Los LOS Neisseria antivirales contra la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus incluyen una amplia gama de clases de medicamentos. El régimen de tratamiento anterior incluía interferón alfa (IFN-α) y ribavirina, que se enfocan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la entrada viral, la inmunomodulación y la replicación viral. Los LOS Neisseria nuevos agentes antivirales de acción directa se dirigen a proteínas no estructurales (NS) específicas del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus ( HCV HCV Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C virus is an RNA virus and a member of the genus Hepacivirus and the family Flaviviridae. The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), importantes para la replicación viral. Estos agentes incluyen inhibidores de la proteasa NS3/4A, inhibidores de la NS5A e inhibidores de la polimerasa NS5B. Los LOS Neisseria antivirales de acción directa se administran a menudo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum terapia combinada y son el tratamiento de elección para la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus debido a su alta tasa de éxito y su perfil de efectos secundarios más leves.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El ARN del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus codifica:
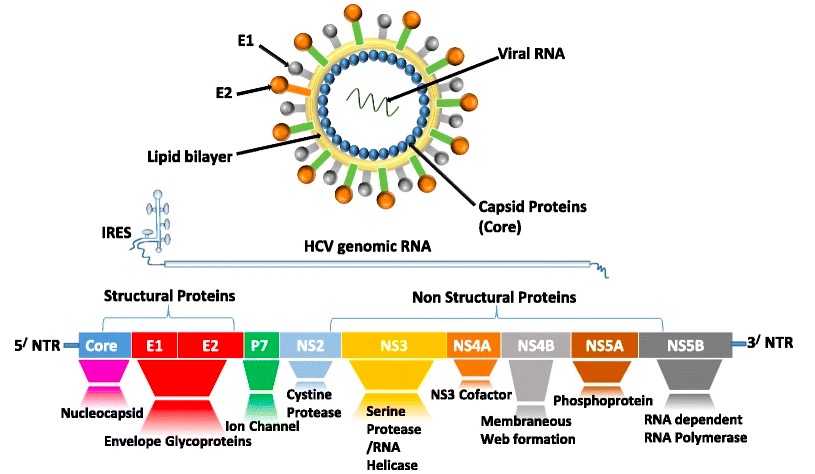
Estructura viral de la hepatitis C y las proteínas que se traducen de su genoma:
Las proteínas estructurales incluyen el núcleo, la envoltura 1 (E1) y E2. NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A y NS5B son proteínas no estructurales, la mayoría de las cuales son los blancos de la terapia antiviral de acción directa.
Los LOS Neisseria interferones son un tipo de proteína de señalización perteneciente a la familia de las citoquinas.
IFN-α funciona a través de varios mecanismos:
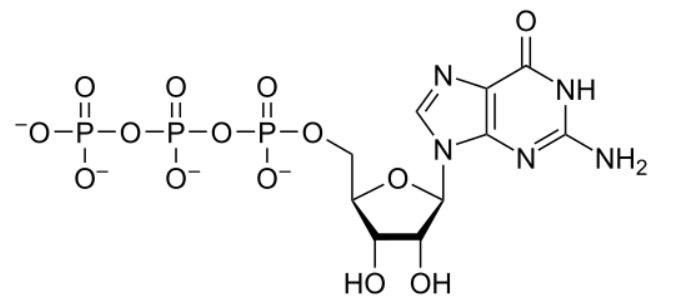
La estructura química del trifosfato de guanosina (GTP)
Imagen: “Chemical structure of GTP” por Hbf878. Licencia: CC0 1.0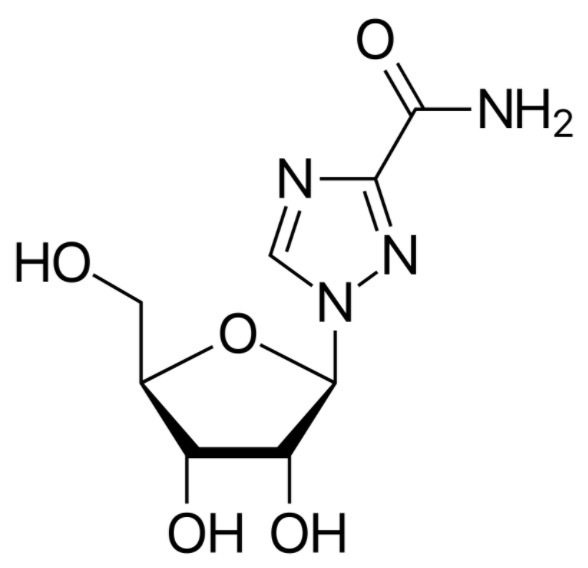
La estructura química de la ribavirina:
Es muy similar a la guanosina, que juega un papel importante en su acción antiviral.
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la proteasa NS3/4A son una clase de medicamento que inhibe la serina proteasa NS3/4A, que es necesaria para la replicación del HCV HCV Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C virus is an RNA virus and a member of the genus Hepacivirus and the family Flaviviridae. The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C Virus.
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la proteasa NS3/4A se usan (generalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum terapia combinada con otro antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B de acción directa) para tratar la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus crónica.
Estos medicamentos se usan (generalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum terapia combinada con otro antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B de acción directa) para el tratamiento de la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus crónica.
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la ARN polimerasa NS5B dependiente de ARN se enfocan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum NS5B (una polimerasa de ARN dependiente de ARN).
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la ARN polimerasa NS5B dependientes de ARN se usan (generalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum terapia combinada con otro antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B de acción directa) para el tratamiento de la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus crónica.