Las paperas son causadas por un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ARN de sentido negativo, lineal y monocatenario de la familia Paramyxoviridae Paramyxoviridae A family of spherical viruses, of the order mononegavirales, somewhat larger than the orthomyxoviruses, and containing single-stranded RNA. Subfamilies include paramyxoviridae and pneumovirinae. Respiratory Syncytial Virus y de la subfamilia Rublavirinae. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de las paperas es contagioso y solo se propaga entre los LOS Neisseria seres humanos por gotitas respiratorias o por transmisión por contacto directo de una persona o un fómite infectado. Las paperas son una enfermedad típica de la infancia, que se manifiesta inicialmente con fiebre, dolor Dolor Inflammation muscular, cefalea, falta de apetito y una sensación general de malestar y clásicamente va VA Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing seguida de una parotitis Parotitis Inflammation of the parotid gland. Mumps Virus/Mumps. Entre las complicaciones se encuentran la meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, la pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis, la sordera permanente y la inflamación testicular, que puede provocar infertilidad. Las paperas se tratan con cuidados de apoyo y se pueden prevenir con la vacunación.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son positivos si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios negativos emplean la ARN polimerasa, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARNm.
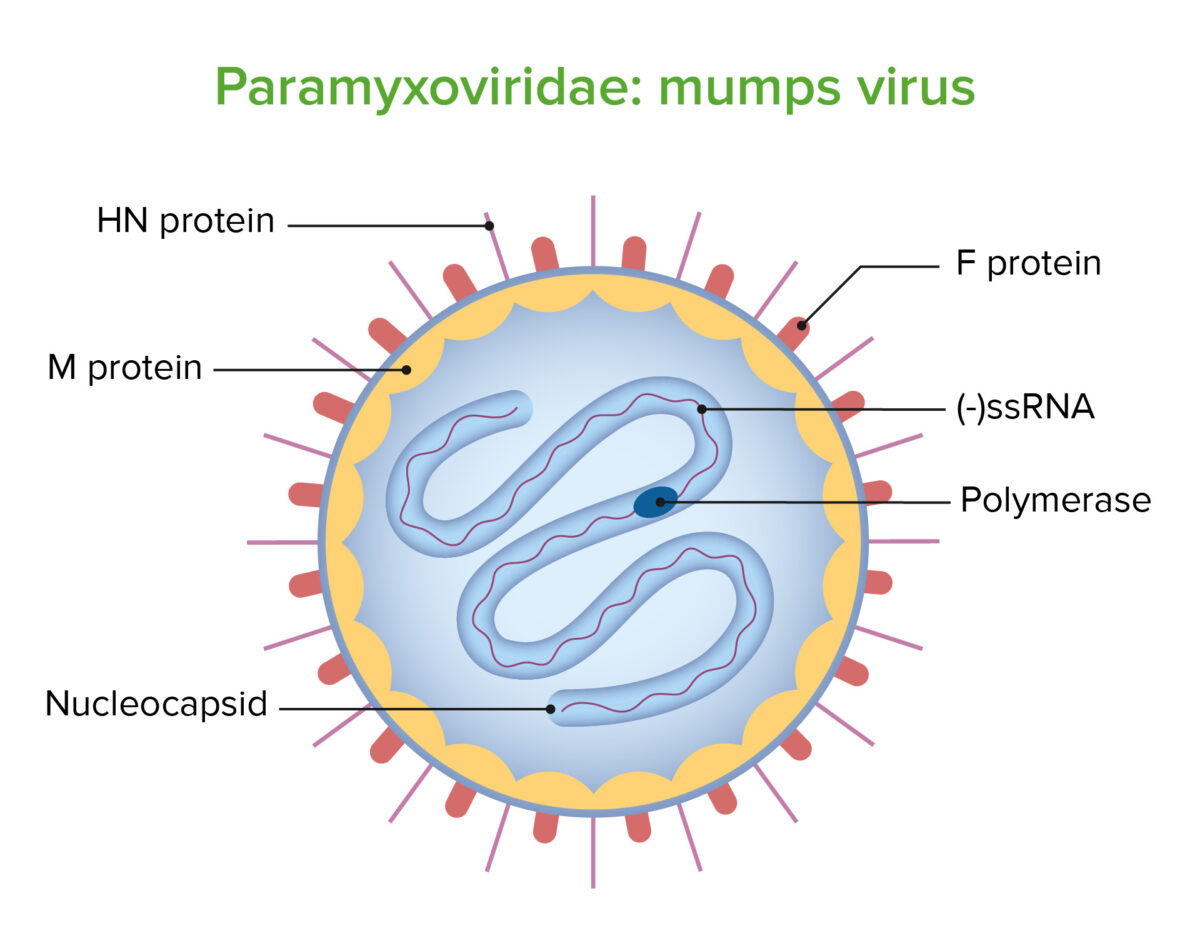
Estructura del virus de las paperas
Imagen de Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0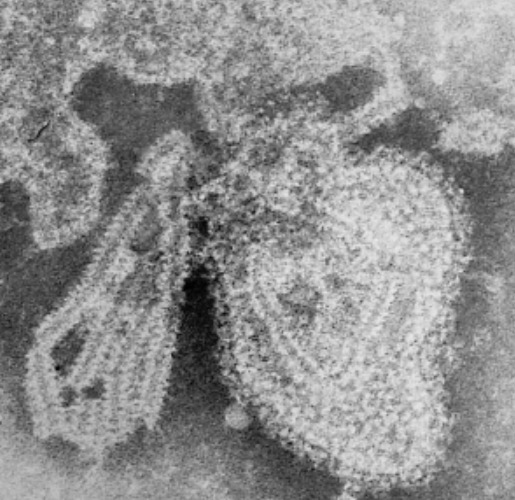
Microscopía electrónica de transmisión del virus de las paperas
Imagen: “TEM micrograph of a mumps virus particle” por CDC/ Dr. F. A. Murphy. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl periodo de incubación es de 2–3 semanas.
Tras el periodo de incubación, se producen síntomas prodrómicos durante 3–5 días, entre ellos:
Tras el periodo prodrómico, el paciente puede presentarse asintomático (20% de los LOS Neisseria casos) o desarrollar síntomas dependiendo del órgano afectado:
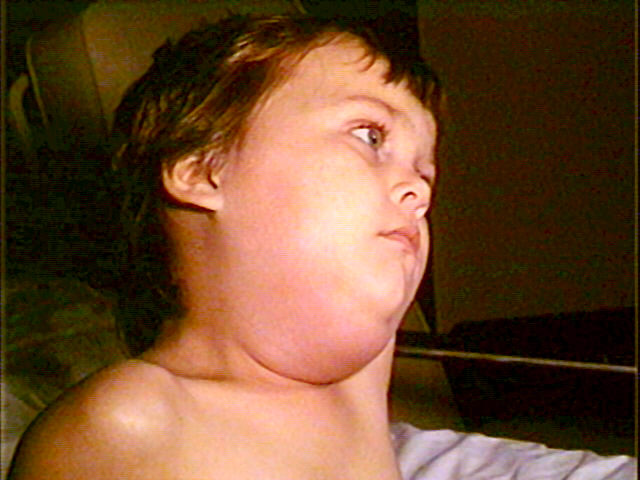
Paciente pediátrico con paperas que presenta una inflamación de la glándula submandibular
Imagen: “Child with mumps” por CDC/NIP/Barbara Rice. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLas paperas suelen diagnosticarse por motivos clínicos y no es necesario realizar pruebas de laboratorio de confirmación.