El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis A Hepatitis A Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. HAV causes an acute, highly contagious hepatitis with unspecific prodromal symptoms such as fever and malaise followed by jaundice and elevated liver transaminases. Hepatitis A Virus ( HAV HAV The hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. The virus replicates in the liver, is excreted in the bile, and is found in high concentrations in the stool of acutely infected individuals. The 2 main routes of infection are consumption of contaminated food or water and direct contact with an infected person. Hepatitis A Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology no envuelto de la familia Picornaviridae Picornaviridae A family of small RNA viruses comprising some important pathogens of humans and animals. Transmission usually occurs mechanically. There are nine genera: aphthovirus; cardiovirus; enterovirus; erbovirus; hepatovirus; kobuvirus; parechovirus; rhinovirus; and teschovirus. Coxsackievirus con ARN monocatenario. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology se replica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hígado, se excreta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la bilis y se encuentra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum altas concentraciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las heces de los LOS Neisseria individuos infectados agudamente. Las 2 principales vías de infección son el consumo de agua o alimentos contaminados y el contacto directo con una persona infectada. El HAV HAV The hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. The virus replicates in the liver, is excreted in the bile, and is found in high concentrations in the stool of acutely infected individuals. The 2 main routes of infection are consumption of contaminated food or water and direct contact with an infected person. Hepatitis A Virus causa una hepatitis aguda, altamente contagiosa, con síntomas prodrómicos inespecíficos como fiebre y malestar, seguidos de ictericia y elevación de las transaminasas hepáticas. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria individuos se recuperan completamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum unos pocos meses, y la inmunidad resultante por la infección por HAV HAV The hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. The virus replicates in the liver, is excreted in the bile, and is found in high concentrations in the stool of acutely infected individuals. The 2 main routes of infection are consumption of contaminated food or water and direct contact with an infected person. Hepatitis A Virus es de por vida. A diferencia de la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus y C, la infección por HAV HAV The hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. The virus replicates in the liver, is excreted in the bile, and is found in high concentrations in the stool of acutely infected individuals. The 2 main routes of infection are consumption of contaminated food or water and direct contact with an infected person. Hepatitis A Virus no produce una infección crónica ni a una enfermedad hepática crónica. La vacunación preventiva contra el HAV HAV The hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. The virus replicates in the liver, is excreted in the bile, and is found in high concentrations in the stool of acutely infected individuals. The 2 main routes of infection are consumption of contaminated food or water and direct contact with an infected person. Hepatitis A Virus está disponible y se recomienda para las personas con mayor riesgo de exposición y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos países como Estados Unidos, para todos los LOS Neisseria niños > 12 meses de edad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación del virus de ARN:
Los virus se pueden clasificar de muchas formas. La mayoría de los virus, sin embargo, tendrán un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus del genoma de ARN pueden caracterizarse además por ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (generalmente extraída de la célula huésped). Si la envoltura está ausente, los virus se denominan virus “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son virus de “sentido positivo” si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios de “sentido negativo” emplean la ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
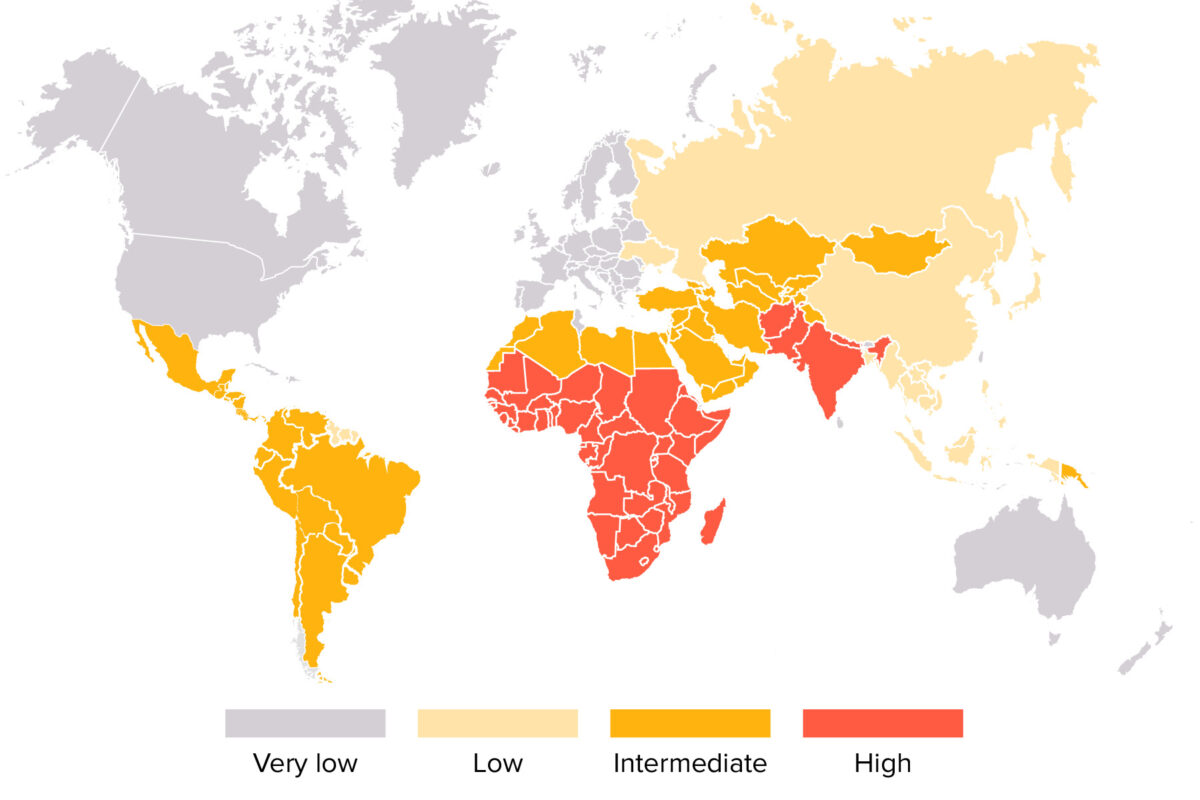
Mapa mundial de la distribución del virus de la hepatitis A
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0La presencia de 1 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes síntomas es una razón para sospechar una infección por hepatitis A Hepatitis A Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. HAV causes an acute, highly contagious hepatitis with unspecific prodromal symptoms such as fever and malaise followed by jaundice and elevated liver transaminases. Hepatitis A Virus, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum presencia de factores de riesgo:
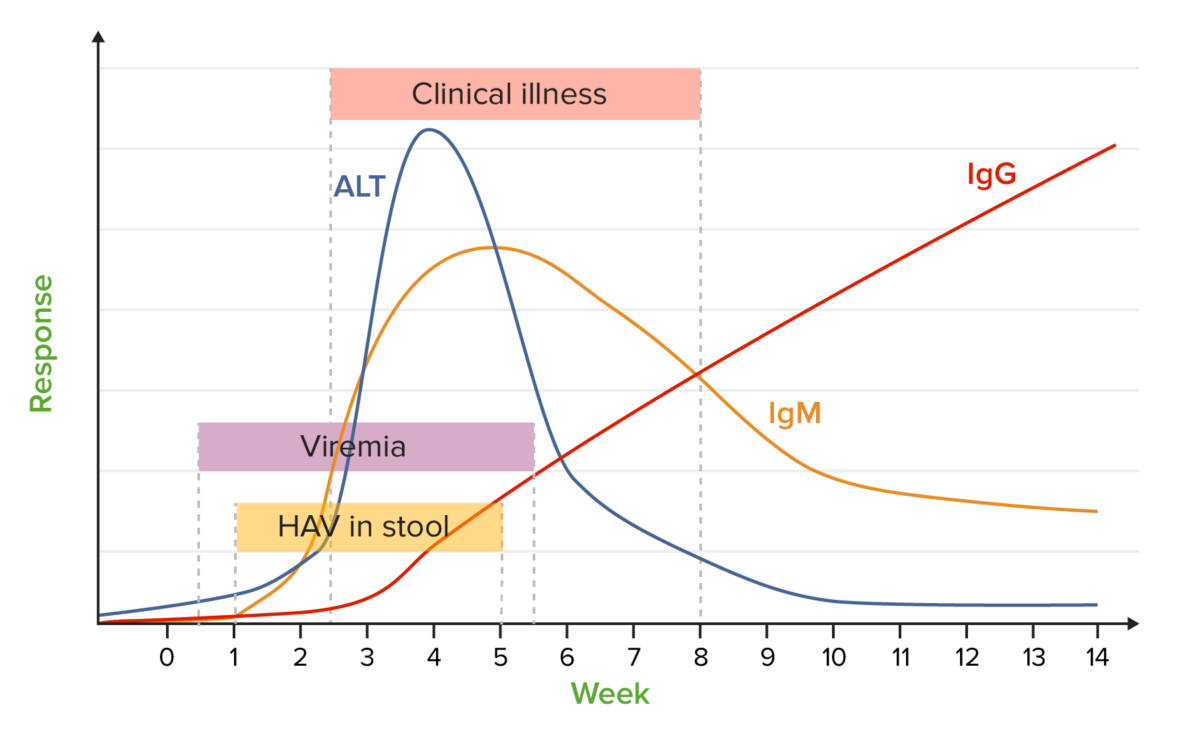
Marcadores de hepatitis A:
gráfico que muestra la evolución típica de los parámetros de laboratorio más importantes con respecto al tiempo después de la infección
ALT: alanina transaminasa
HAV: virus de la hepatitis A (por sus siglas en inglés)
Ig: inmunoglobulina
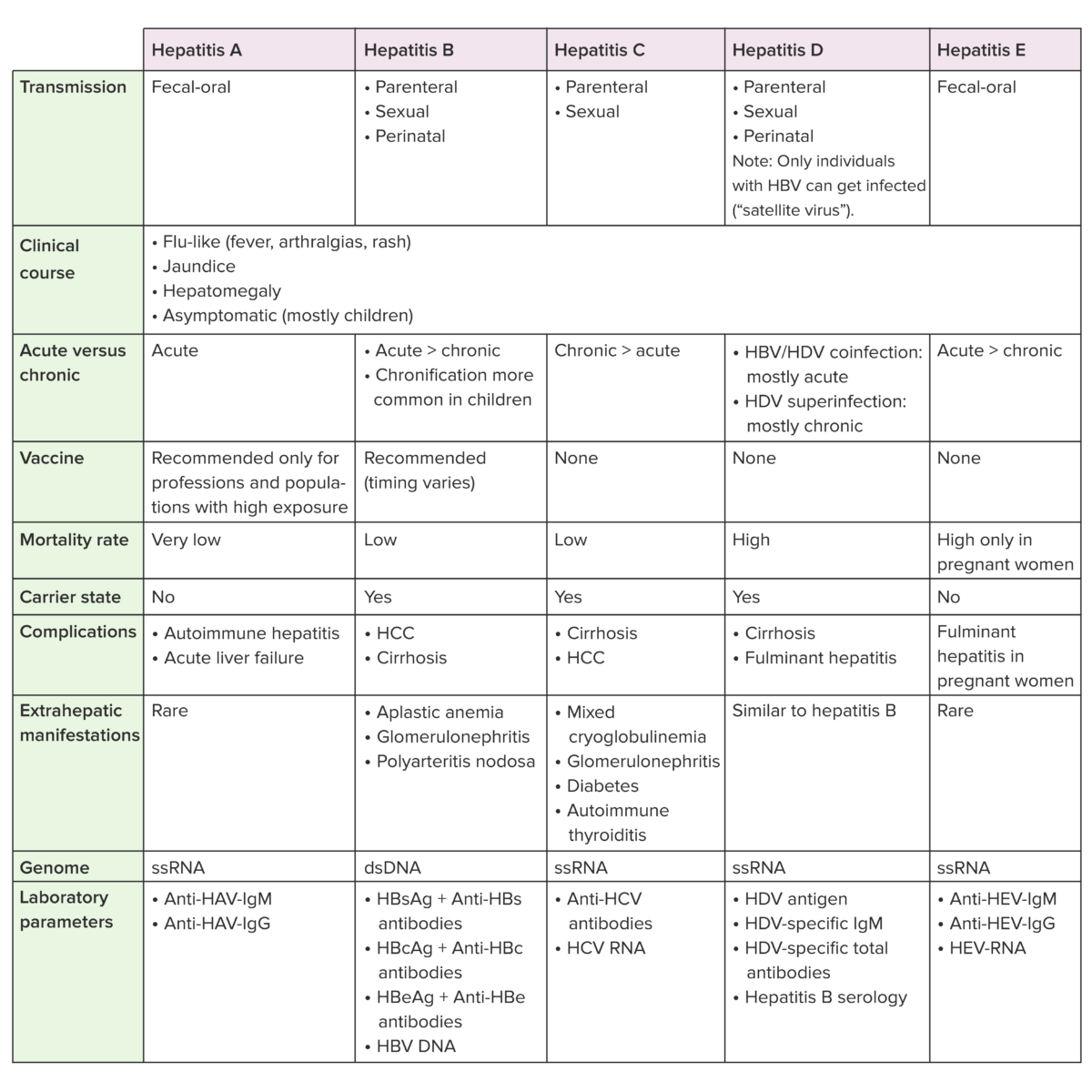
Anti-HBc: anticuerpos del núcleo de la hepatitis B (por sus siglas en inglés)
Anti-HBs: anticuerpos de superficie contra la hepatitis B (por sus siglas en inglés)
HBcAg: antígeno del núcleo de la hepatitis B (por sus siglas en inglés)
HBsAg: antígeno de superficie de la hepatitis B (por sus siglas en inglés)
HBV: virus de la hepatitis B (por sus siglas en inglés)
HCC: carcinoma hepatocelular (por sus siglas en inglés)
HCV: virus de la hepatitis C (por sus siglas en inglés)
HDV: virus de la hepatitis D (por sus siglas en inglés)