El síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich, también conocido como síndrome de eczema-trombocitopenia-inmunodeficiencia, IMD2 IMD2 Wiskott-aldrich syndrome (WAS), also known as eczema-thrombocytopenia-immunodeficiency syndrome, IMD2, or immunodeficiency 2, is a rare genetic mixed disorder of B- and T-cell deficiency that follows an X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. It is caused by a WAS gene mutation that leads to impaired actin cytoskeleton, phagocytosis and chemotaxis, impaired platelet development, and, in general, a loss of humoral and cellular responses. Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome o inmunodeficiencia 2, es un raro trastorno genético mixto de deficiencia de células B y T que sigue un patrón de herencia recesivo ligado al AL Amyloidosis cromosoma X. Es causado por una mutación del gen WAS que provoca una alteración del citoesqueleto de actina, de la fagocitosis y de la quimiotaxis, una alteración del desarrollo de las plaquetas y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, una pérdida de las respuestas humoral y celular. El síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich se presenta con una tríada clásica de eczema Eczema Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic, relapsing, pruritic, inflammatory skin disease that occurs more frequently in children, although adults can also be affected. The condition is often associated with elevated serum levels of IgE and a personal or family history of atopy. Skin dryness, erythema, oozing, crusting, and lichenification are present. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), diátesis hemorrágica e infecciones oportunistas recurrentes, pero también conlleva un alto riesgo de desarrollo de autoinmunidad y malignidad. El tratamiento incluye el trasplante de células madre hematopoyéticas, la terapia de sustitución de inmunoglobulina, los LOS Neisseria antibióticos profilácticos y terapéuticos, y los LOS Neisseria esteroides sistémicos. Sin el trasplante de células madre hematopoyéticas el pronóstico no es bueno y la expectativa de vida se reduce.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
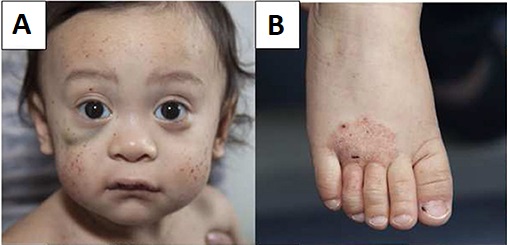
Paciente joven con síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich que presenta múltiples petequias en la cara y un hematoma bajo el ojo derecho (A) y eczema en el pie (B)
Imagen: “Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome” por Michael H. Albert and Alexandra F. Freeman, on behalf of the Inborn Errors Working Party (IEWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Licencia: CC BY 4.0Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales para el síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich: