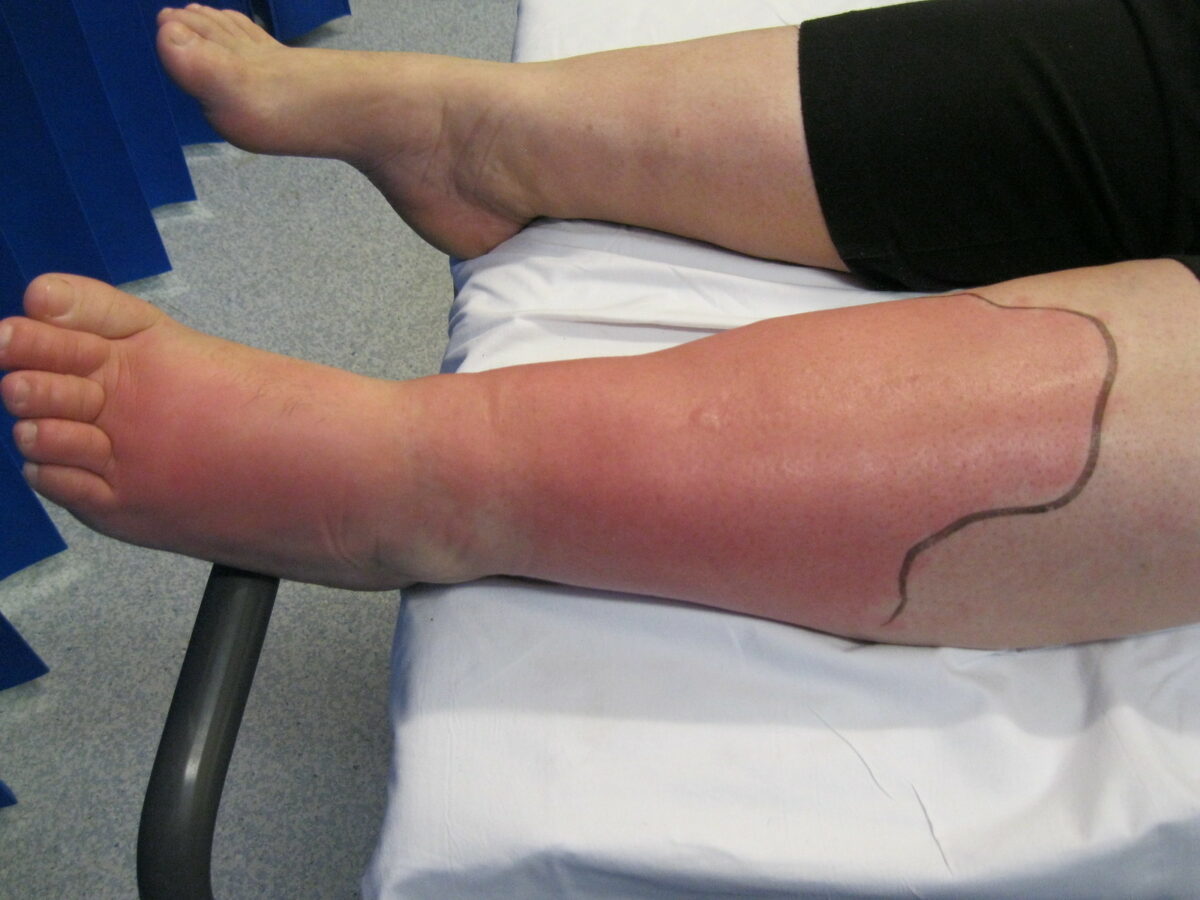
Celulitis de la extremidad inferior izquierda:
Se notan edema y eritema de la piel en la pierna y el pie izquierdos.
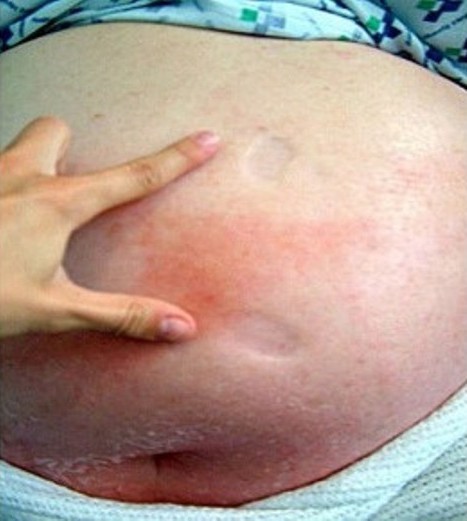
Celulitis de la pared abdominal:
La imagen muestra un marcado edema con fóvea y eritema con bordes mal delimitados debido a la celulitis.
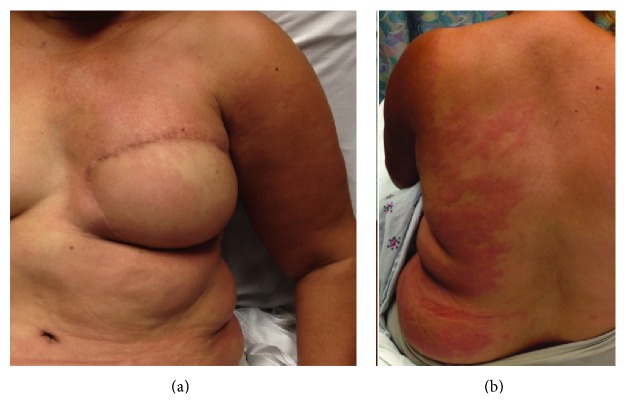
Celulitis por linfedema:
La linfa estancada es un medio ideal para el crecimiento bacteriano y la progresión puede ser rápida debido a una menor capacidad para combatir infecciones en el área afectada. Las infecciones suelen ser causadas por bacterias cocos grampositivos.
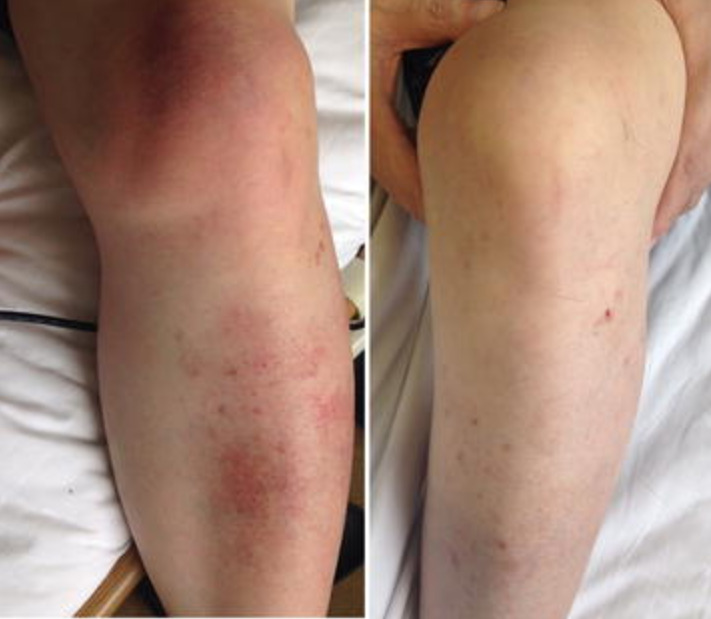
Celulitis en la parte inferior de la pierna izquierda y la rodilla:
Izquierda: hinchazón local con decoloración de la piel de color rosa salmón y calor local es evidente.
Derecha: pierna después de 6 semanas de terapia con antibióticos