La estructura y la función normales de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity son esenciales para un embarazo saludable. Algunas de las anomalías más comunes de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity son las anomalías estructurales (como la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity succenturiata o la inserción velamentosa del cordón), anomalías de implantación (como la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity acreta y la placenta previa Placenta Previa Abnormal placentation in which the placenta implants in the lower segment of the uterus (the zone of dilation) and may cover part or all of the opening of the cervix. It is often associated with serious antepartum bleeding and premature labor. Placental Abnormalities) y las anomalías funcionales (como la insuficiencia placentaria). La placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity suele verse bien en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ultrasonido, y la evaluación de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity forma parte del tamizaje prenatal rutinario, que es cuando se identifican la mayoría de las anomalías estructurales y de implantación. Debido a la amplia circulación materna y fetal a través de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity, las anomalías placentarias pueden aumentar significativamente el riesgo de hemorragia grave antes o después del parto. Las anomalías de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity también suelen influir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las decisiones relativas al AL Amyloidosis momento y la vía del parto.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity es una estructura importante para el crecimiento y el desarrollo del feto durante su vida embrionaria y fetal. Las anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su estructura, función o implantación pueden provocar complicaciones graves y potencialmente mortales tanto para el feto como para la madre.
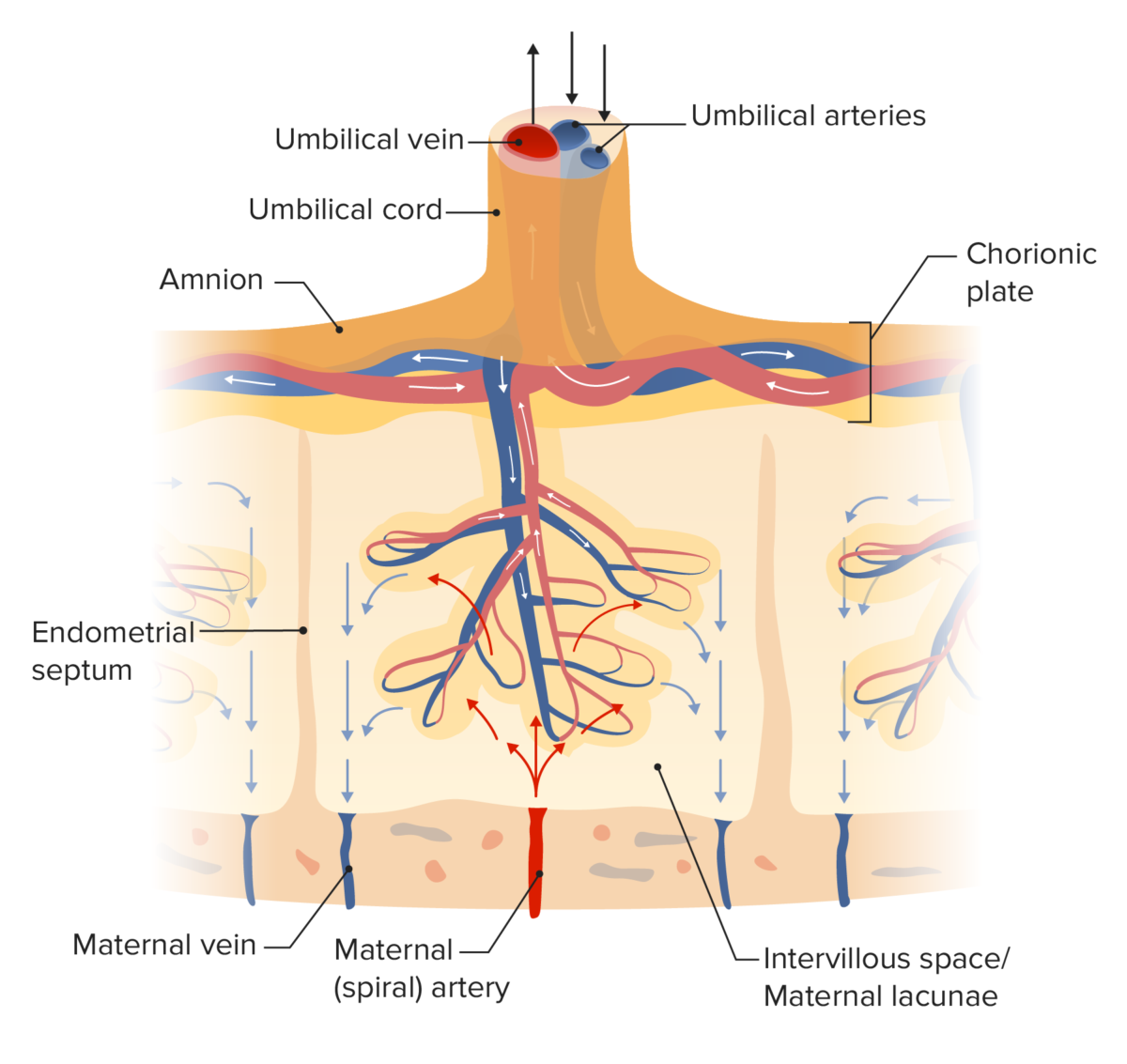
