No cérebro humano, a informação é transmitida na forma de impulsos bioelétricos e moléculas de sinalização química. Estas moléculas, chamadas neurotransmissores, são moléculas de proteínas usadas pelos neurónios para emitir um sinal específico. Os sinais são captados na membrana plasmática de neurónios adjacentes por recetores, que são complexos de subunidades proteicas responsáveis por detetar estímulos relevantes e colocar em movimento a maquinaria celular necessária para produzir uma resposta desejada.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
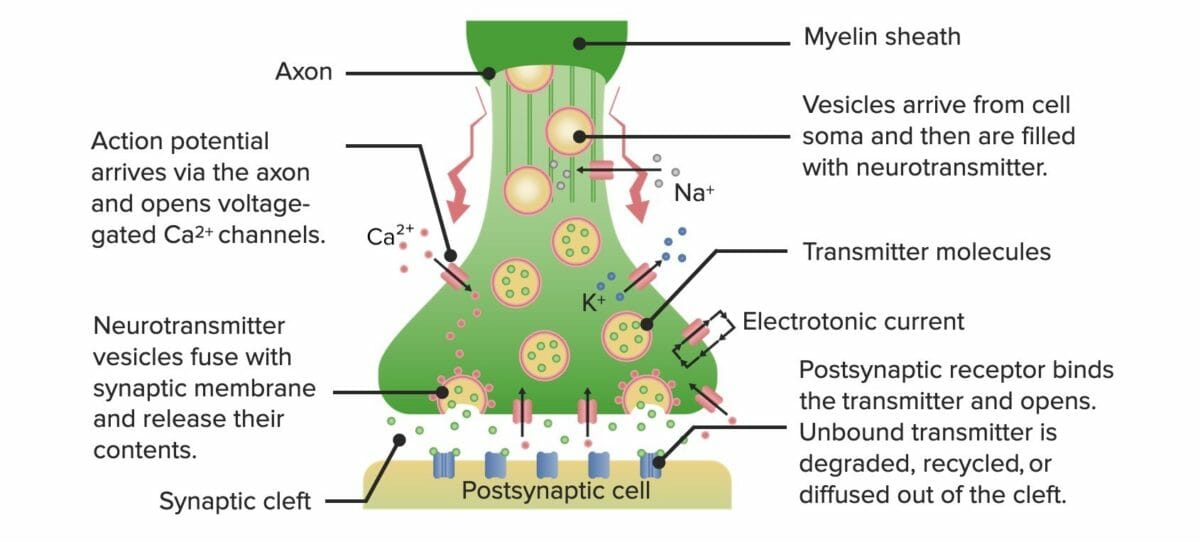
Diagrama mostra o processo de neurotransmissão
Image por Lecturio.Mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome de 500 neurotransmissores únicos foram identificados em humanos.
| Via | Origem do neurónio | Local de projeção do neurónio | Funções |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesolímbica | Área tegmental ventral |
|
|
| Mesocortical | Área tegmental ventral | Córtex pré-frontal |
|
| Nigroestriatal | Substância Nigra | Estriado | Controlo locomotor |
| Tuberoinfundibular | Núcleo arqueado | Hipófise | Inibe a secreção de prolactina |
| Neurotransmissor | Efeito | Local de síntese |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamina | Excitatório e inibitório | SNC: substância nigra, área tegmental ventral e outros |
| Norepinefrina | Excitatório | SNC: locus Locus Specific regions that are mapped within a genome. Genetic loci are usually identified with a shorthand notation that indicates the chromosome number and the position of a specific band along the P or Q arm of the chromosome where they are found. For example the locus 6p21 is found within band 21 of the P-arm of chromosome 6. Many well known genetic loci are also known by common names that are associated with a genetic function or hereditary disease. Basic Terms of Genetics coeruleus, sistema nervoso simpático e medula da suprarrenal |
| Epinefrina | Excitatório | Medula da suprarrenal |
| Serotonina |
|
SNC: núcleo da rafe e células enterocromafins |
| Histamina | Excitatório e inibitório |
|
| Acetilcolina | Excitatório (habitualmente) | Junções neuromusculares, sinapses pré-simpáticas e sinapses simpáticas pré-ganglionares |
| Glutamato |
|
SNC: em quase todas as partes do sistema nervoso |
| GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS |
|
SNC |
| Glicina | Inibitório | SNC: medula espinhal, tronco cerebral e retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy |
| Encefalinas | Inibitório (dor) | SNC |
| Endorfinas | Inibitório | SNC e SNP |
| Neuroquininas | Trato GI: modula a motilidade, a secreção de fluidos e eletrólitos | Neurónios entéricos intrínsecos e fibras nervosas aferentes primárias extrínsecas |
| Recetor | Localização | Efetor de sinalização (da ligação de 5-HT 5-HT A biochemical messenger and regulator, synthesized from the essential amino acid l-tryptophan. In humans it is found primarily in the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and blood platelets. Serotonin mediates several important physiological functions including neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility, hemostasis, and cardiovascular integrity. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS) | Mensageiros secundários | Função |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5- HT1A |
|
Inibe AC | ↓ AMPc |
|
| 5- HT2A |
|
Ativa o PLC | ↑ IP 3 , DAG DAG Second Messengers, Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) 2+ |
|
| 5- HT2C |
|
|
↑ IP 3 , DAG DAG Second Messengers, Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) 2+ | Apetite |
| 5 -HT3 |
|
Canal iónico controlado por ligante → influxo de Na + , Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) 2+ | — |
|
| Recetor | Localização | Efetor de sinalização (da ligação à dopamina) | Participação na via dopaminérgica | Função |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D 1 |
|
Ativa CA CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) | Mesocortical |
|
| D 1 |
|
Ativa CA CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) | Periférica |
|
| D 2 |
|
Inibe AC |
|
|
| D 2 |
|
Inibe AC | Periférica |
|
| D 3 |
|
Inibe AC | Mesolímbica |
|
| D 3 | Rins | Inibe AC | Periférica | ↓ Secreção de renina |
| Recetor | Localização | Efetor de sinalização (agonismo de glutamato) | Mensageiros secundários | Função | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agonismo | Antagonismo | ||||
| AMPA | SNC | Ionotrópica → influxo de Na + → EPSP → expele Mg 2+ do receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors NMDA | — | EPSP rápido | Bloqueio de condução |
| NMDA |
|
Ionotrópica → EPSP de AMPA → Mg 2+ é expelido → influxo de Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) 2+ → despolarização adicional | — |
|
|
| mGlur grupo I | Autorrecetores em neurónios glutamatérgicos | Ativa o PLC | ↑ IP 3 , DAG DAG Second Messengers, Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) 2+ | Significado clínico desconhecido | |
| mGlur grupo II | Inibe AC | ↓ AMPc | |||
| mGlur grupo III | Inibe AC | ↓ AMPc | |||