El trabajo de parto prematuro se refiere a las contracciones uterinas regulares que conducen a un cambio cervical antes de las 37 semanas de gestación; el nacimiento prematuro se refiere al AL Amyloidosis nacimiento antes de las 37 semanas de gestación. El nacimiento prematuro puede ser espontáneo, debido a un trabajo de parto prematuro, una rotura prematura de membranas (RPM) o una insuficiencia cervical. El nacimiento prematuro también puede ser iniciado por el proveedor de salud por una variedad de indicaciones maternas o fetales. El diagnóstico incluye evaluaciones para detectar cambios cervicales y monitorear contracciones uterinas regulares. El tratamiento depende de la edad gestacional, pero suele incluir la administración de corticosteroides (para mejorar la madurez pulmonar del feto), sulfato de magnesio (para la neuroprotección del feto contra la parálisis cerebral), profilaxis contra el estreptococo del grupo B y 48 horas de tocolíticos para ayudar a los LOS Neisseria pacientes a completar un tratamiento completo de esteroides.
Last updated: Jan 20, 2026
El trabajo de parto prematuro se define como las contracciones uterinas regulares que condicionan un cambio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dilatación y/o borramiento cervical antes de las 37 semanas de gestación.
El nacimiento prematuro se define como el nacimiento a una edad gestacional de entre 20-37 semanas.
Trabajo de parto prematuro:
Nacimiento prematuro:
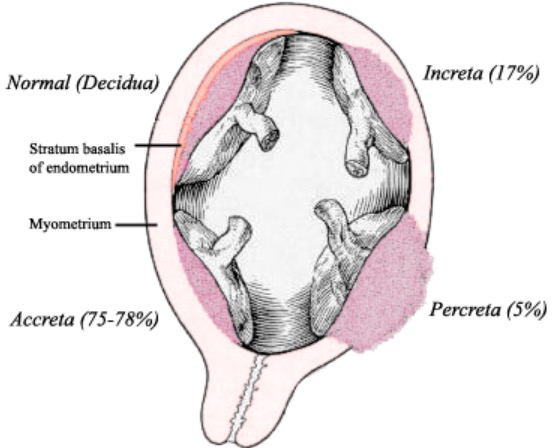
Placenta acreta:
La placenta acreta, una etiología conocida indicada para el nacimiento prematuro, describe una placenta que invade el miometrio a diferentes profundidades.
Dado que el trabajo de parto prematuro es una de las principales etiologías del nacimiento prematuro, todos los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo de trabajo de parto prematuro son también factores de riesgo de nacimiento prematuro espontáneo.
Vía final común para iniciar el trabajo de parto prematuro:
Vías primarias (4) que conducen a la vía final común:
Todas las vías que conducen al AL Amyloidosis trabajo de parto prematuro (antes mencionadas) pueden evolucionar hacia un nacimiento prematuro.
El nacimiento prematuro también puede ser causado por una insuficiencia cervical:
Mujeres embarazadas de < 37 semanas de edad gestacional que presentan:
La clave para diagnosticar el trabajo de parto prematuro es determinar si se están produciendo cambios cervicales y si las contracciones regulares son la causa de esos cambios. La longitud cervical también es importante para ayudar a predecir un nacimiento prematuro independientemente de las contracciones.
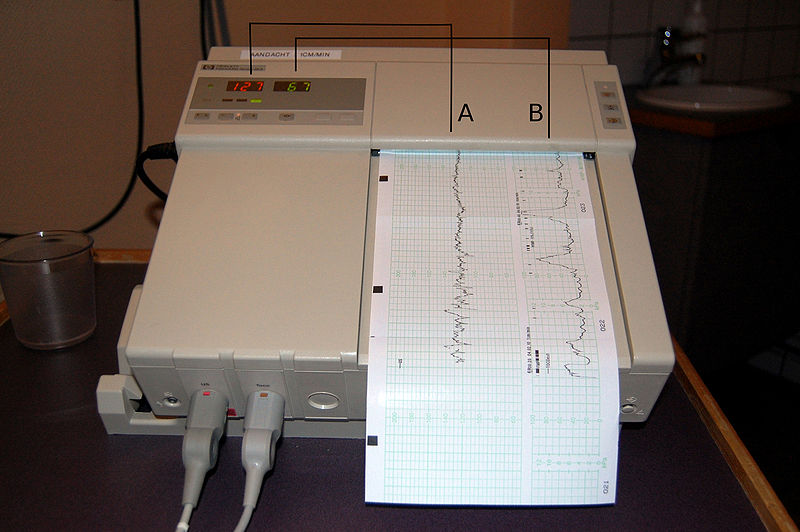
Monitoreo fetal con tocometría:
A: Registro de la frecuencia cardíaca fetal determinada por ultrasonido externo
B: Registro de las contracciones uterinas medidas por un transductor de presión externo
Los valores se registran continuamente a lo largo del tiempo.
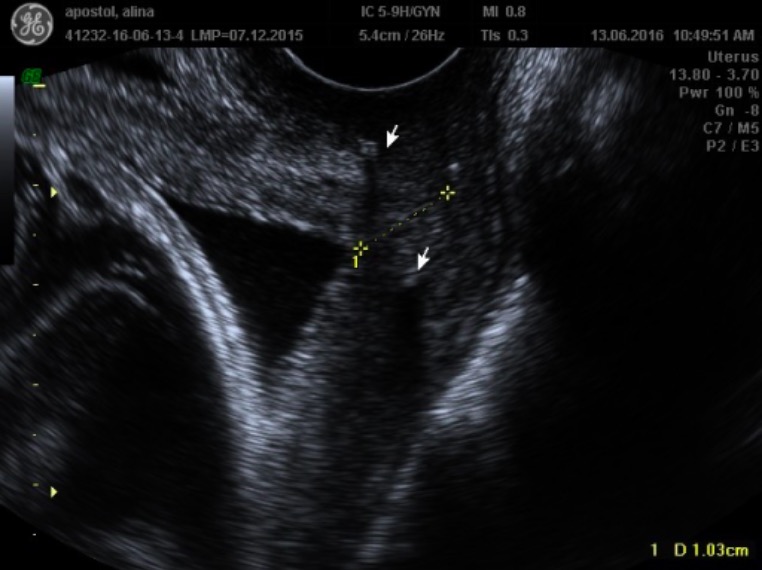
Una imagen de un ultrasonido transvaginal que demuestra un cérvix acortado de 1,0 cm (línea amarilla punteada):
Las flechas indican la sutura hiperecoica del cerclaje.
El diagnóstico de trabajo de parto prematuro requiere la presencia de contracciones uterinas más cambios cervicales:
Las pacientes con diagnóstico de trabajo de parto prematuro deben ser hospitalizadas para observación de la evolución del trabajo de parto y para su tratamiento.
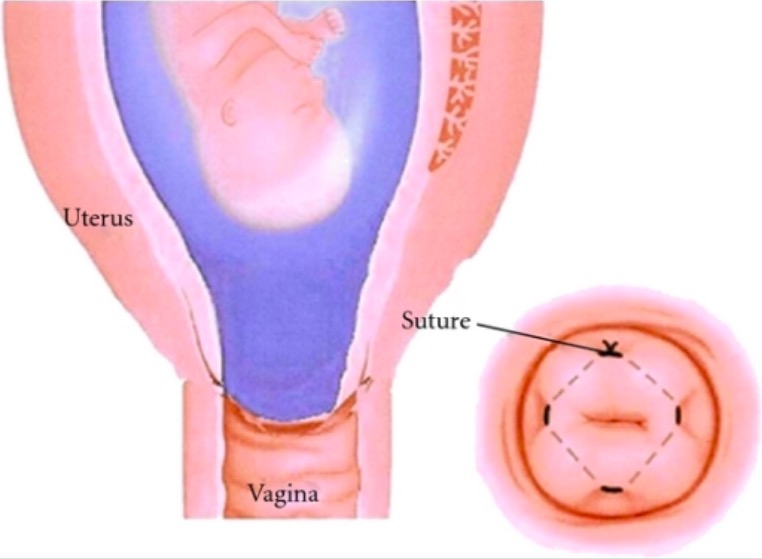
Cerclaje cervical:
La imagen más grande muestra un cérvix dilatado con membranas visibles en especuloscopía estéril. Se coloca una sutura de cerclaje circunferencialmente en forma de bolsa alrededor del cérvix.