Diagrama de la circulación placentaria: Las arterias espirales maternas llevan sangre oxigenada a la placenta. En las zonas que rodean las vellosidades coriónicas, las arterias espirales se “rompen” y la sangre circula por los espacios, que se conocen como lagunas maternas. La sangre fetal desoxigenada entra en la placenta a través de las arterias umbilicales. La sangre circula a través de las vellosidades coriónicas. El intercambio de gases y moléculas se produce entre la sangre materna en las lagunas y la sangre fetal en las vellosidades coriónicas. La sangre fetal oxigenada sale de la placenta a través de la vena umbilical, mientras que la sangre materna desoxigenada sale a través de la vena materna. La sangre materna y la fetal nunca se mezclan directamente.
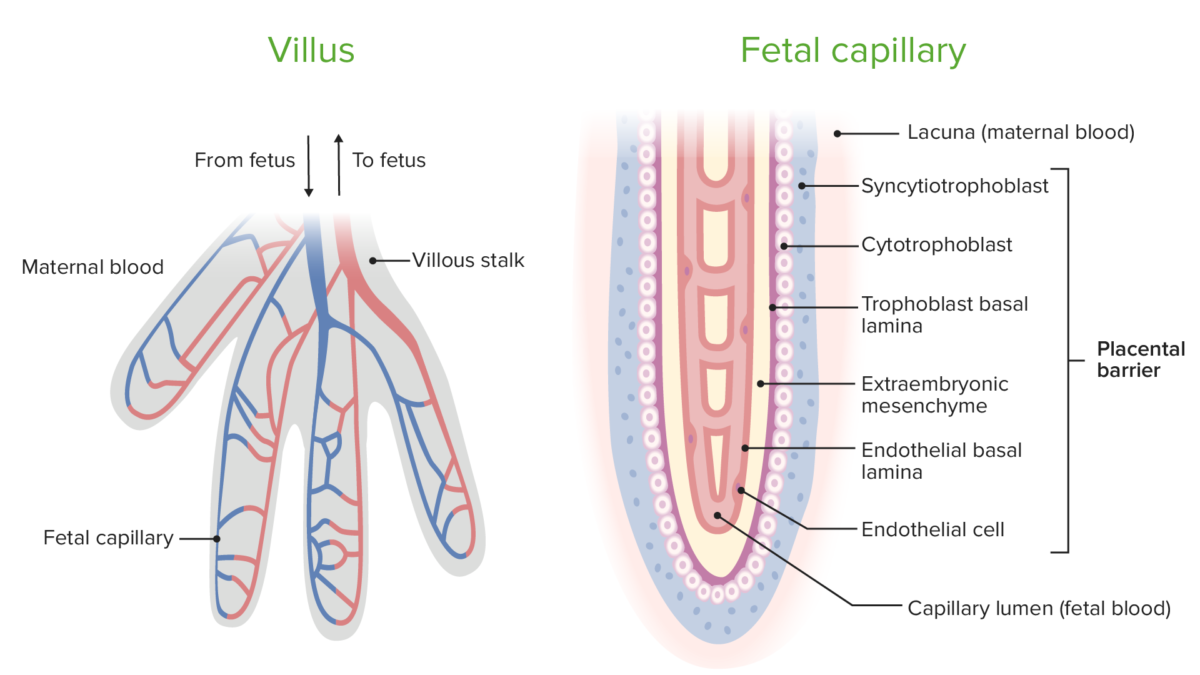
Diagrama que muestra la circulación dentro de las vellosidades coriónicas y los componentes de la barrera placentaria
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0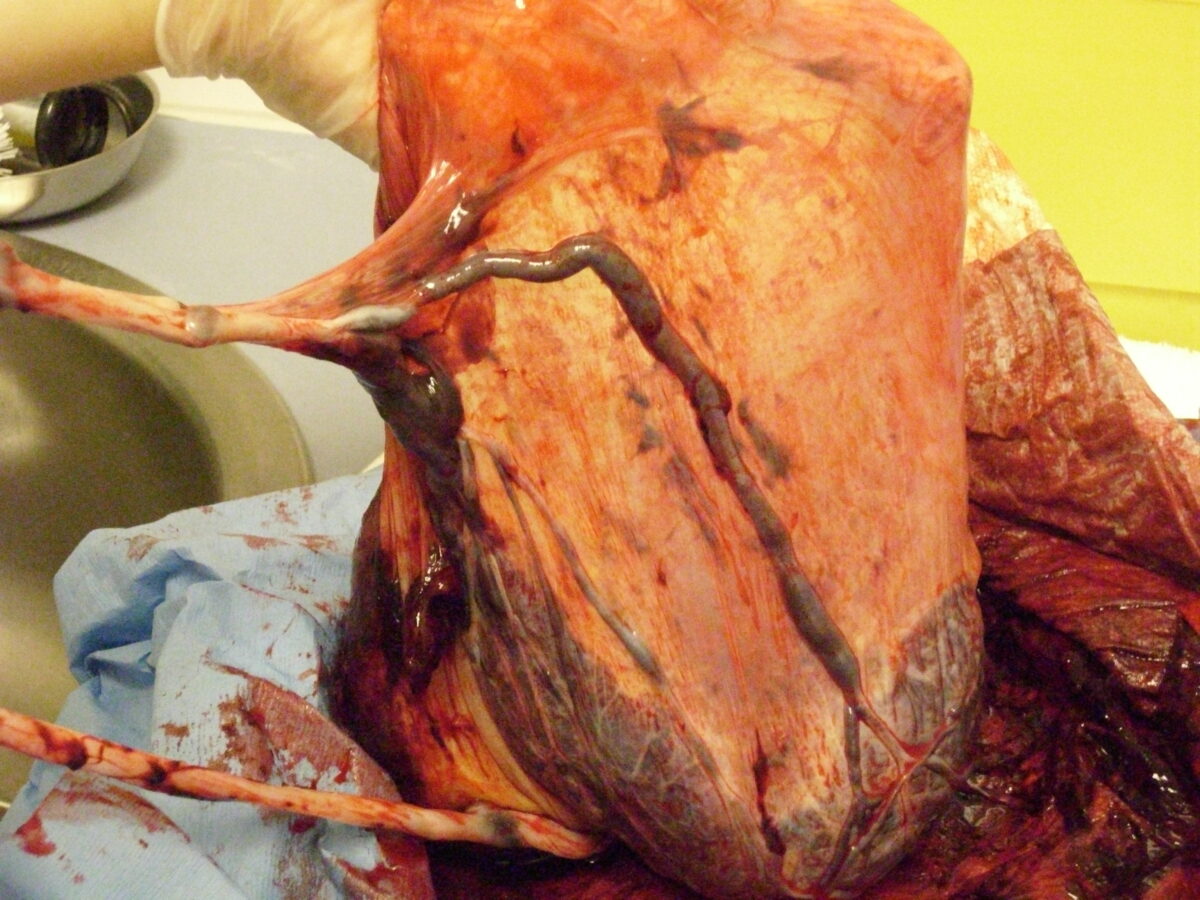
Inserción de cordón velamentoso:
Obsérvese que en los últimos centímetros no hay gelatina de Wharton protectora que rodee los vasos; solo están cubiertos por una fina membrana fetal.
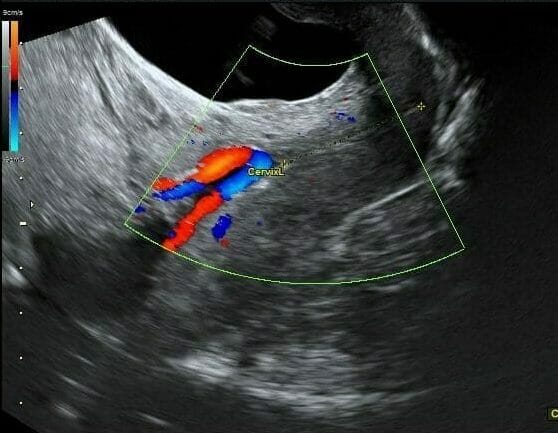
Imagen de ultrasonido de vasa previa:
El flujo doppler en color ilumina los vasos fijos que atraviesan el orificio cervical interno. El canal cervical se muestra con una línea de puntos amarilla.
El espectro de placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity acreta describe un espectro de placentación anormal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity se adhiere de forma anormal y firme a la pared uterina. Los LOS Neisseria 3 grados de espectro de placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity acreta son:
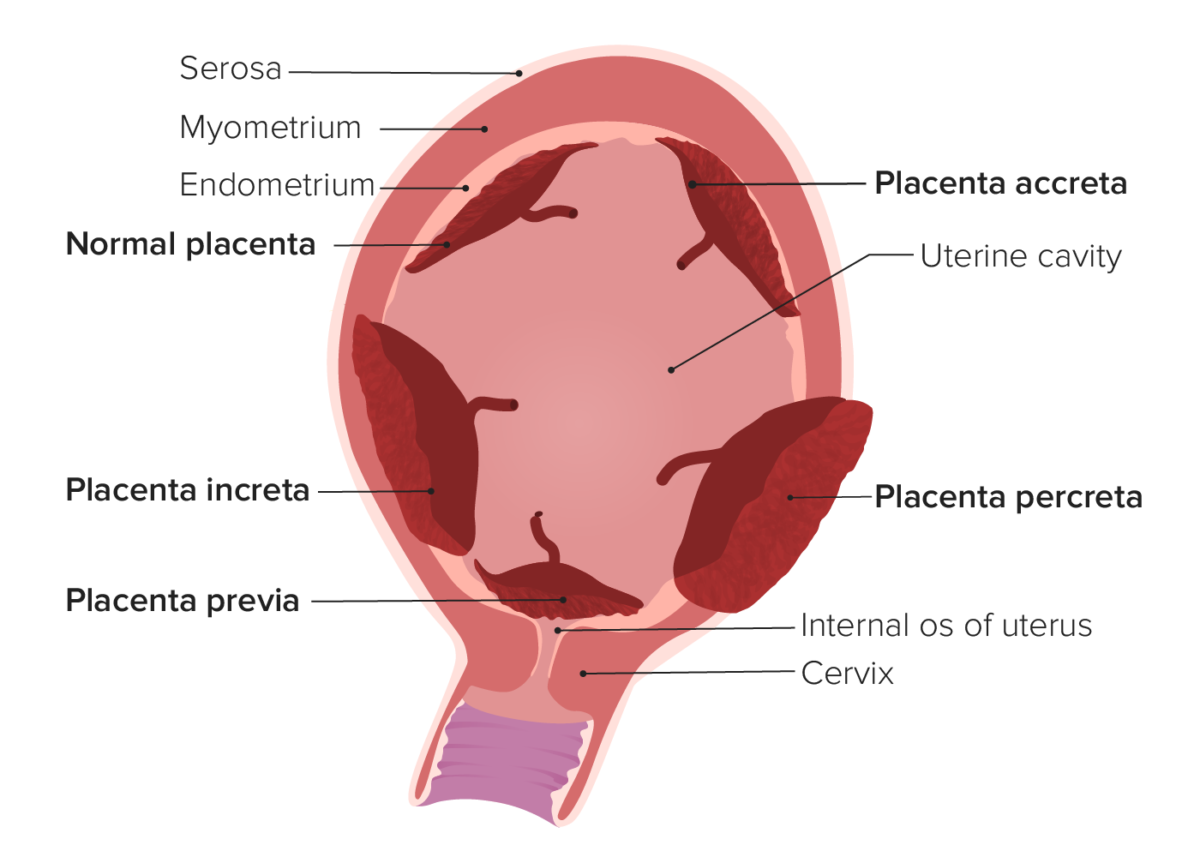
Tipos de placentación anormal
En la placenta acreta, la placenta se adhiere (al menos en parte) al miometrio subyacente. En la placenta increta, las vellosidades de la placenta invaden el miometrio. En la placenta percreta, las vellosidades de la placenta invaden toda la pared uterina y pueden invadir las estructuras circundantes (e.g., la vejiga). La placenta previa se produce cuando la placenta cubre el orificio cervical interno.La placenta previa Placenta Previa Abnormal placentation in which the placenta implants in the lower segment of the uterus (the zone of dilation) and may cover part or all of the opening of the cervix. It is often associated with serious antepartum bleeding and premature labor. Placental Abnormalities se refiere a la presencia de tejido placentario que cubre el orificio cervical interno. Cuando el cuello uterino comienza a dilatarse, la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity se “desprende” sobre el orificio cervical que se está abriendo, lo que provoca una hemorragia fetal potencialmente mortal.
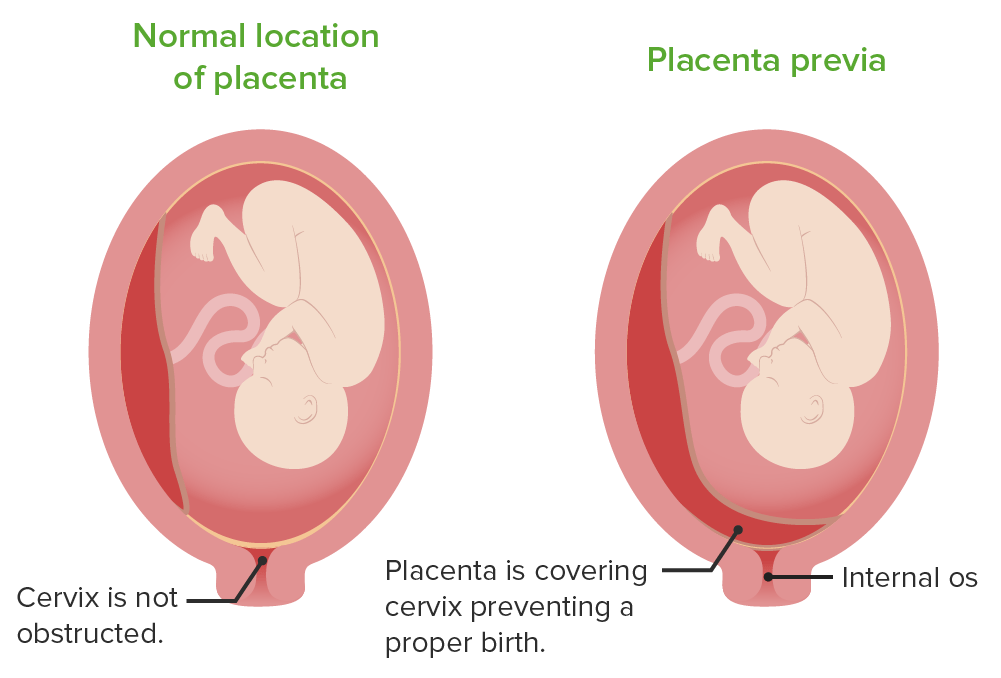
The location of the placenta in placenta previa
Image by Lecturio.La insuficiencia útero-placentaria puede ser aguda o crónica y se refiere a la incapacidad de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity para proporcionar un suministro suficiente de O2 y nutrientes al AL Amyloidosis feto.
La insuficiencia útero-placentaria crónica provoca una restricción del crecimiento fetal y complicaciones asociadas.
Las complicaciones clínicas más comunes de la placentación anormal son la hemorragia preparto y posparto, que pueden ser graves y poner en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum peligro la vida, dependiendo de la situación clínica. Además, la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity puede infectarse o desarrollar una neoplasia.