La amigdalitis es la inflamación de las amígdalas palatinas. Cuando la amigdalitis es causada por una infección, se denomina amigdalitis infecciosa, causada por virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology (el más común), bacterias u hongos. Entre las bacterias, el estreptococo del grupo A es la etiología más frecuente. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos, con la realización de pruebas, si están indicadas, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la evaluación inicial. Las pruebas para detectar la infección por Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus del grupo A (GAS, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el contexto de la amigdalitis son esenciales, ya que esta infección puede provocar fiebre reumática y glomerulonefritis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños y adolescentes. Se recomienda el tratamiento antibiótico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una infección confirmada por GAS para esta población. Para otras etiologías, el manejo depende del organismo causante y del tratamiento disponible.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
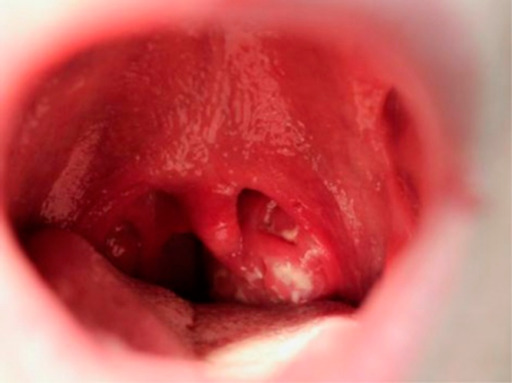
Faringitis por mononucleosis infecciosa que muestra una amigdalitis exudativa y una úvula agrandada en un estudiante universitario de 19 años, 5 días después del inicio de la mononucleosis infecciosa
Imagen: “PMC4346501_cti20151f1” por Balfour HH, Dunmire SK, Hogquist KA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0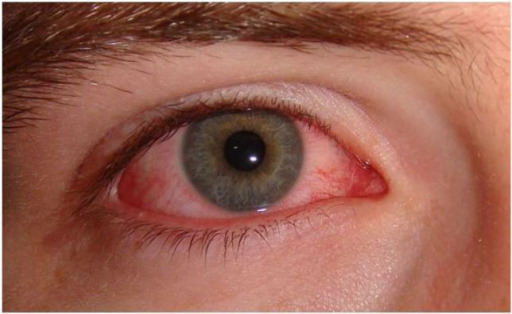
Presentación de la conjuntivitis de la amigdalitis viral, que se observa normalmente en la infección viral de la faringe
Imagen: “Acute viral conjunctivitis” por Wikimedia Creative Commons. Licencia: CC BY 4.0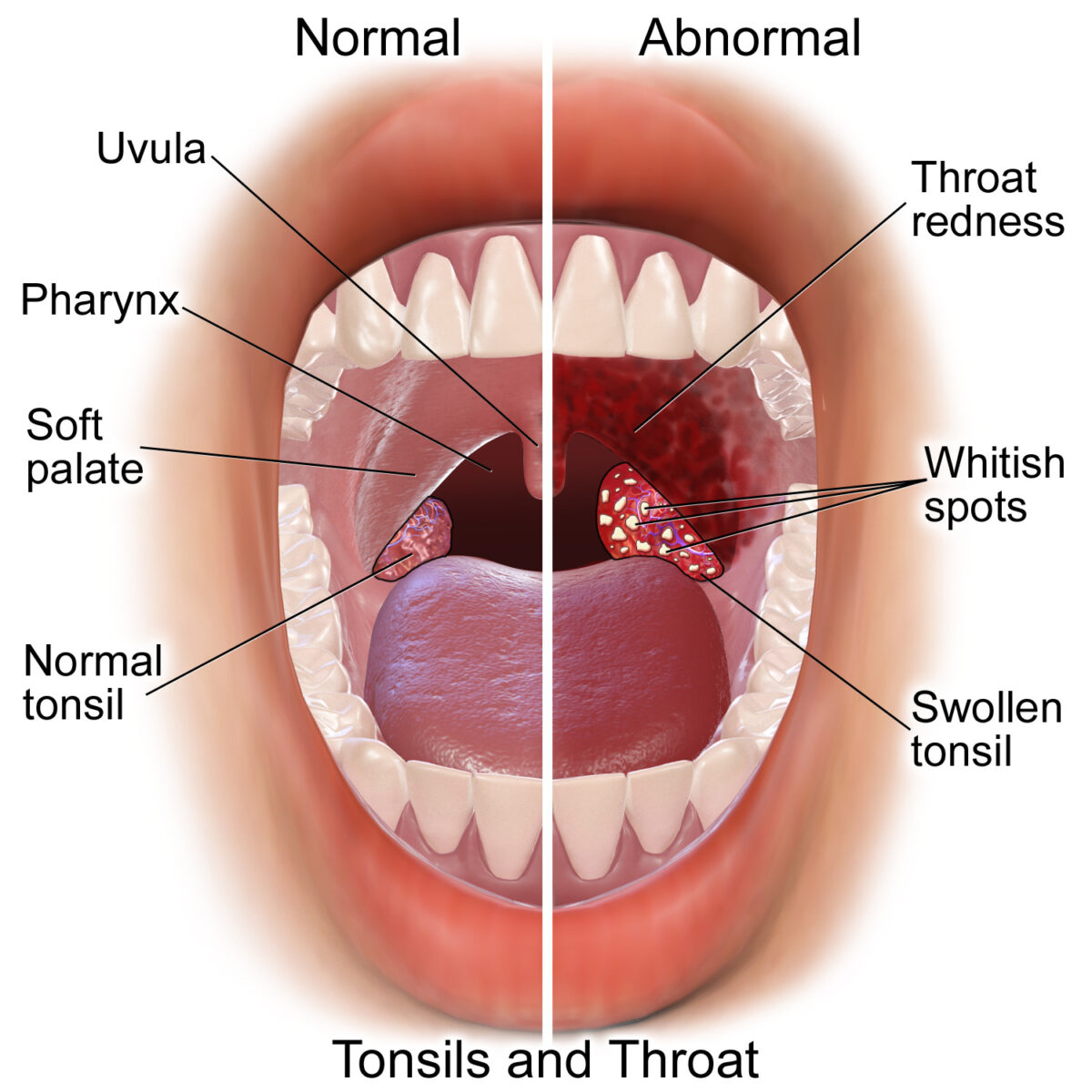
Comparación entre la orofaringe normal y la faringitis/amigdalitis aguda con eritema, exudados amigdalinos o faríngeos y amígdalas inflamadas
Imagen: “Blausen 0860 Tonsils&Throat Anatomy” por Blausen.com staff (2014). Licencia: Dominio Público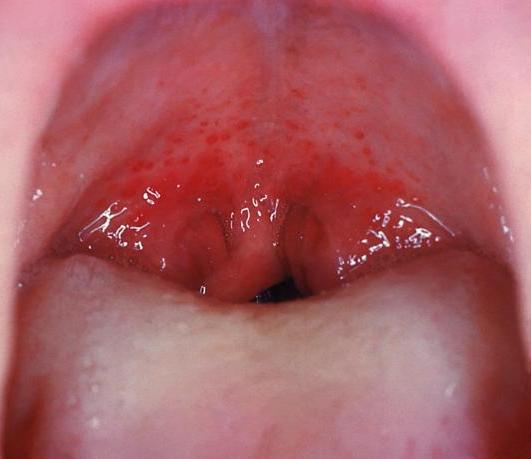
Faringoamigdalitis estreptocócica:
Amígdalas inflamadas y petequias palatinas observadas en esta infección secundaria al estreptococo del grupo A
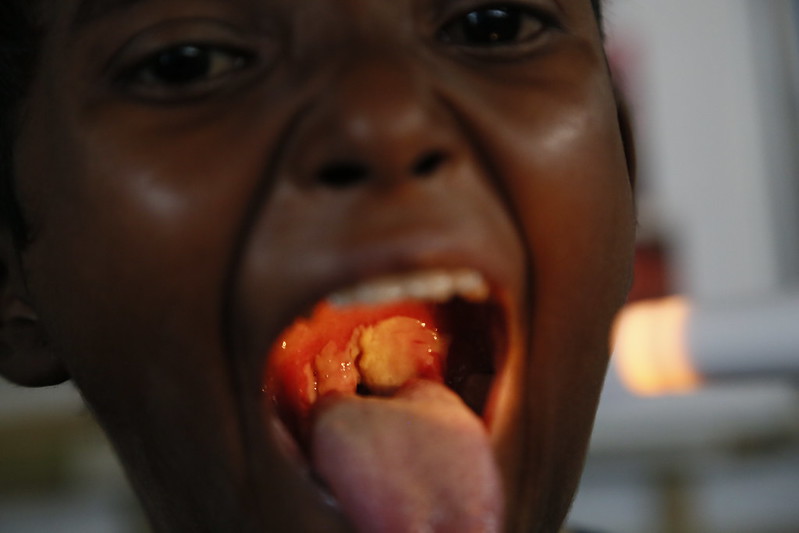
Difteria: paciente pediátrico con difteria que presenta la característica membrana blanco-grisácea que cubre la pared faríngea posterior.
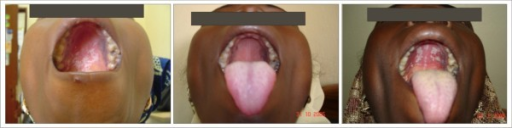
Candidiasis pseudomembranosa en un paciente con infección por candidiasis orofaríngea
En estas imágenes, se observa que la infección afecta el paladar.
El diagnóstico es clínico, ya que se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos de la exploración física.
Infección por Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus del grupo A:
Chequeo de otras etiologías:
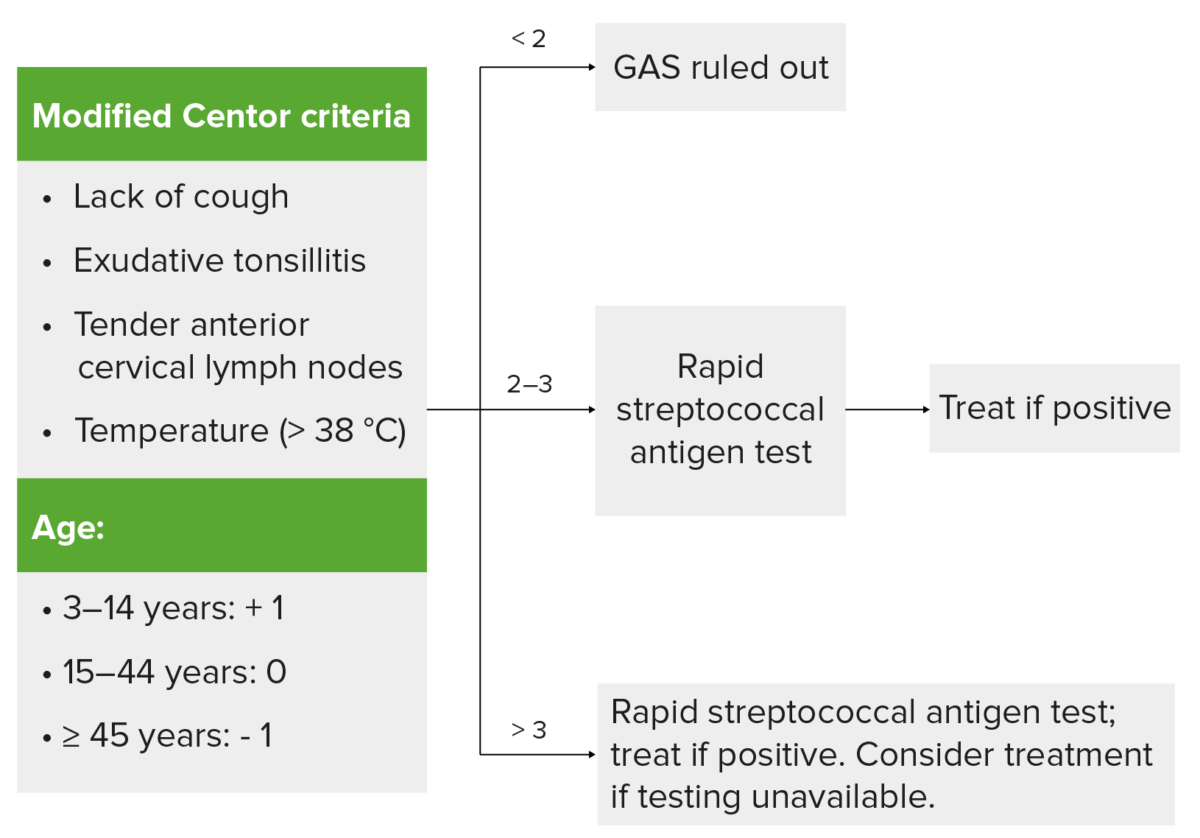
Uso de los criterios de Centor para la infección por estreptococos del grupo A (GAS, por sus siglas en inglés)
Los hallazgos en la izquierda reciben un punto cada uno (puntuación modificada en función de la edad). Si la puntuación es de < 2, la infección por GAS (amigdalitis) es poco probable. Si la puntuación es de 2-3, se realiza una prueba rápida de detección de antígenos. Si la puntuación es > 3, se deben efectuar las pruebas y tratar si son positivas. En los casos en que la prueba no esté disponible, se considera el tratamiento con antibióticos. Se sigue recomendando el juicio clínico para determinar los estudios y el tratamiento
Las siguientes son las complicaciones asociadas a la amigdalitis/faringitis bacteriana:
Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la amigdalitis: