Os fármacos insulinotrópicos são utilizados no tratamento da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2 através do aumento da secreção de insulina, que resulta na diminuição dos níveis de glicose. Este grupo de fármacos inclui as sulfonilureias, meglitinidas, agonistas do recetor do péptido-1 semelhante ao glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions ( GLP-1 GLP-1 A peptide of 36 or 37 amino acids that is derived from proglucagon and mainly produced by the intestinal l cells. Glp-1(1-37 or 1-36) is further n-terminally truncated resulting in glp-1(7-37) or glp-1-(7-36) which can be amidated. These glp-1 peptides are known to enhance glucose-dependent insulin release, suppress glucagon release and gastric emptying, lower blood glucose, and reduce food intake. Insulinomas) e inibidores da DPP-4. Estes fármacos são normalmente utilizados em combinação com outros tratamentos para o controlo da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus. As sulfonilureias e as meglitinidas estão associadas ao aumento de peso, enquanto os agonistas GLP-1 GLP-1 A peptide of 36 or 37 amino acids that is derived from proglucagon and mainly produced by the intestinal l cells. Glp-1(1-37 or 1-36) is further n-terminally truncated resulting in glp-1(7-37) or glp-1-(7-36) which can be amidated. These glp-1 peptides are known to enhance glucose-dependent insulin release, suppress glucagon release and gastric emptying, lower blood glucose, and reduce food intake. Insulinomas podem proporcionar um benefício adicional de perda de peso. Outros efeitos adversos variam conforme as diferentes classes de fármacos. Nenhum dos fármacos deve ser utilizado no tratamento da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 1 ou da cetoacidose diabética.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Os fármacos hipoglicemiantes podem ser classificados com base no seu mecanismo de ação:
Fármacos insulinotrópicos (↑ secreção de insulina):
Fármacos não insulinotrópicos (não afetam a libertação de insulina):
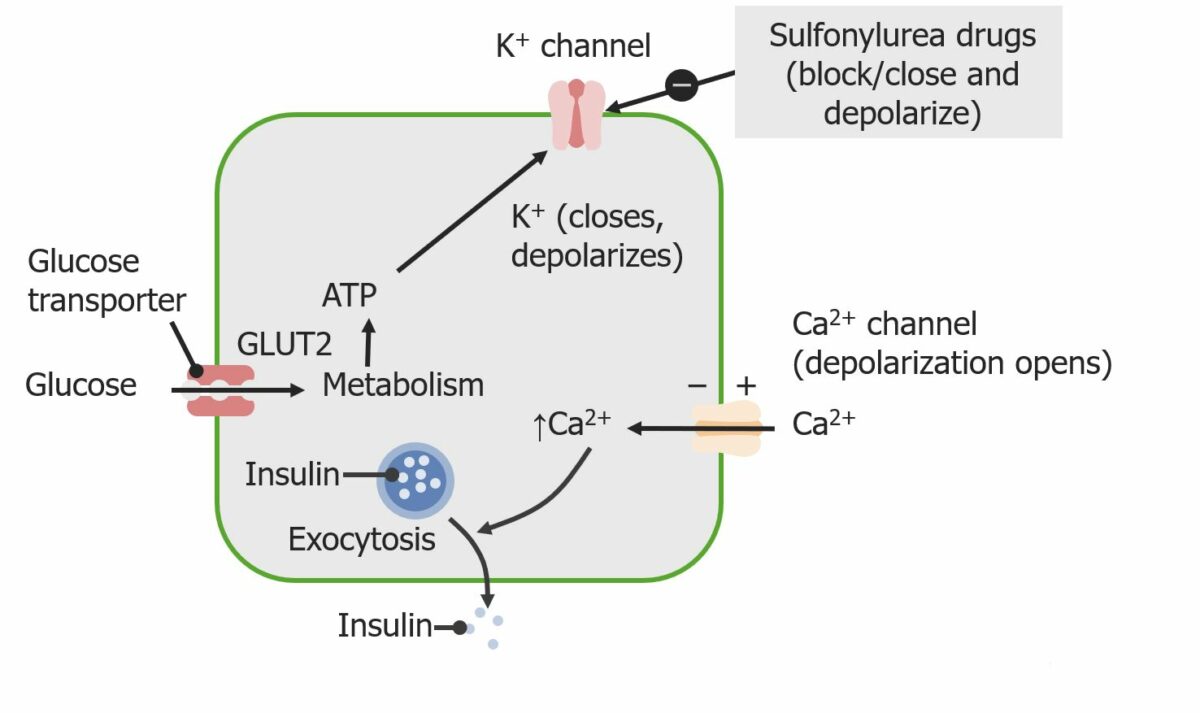
As sulfonilureias estimulam a secreção de insulina ao atuar nos canais de potássio das células beta pancreáticas.
