La rubéola (también conocida como sarampión alemán o sarampión de tres días) es causada por un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ARN monocatenario de sentido positivo de la familia Matonaviridae y del género Rubivirus Rubivirus A genus of the family togaviridae containing only one recognized species, rubella virus. Transmission is primarily by aerosolization. Rubella Virus. La rubéola solo infecta a los LOS Neisseria humanos y se propaga prenatalmente a través de transmisión vertical o posnatalmente a través del contacto con gotitas. La rubéola congénita es particularmente devastadora y se asocia con una tríada clásica de síntomas: cataratas, defectos cardiacos y sordera. La infección en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños y adultos puede ser leve y presentarse con síntomas constitucionales junto con un exantema viral parecido al AL Amyloidosis virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del sarampión. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente y se confirma con la detección del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum suero y estudios serológicos. El tratamiento es de apoyo y puede dirigirse según el sistema de órganos involucrado. La prevención se logra mediante la vacunación infantil con la vacuna contra el sarampión, las paperas y la rubéola (SPR).
Last updated: Jan 29, 2026

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son positivos si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios negativos emplean la ARN polimerasa, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARNm.
Estructura:
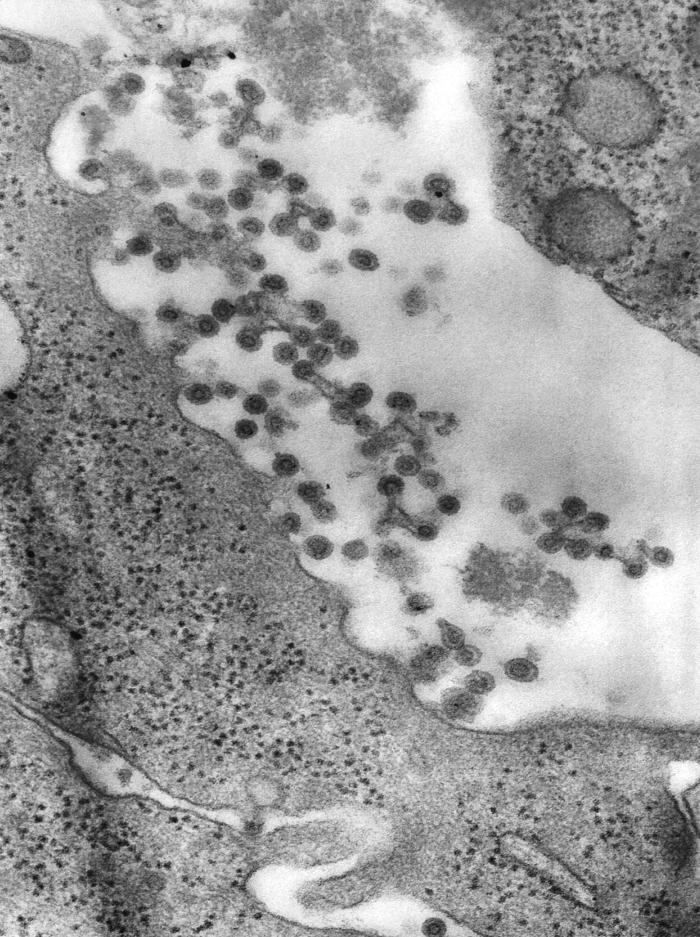
Micrografía electrónica de viriones del virus de la rubéola
Imagen: “This transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image revealed the presence of rubella virus virions” por CDC. Licencia: Public DomainPrenatal:
Posnatal:
Las infecciones primarias posnatales con rubéola se someten a un proceso patogénico secuencial:
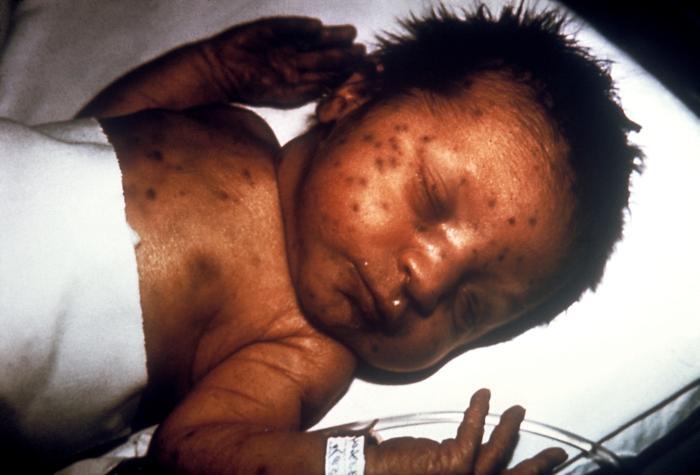
Lactante con una “erupción de muffin de arándanos” por rubéola congénita
Imagen: “Infant presented with ‘blueberry muffin’ skin lesions indicative of congenital rubella” por CDC. Licencia: Public Domain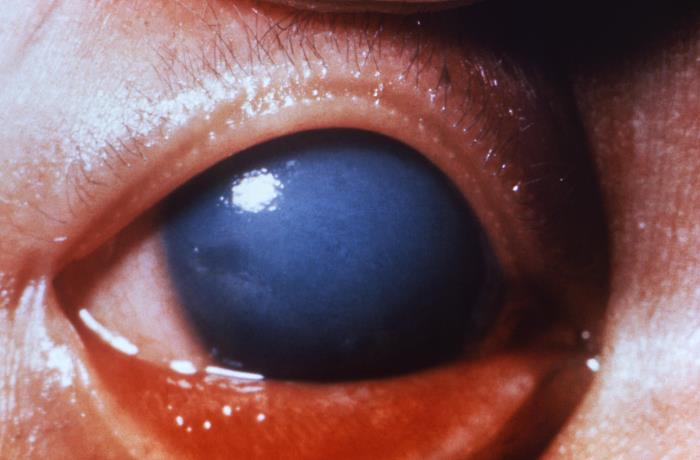
Glaucoma congénito en un lactante debido a rubéola congénita
Imagen: “This image depicts a close view of the right eye of a 3-year-old infant, who exhibited symptoms of a condition known as congenital glaucoma, due to a case of congenital rubella.” por CDC. Licencia: Public Domain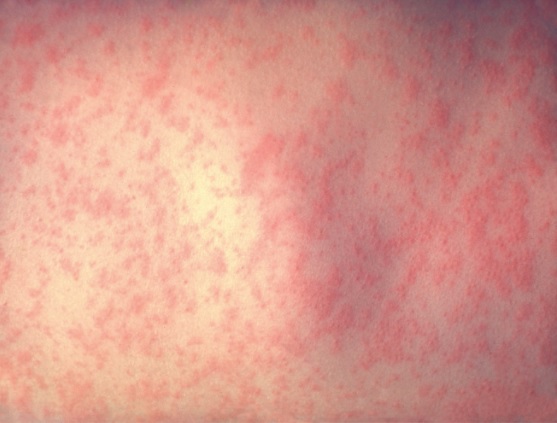
Exantema típico de la infección por rubéola:
La propagación y la distribución son similares a las del sarampión; sin embargo, las lesiones son menos roji-intensas y menos confluentes.
El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente y se confirma con la detección del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum suero y estudios serológicos.
El tratamiento es de apoyo y dirigido según el sistema de órganos involucrado. La prevención se logra mediante la vacunación SPR o SPRV (sarampión, paperas, rubéola, varicela).
| Número | Otros nombres de la enfermedad | Etiología | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1ra enfermedad |
|
Morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus del sarampión |
|
| 2da enfermedad |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3ra enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rubéola |
|
| 4ta enfermedad |
|
Debido a las cepas de Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess que fabrican la toxina epidermolítica (exfoliativa) |
|
| 5ta enfermedad | Eritema infeccioso | Eritrovirus o parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (eritroparvovirus 1 de primates) |
|
| 6ta enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del herpes humano 6B o 7 |
|