Os agentes de quimioterapia antimetabolitos pertencem aos fármacos específicos do ciclo celular, que atuam numa fase específica do ciclo celular. As células cancerígenas dividem-se mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome rapidamente do que as células normais, tornando-as um alvo fácil para a quimioterapia. As diferentes fases do ciclo celular incluem G1, S, G2 e M. Os antimetabolitos têm como alvo a fase S, quando ocorre a replicação de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, inibindo assim a síntese de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure das células tumorais. Neste grupo, os fármacos incluem antifolatos (que bloqueiam a atividade do ácido fólico, um componente essencial dos precursores de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure e de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure), análogos de pirimidina e purina (que interferem no processo de síntese do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure) e inibidores da ribonucleótido redutase (que reduzem a produção de desoxirribonucleótidos). Os fármacos de quimioterapia específicos para o ciclo celular não conseguem diferenciar as células saudáveis das cancerígenas, sendo observados efeitos adversos. A mielossupressão é um achado comum durante o tratamento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
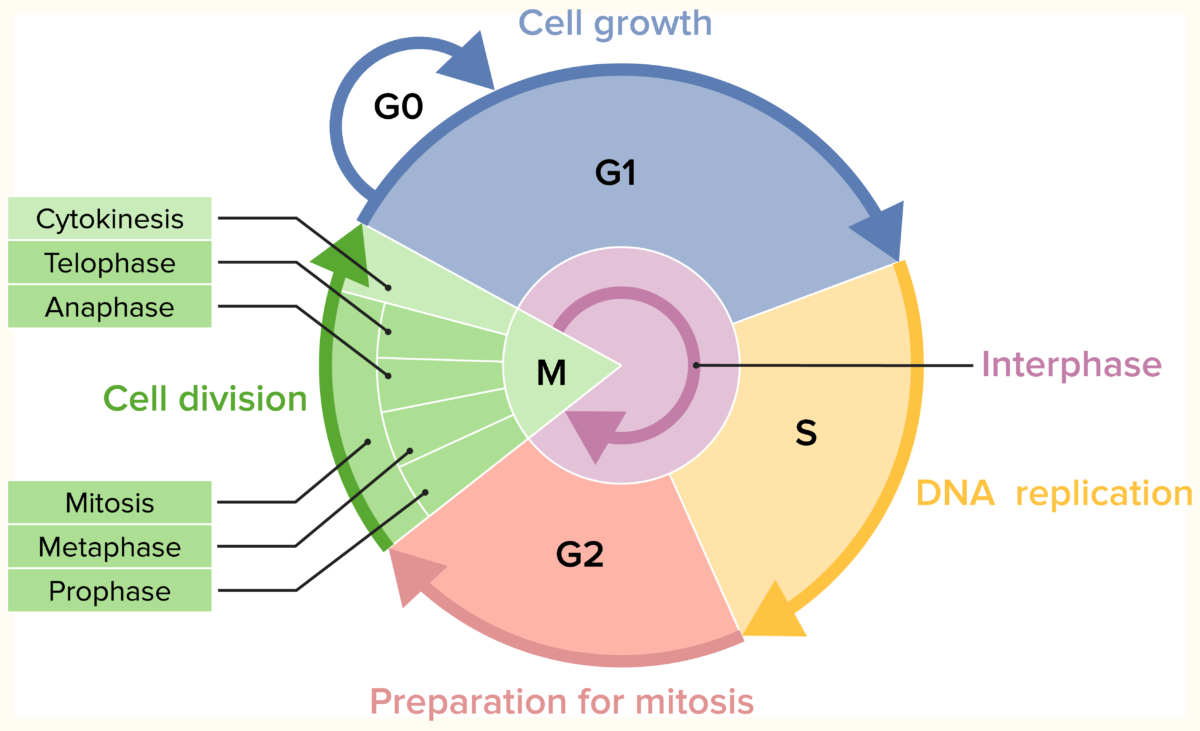
Fases do ciclo celular
Imagem por Lecturio.Os subtipos dos agentes de quimioterapia antimetabolitos são:
| Agente | Mecanismo de ação | Indicações rotuladas | Efeitos adversos | Considerações adicionais |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metotrexato | Inibem a DHFR |
|
|
Adicionar leucovorina para recuperar as células da toxicidade. |
| Pemetrexed Pemetrexed A guanine-derived antineoplastic agent that functions as a nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor through its binding to, and inhibition of, thymidylate synthase. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Inibe:
|
|
|
Adicionar vitamina B12 e folato para ↓ toxicidade. |
| Pralatrexato |
|
Linfoma periférico de células T |
|
Adicionar vitamina B12 e folato para ↓ toxicidade |
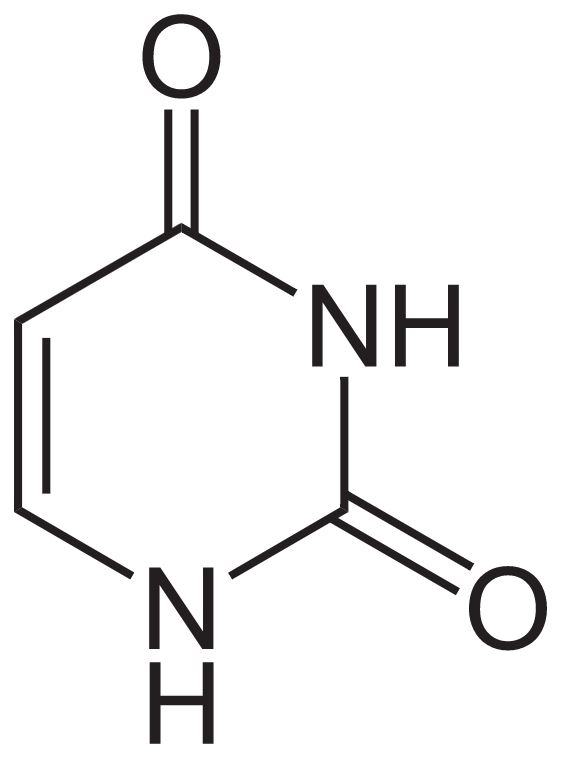
Estrutura do uracilo
Imagem: “Uracil” by NEUROtiker. Licença: Public Domain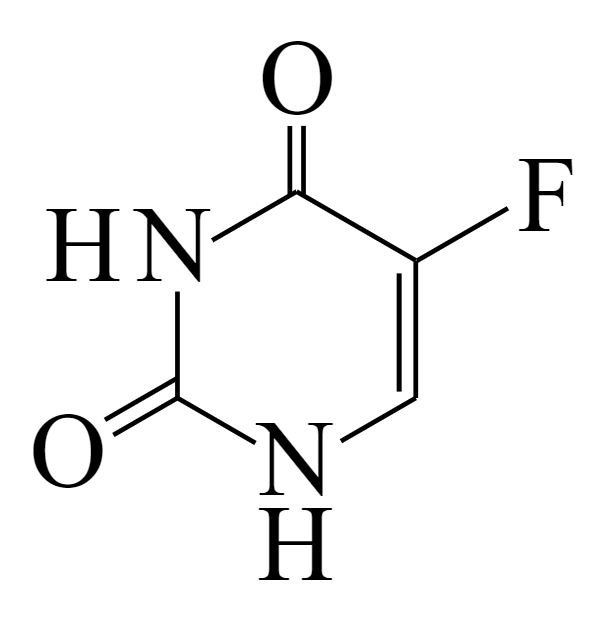
Estrutura de 5-fluorouracilo
Imagem: “5-Fluorouracil” by すじにくシチュー. Licença: CC0 1.0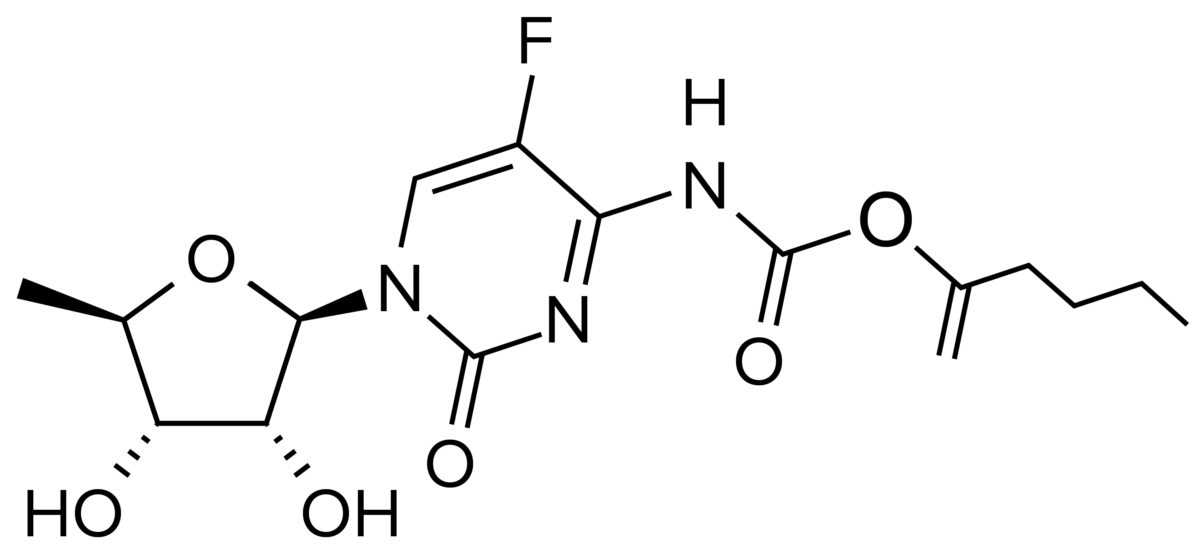
Estrutura da capecitabina
Imagem pro Lecturio.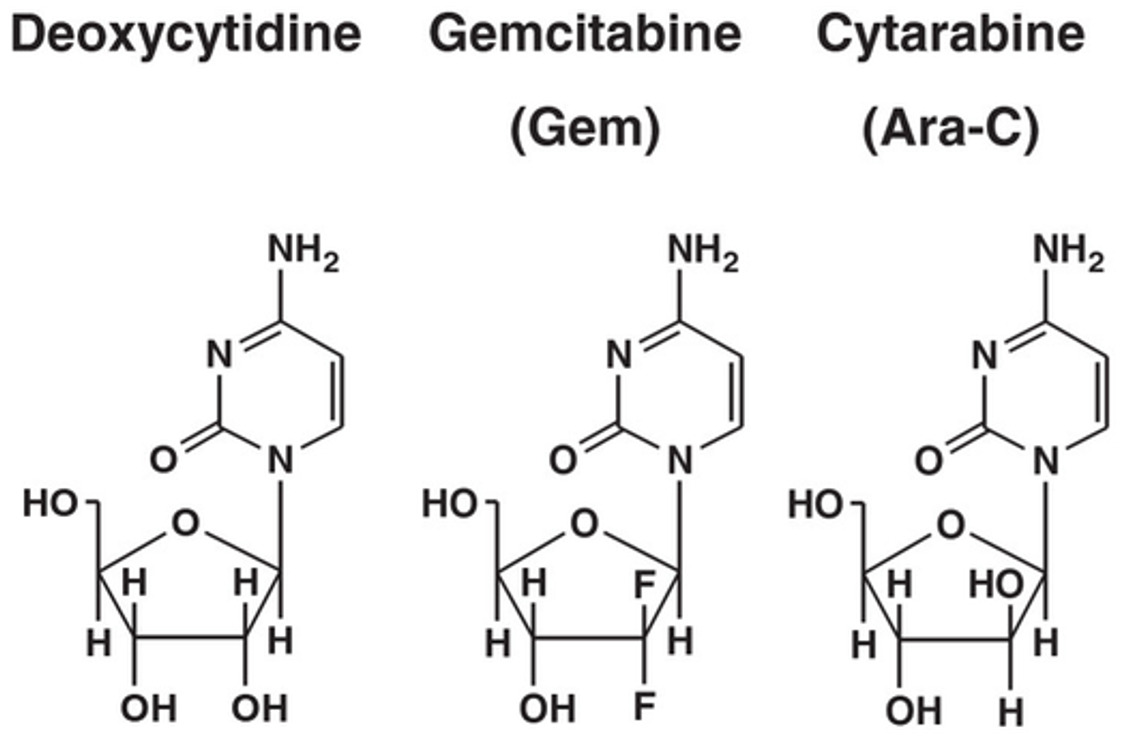
Desoxicitidina e análogos:
Gemcitabina (análogo difluoro) e citosina (citosina arabinosídeo)
| Agente | Mecanismo de ação | Indicações rotuladas | Efeitos adversos | Considerações adicionais |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-FU 5-FU A pyrimidine analog that is an antineoplastic antimetabolite. It interferes with DNA synthesis by blocking the thymidylate synthetase conversion of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Inibe a timidilato sintetase |
|
|
Na deficiência de DPD: ↑ toxicidade |
| Capecitabina | Pró-fármaco do 5-FU 5-FU A pyrimidine analog that is an antineoplastic antimetabolite. It interferes with DNA synthesis by blocking the thymidylate synthetase conversion of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy (inibe a timidilato sintetase) |
|
|
Na deficiência de DPD: ↑ toxicidade |
| Citarabina | Inibe a DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure polimerase |
|
|
|
| Gemcitabina | Inibe a DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure polimerase e a ribonucleótido redutase |
|
|
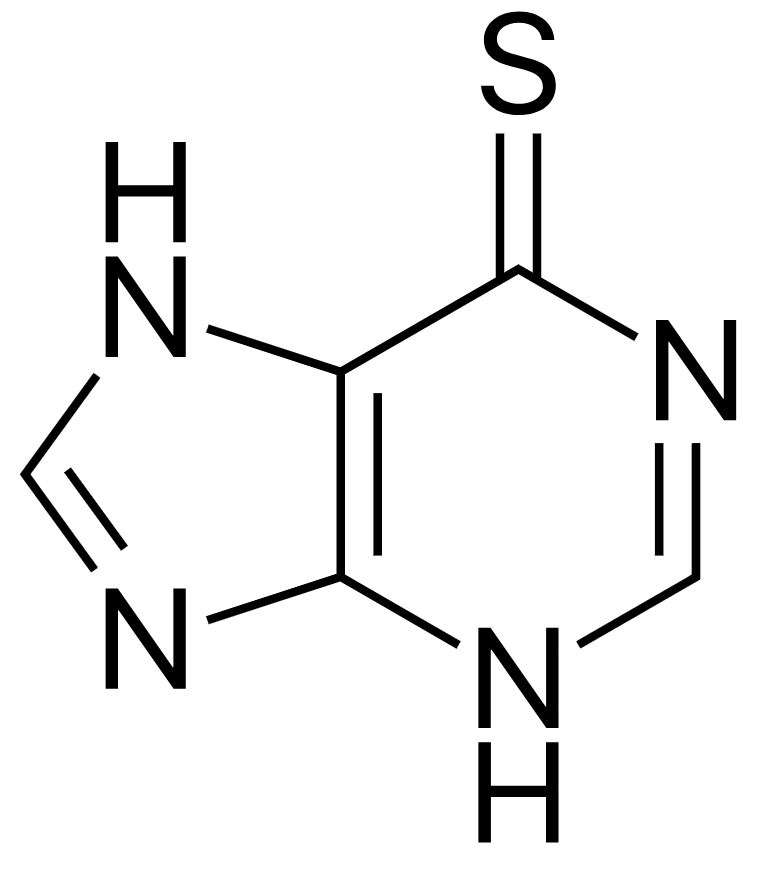
Estrutura da 6-mercaptopurina
Imagem: “Mercaptopurine” by Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain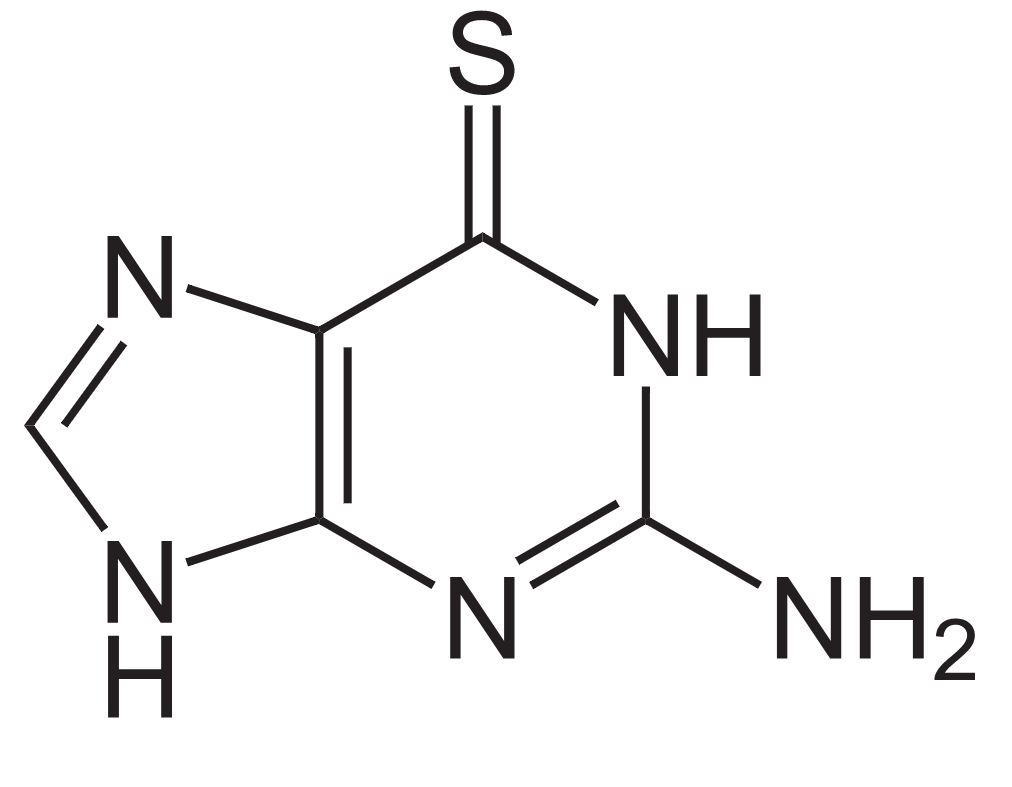
Estrutura de 6-tioguanina
Imagem: “6-Thioguanin” by NEUROtiker. Licença: Public Domain
Estrutura da fludarabina
Imagem: “Fludarabine” by Yikrazuul. Licença: Public Domain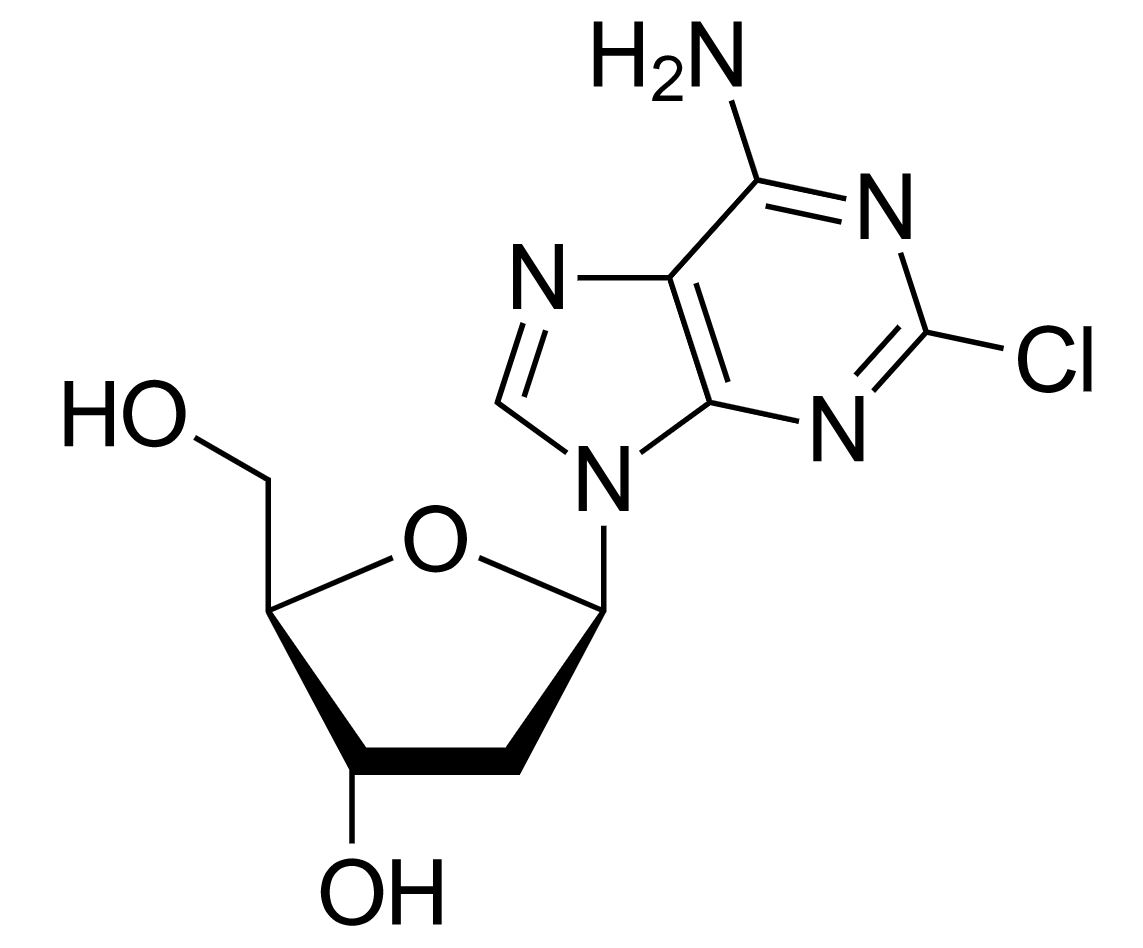
Estrutura do cladribina
Imagem: “Cladribine” by Yikrazuul. Licença: Public Domain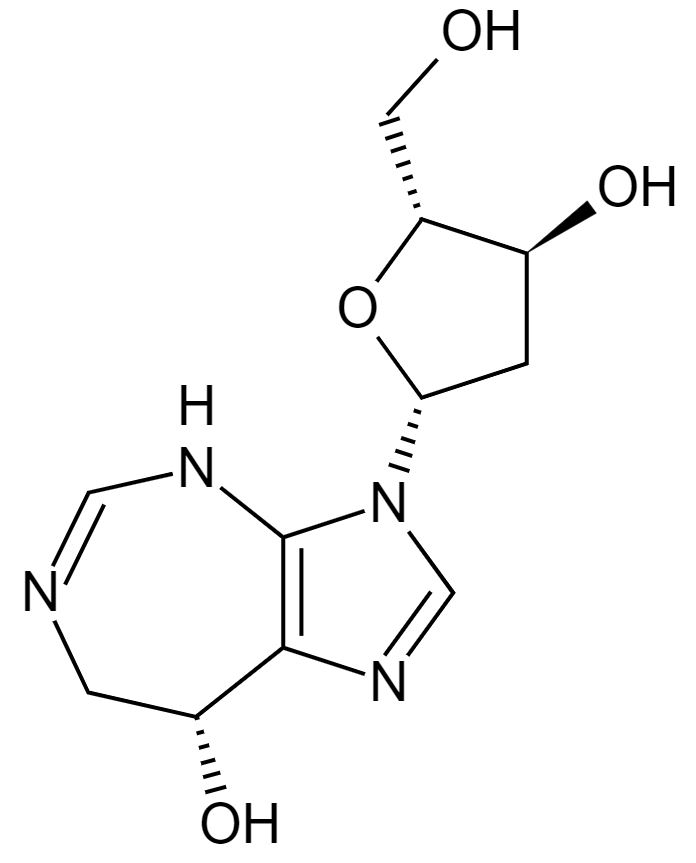
Estrutura da pentostatina
Imagem: “Pentostatin” by Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain| Agente | Mecanismo de ação | Indicações rotuladas | Efeitos adversos | Considerações adicionais |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-MP 6-MP An antimetabolite antineoplastic agent with immunosuppressant properties. It interferes with nucleic acid synthesis by inhibiting purine metabolism and is used, usually in combination with other drugs, in the treatment of or in remission maintenance programs for leukemia. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Antagonista de purinas (inibe a síntese de nucleótidos de purina) | Leucemia Linfoblástica Aguda (LLA) |
|
↓ Dose se estiver a tomar alopurinol |
| 6-TG 6-TG An antineoplastic compound which also has antimetabolite action. The drug is used in the therapy of acute leukemia. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Antagonista de purinas | LMA |
|
|
| Fludarabina | Inibe:
|
LLC |
|
Evitar pentostatina (↑ toxicidade pulmonar) |
| Cladribina | Inibe:
|
Leucemia das células cabeludas |
|
|
| Pentostatina | Inibe a adenosina desaminase (↓ síntese de ADN) | Leucemia das células cabeludas |
|
Evitar fludarabina (↑ toxicidade pulmonar) |
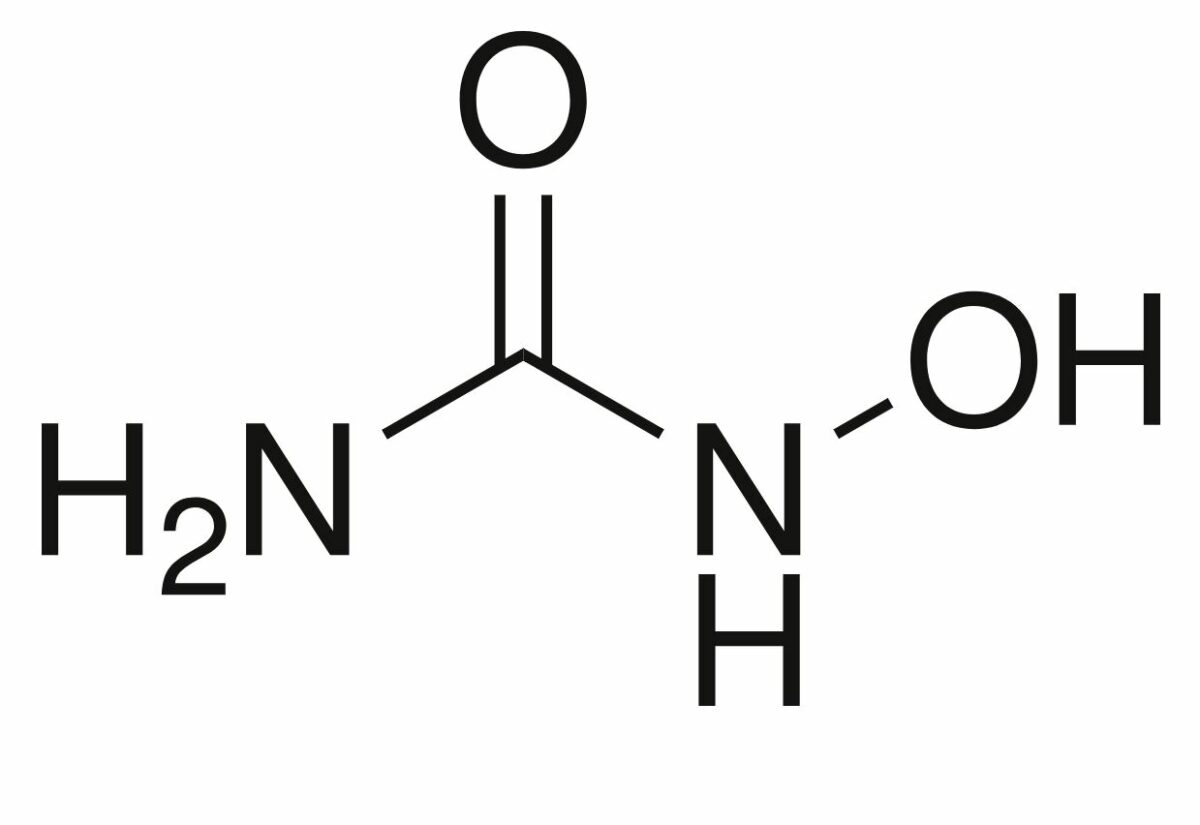
Estrutura da hidroxiureia
Imagem: “Hydroxyurea-2D-skeletal” by Chem Sim 2001. Licença: Public Domain| Classe do fármaco | Fase do ciclo celular afetada | Mecanismo de ação |
|---|---|---|
| Antifolatos | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibem:
|
| Fluoropirimidinas | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibem a timidilato sintetase |
| Análogos de desoxicitidina | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibem:
|
| Análogos de purina | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibição da síntese de novo de purinas |
| Inibidores da topoisomerase II Topoisomerase II DNA topoisomerases that catalyze ATP-dependent breakage of both strands of DNA, passage of the unbroken strands through the breaks, and rejoining of the broken strands. These enzymes bring about relaxation of the supercoiled DNA and resolution of a knotted circular DNA duplex. Fluoroquinolones | Paragem do ciclo celular nas fases S e G2 | Inibem a topoisomerase II Topoisomerase II DNA topoisomerases that catalyze ATP-dependent breakage of both strands of DNA, passage of the unbroken strands through the breaks, and rejoining of the broken strands. These enzymes bring about relaxation of the supercoiled DNA and resolution of a knotted circular DNA duplex. Fluoroquinolones |
| Taxanos | Paragem do ciclo celular na metáfase da fase M | Hiperestabilização de microtúbulos |
| Alcalóides da vinca | Paragem celular durante a metáfase da fase M | Liga-se à beta-tubulina e previne a polimerização de microtúbulos |
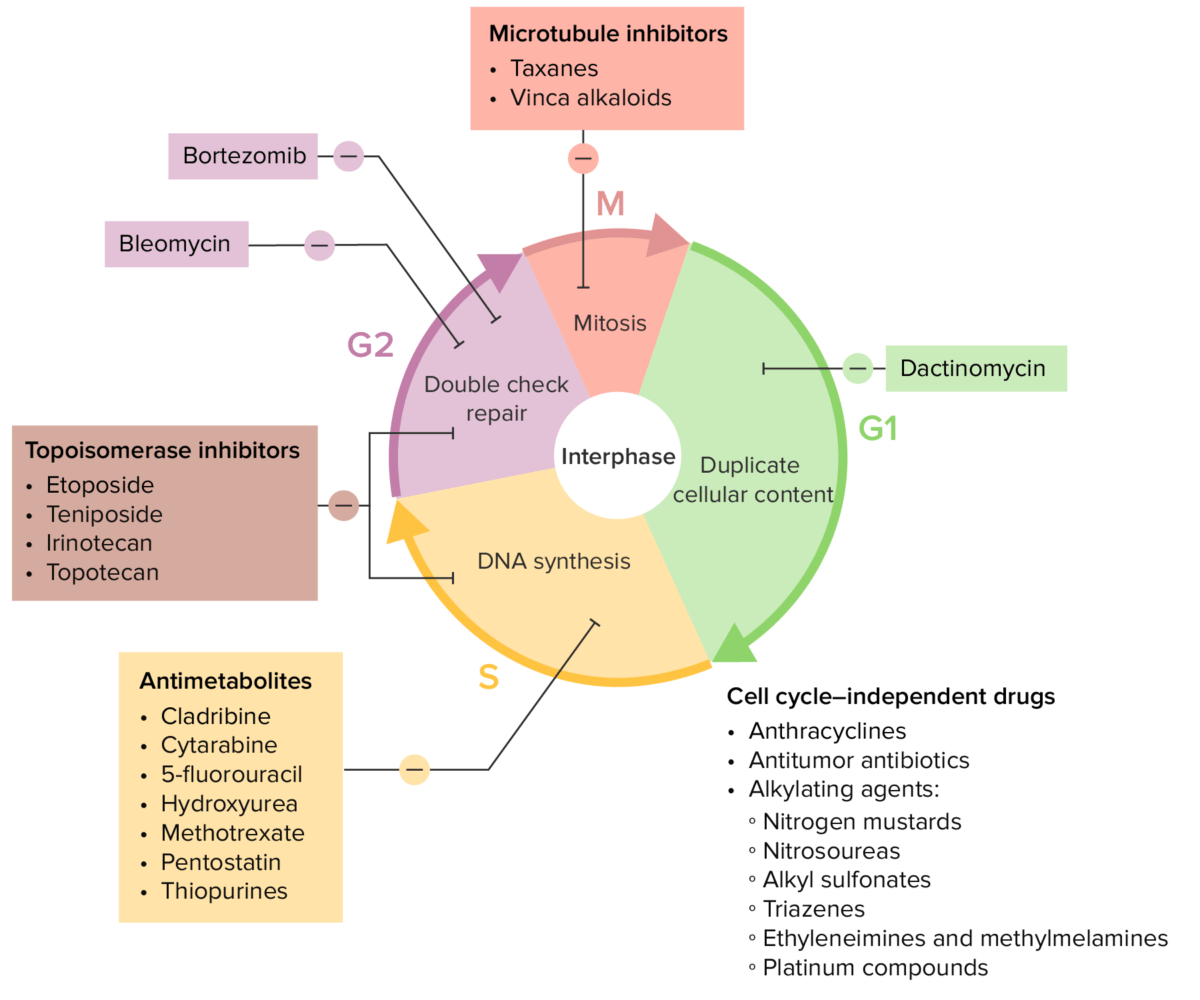
Vários fármacos de quimioterapia e os seus efeitos sobre o ciclo celular
Imagem por Lecturio.