Imagem por Lecturio.Descrição da farmacocinética das sulfonilureias de 2.ª geração:
As sulfonilureias são utilizadas no tratamento da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
As meglitinidas são utilizadas na diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
Um aumento do efeito hipoglicemiante pode ser observado com:
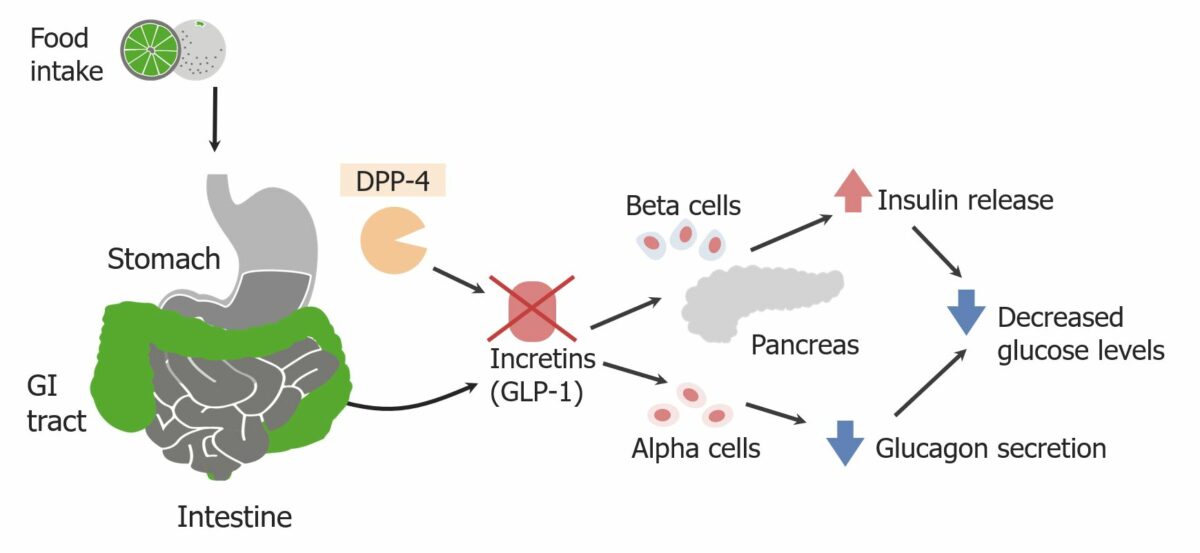
Função normal da DPP-4: a inibição da enzima evita a degradação do péptido-1 semelhante ao glucagon (GLP-1), permitindo o aumento da libertação de insulina e a diminuição da secreção do glucagon.
Imagem por Lecturio.Os inibidores da DPP-4 são utilizados no tratamento da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
A tabela seguinte compara fármacos não insulínicos para o tratamento da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
| Fármaco | Mecanismo | Indicações | Efeitos adversos |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonilureias |
|
|
|
| Meglitinidas |
|
|
|
| Agonistas do péptido-1 semelhante ao glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions ( GLP-1 GLP-1 A peptide of 36 or 37 amino acids that is derived from proglucagon and mainly produced by the intestinal l cells. Glp-1(1-37 or 1-36) is further n-terminally truncated resulting in glp-1(7-37) or glp-1-(7-36) which can be amidated. These glp-1 peptides are known to enhance glucose-dependent insulin release, suppress glucagon release and gastric emptying, lower blood glucose, and reduce food intake. Insulinomas) |
|
|
|
| Inibidores da DPP-4 |
|
Tratamento adjuvante |
|
| Biguanidas |
|
|
|
| Tiazolidinedionas |
|
|
|
| Inibidores da alfa-glicosidase |
|
|
|
| Inibidores da proteína de transporte de sódio-glicose 2 (SGLT2) |
|
|
|
| Análogos da amilina |
|
|
|
Os efeitos dos fármacos para a diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus no peso podem ser um fator na escolha do tratamento de um indivíduo: