El síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos, también conocido como enfermedad de Ritter o necrólisis epidérmica estafilocócica, es una afección mediada por toxinas causada por Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess. La toxina exfoliativa producida se disemina y escinde la desmogleína 1 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la epidermis Epidermis The external, nonvascular layer of the skin. It is made up, from within outward, of five layers of epithelium: (1) basal layer (stratum basale epidermidis); (2) spinous layer (stratum spinosum epidermidis); (3) granular layer (stratum granulosum epidermidis); (4) clear layer (stratum lucidum epidermidis); and (5) horny layer (stratum corneum epidermidis). Skin: Structure and Functions, provocando la separación y desprendimiento de la piel. El síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos afecta con mayor frecuencia a los LOS Neisseria niños pequeños. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas prodrómicos preceden al AL Amyloidosis eritema cutáneo difuso, la sensibilidad, la formación de ampollas y la descamación superficial. No se comprometen las membranas mucosas. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente y se puede confirmar con datos de cultivo (dirigidos a los LOS Neisseria posibles sitios de infección primaria) y biopsia. Sin embargo, los LOS Neisseria cultivos de las ampollas no son útiles. Se deben iniciar antibióticos y cuidados de soporte tan pronto como se sospeche el diagnóstico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
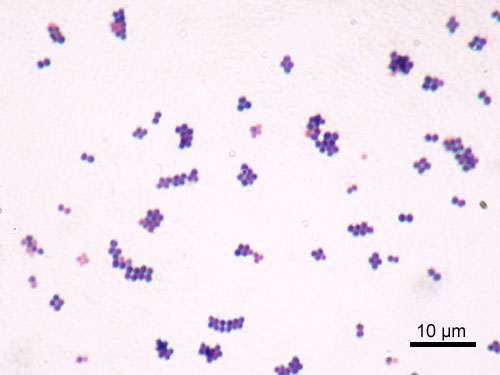
Imagen microscópica de Staphylococcus aureus
Imagen: “Staphylococcus aureus Gram” por Y Tambe. Licencia: CC BY-SA 3.0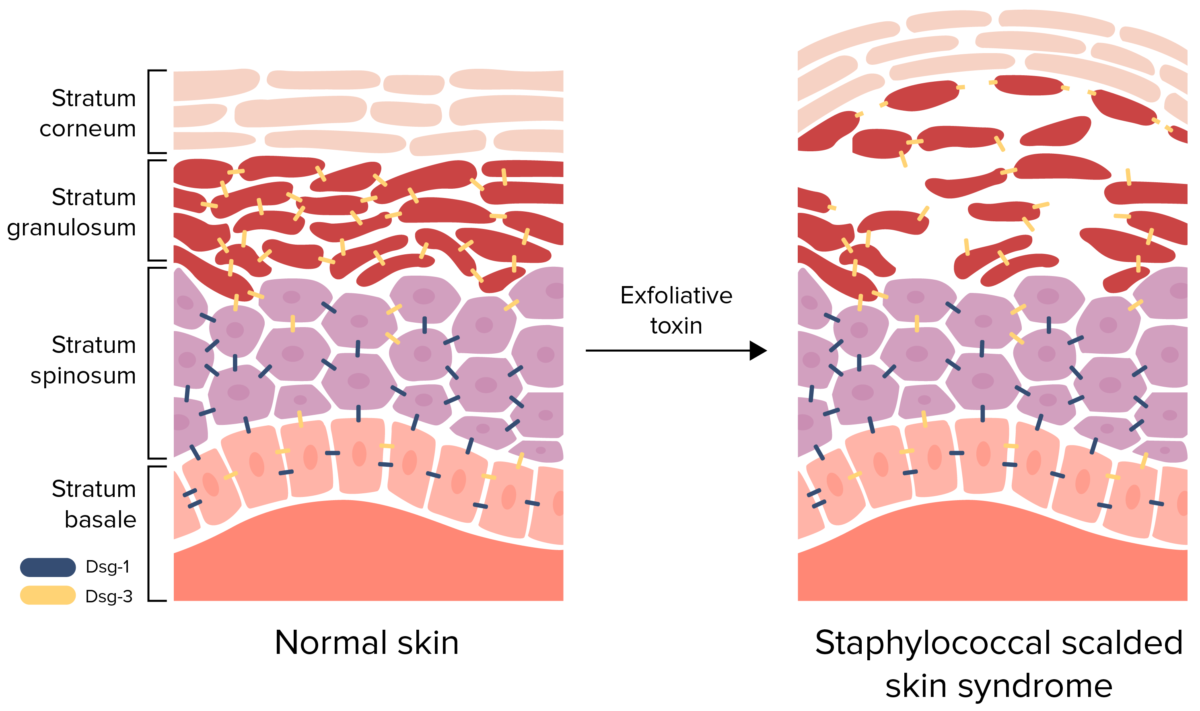
Fisiopatología del síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos:
La toxina exfoliativa escinde la desmogleína (Dsg) 1, interrumpiendo la adhesión célula a célula del estrato granuloso. Este desprendimiento de la epidermis superficial provoca la formación de ampollas y descamación.
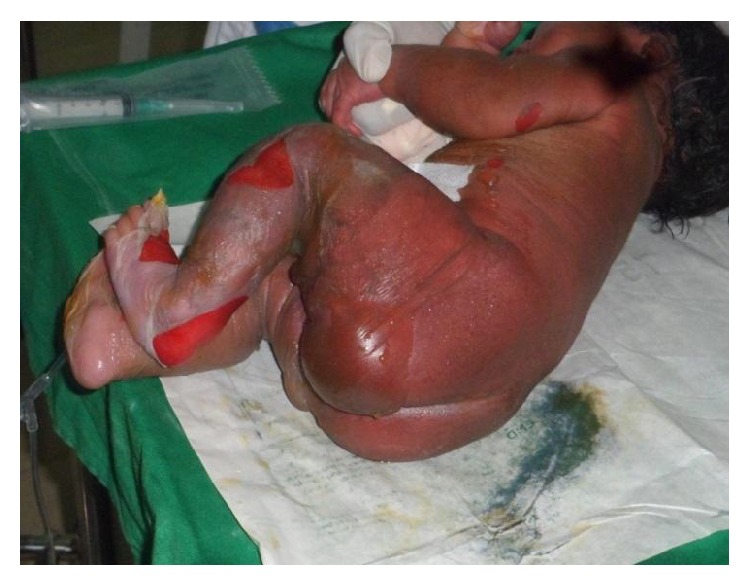
Síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos en un recién nacido:
Esta imagen muestra eritema difuso, formación de ampollas y descamación de la piel.
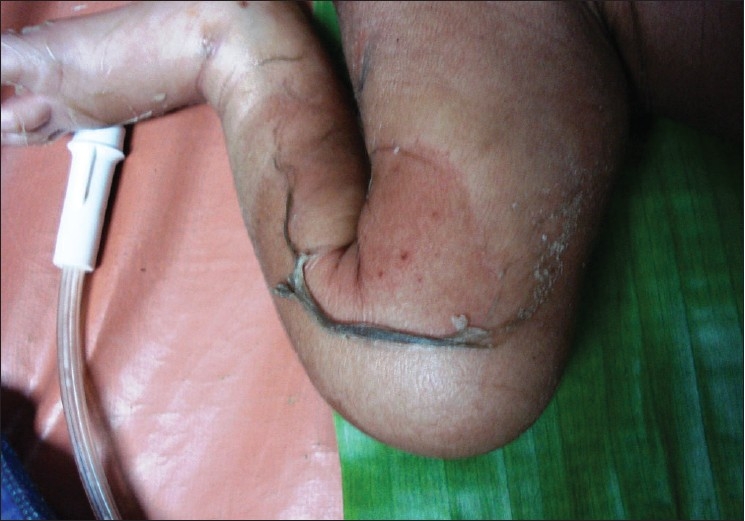
Manifestaciones cutáneas del síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos:
Se observa descamación de la piel y eritema sobre el muslo.

Manifestaciones cutáneas del síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos:
Eritema, descamación de la piel y costras en la cara
El tratamiento del síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos incluye un tratamiento agresivo para la infección primaria y medidas de soporte.
| Número | Otros nombres de la enfermedad | Etiología | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1ra enfermedad |
|
Morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus del sarampión |
|
| 2da enfermedad |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3ra enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rubéola |
|
| 4ta enfermedad |
|
Debido a cepas de Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess que producen la toxina epidermolítica (exfoliativa) |
|
| 5ta enfermedad | Eritema infeccioso | Eritrovirus o parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (eritroparvovirus 1 de primates) |
|
| 6ta enfermedad | Herpesvirus humano (HHV, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés)-6B o HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 |
|