Tardive Dyskinesia
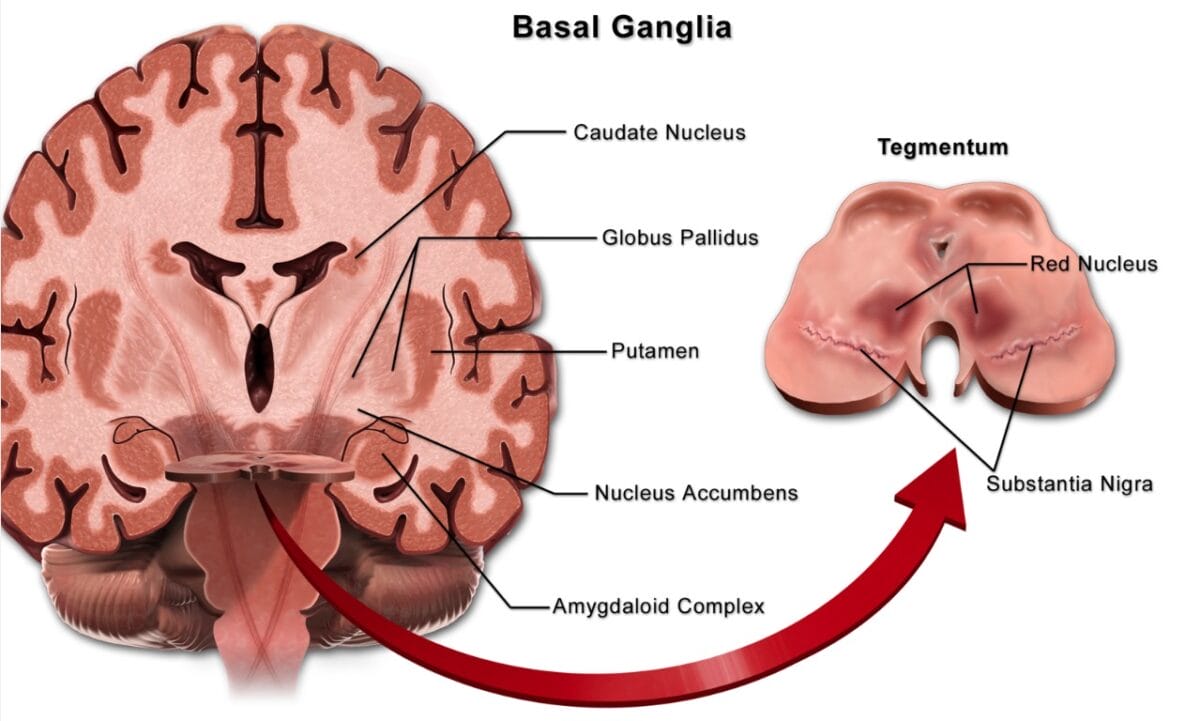
Overview Definition Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a hyperkinetic, medication-induced, involuntary movement disorder. Etiology Causative agents include medications with dopamine receptor-blocking mechanisms of action: Risk factors Pathophysiology The underlying pathophysiology of hyperkinetic movement in TD is not fully understood, but may be related to structural and biochemical disturbances in the basal ganglia of the brain, which […]
Wernicke Encephalopathy and Korsakoff Syndrome (Clinical)
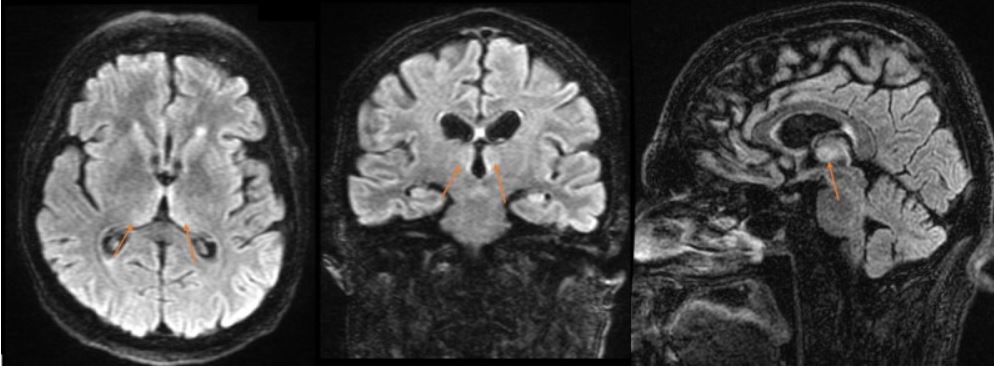
Overview Definition[1,3] Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome are neurologic conditions that arise because of thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency. Epidemiology[1] Etiology[1,3] Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome are caused by a severe deficiency of thiamine. This deficiency is most commonly due to: Pathophysiology The pathologic sequelae of Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome stem from the downstream effects […]
Coma
Overview Definition Table: Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Description Points Eye opening Spontaneous 4 Responds to speech 3 Responds to pain 2 None 1 Best verbal response Oriented 5 Confused 4 Inappropriate words 3 Incomprehensible words 2 None 1 Best motor response Obeys commands 6 Localizes pain 5 Withdraws from pain 4 Decorticate posturing (flexion) 3 […]
Wernicke Encephalopathy and Korsakoff Syndrome
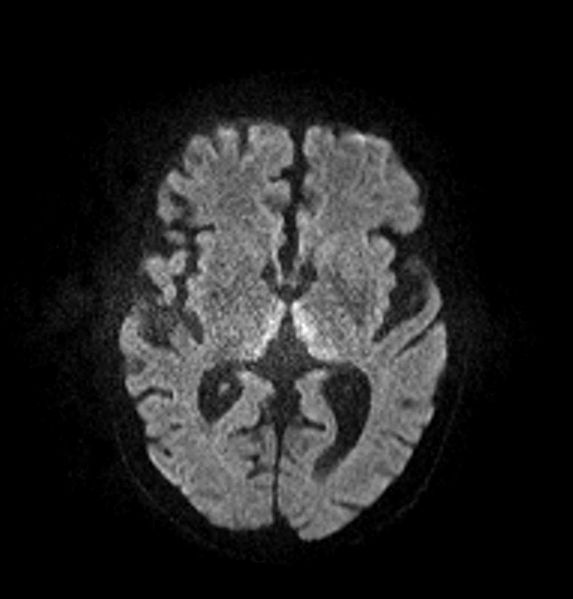
Overview Definition Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome are neurologic conditions that arise because of thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency. Epidemiology Etiology Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome are caused by a severe deficiency of thiamine. This deficiency is most commonly due to: Pathophysiology The pathologic sequelae of Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome stem from the downstream effects […]