La reacción de hipersensibilidad tipo IV, o hipersensibilidad retardada, es una respuesta mediada por células a la exposición de antígenos. La reacción implica a los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T, no a los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos, y se desarrolla durante varios días. Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T previamente sensibilizados inician la defensa inmune, lo que provoca daño tisular. Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T colaboradores activan un proceso mediado por citoquinas, mientras que los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T citotóxicos liberan directamente citotoxinas a las células infectadas o disfuncionales, provocando lisis celular. Las manifestaciones clínicas dependen del sistema implicado, por lo que las pruebas de diagnóstico se basan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos. El tratamiento incluye el control de los LOS Neisseria efectos de la respuesta inmune con glucocorticoides y terapia inmunosupresora, al AL Amyloidosis mismo tiempo que se controlan las complicaciones asociadas a la enfermedad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Fase de sensibilización
Fase efectora
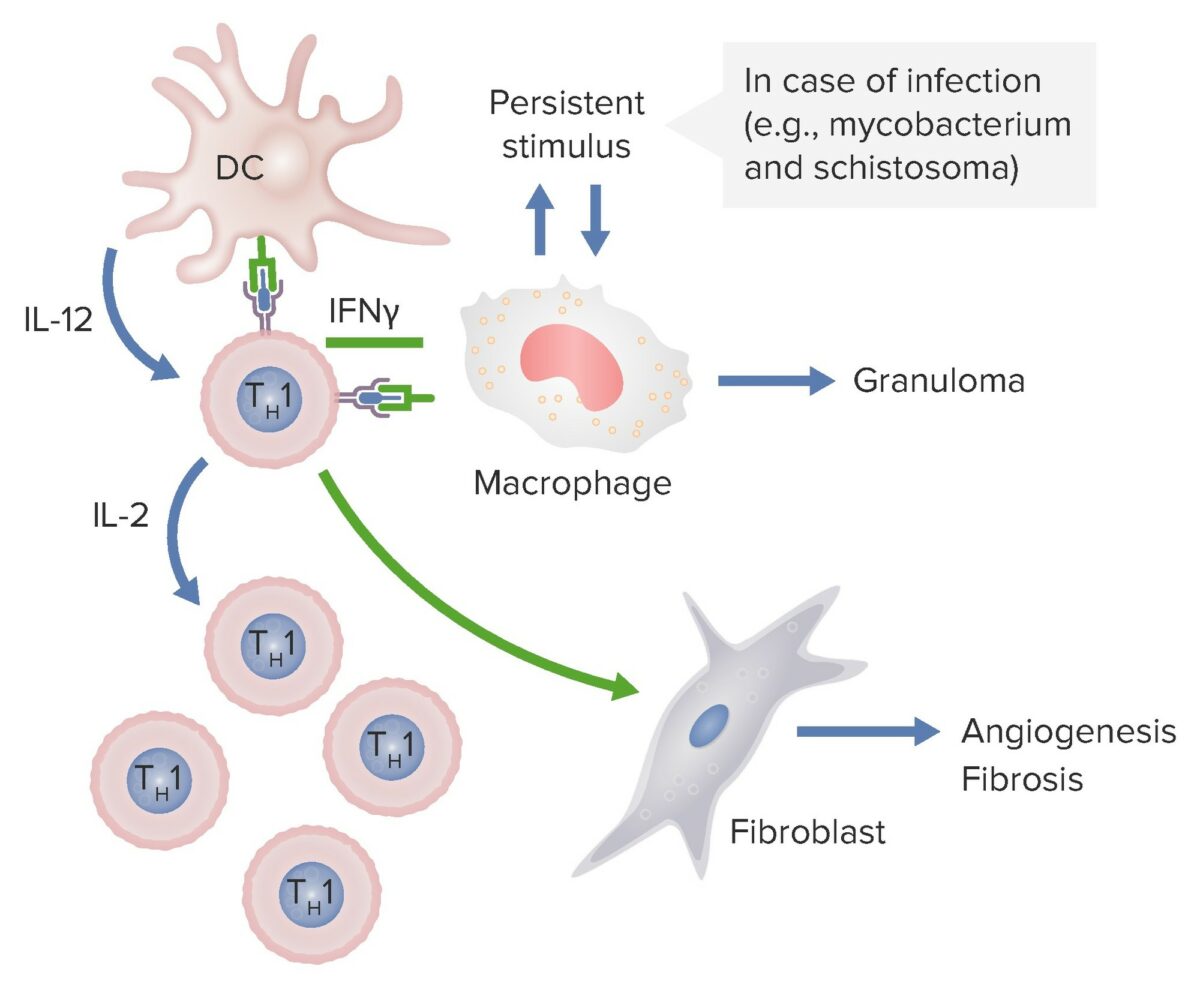
En el diagrama anterior, las células dendríticas están liberando IL-12 que activa a los linfocitos Th1 CD4. Estos linfocitos Th1 producen IL-2 estimulando la producción de más subconjuntos de linfocitos T Th1. Los linfocitos colaboradores también liberan interferon-gamma, que activa a los macrófagos y a los fibroblastos para causar angiogénesis y fibrosis. Si estos macrófagos son estimulados persistentemente por patógenos como micobacterias y esquistosoma, se forman granulomas.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Inflamación mediada por citoquinas y linfocitos T citotóxicos en la hipersensibilidad tipo IV.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Mecanismo del Granuloma en la hipersensibilidad Tipo IV.
Imagen por Lecturio.| Enfermedad | Antígeno diana | Efectos |
|---|---|---|
| Dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) de contacto alérgica | Productos químicos ambientales como el urushiol Urushiol Toxicology of Plants (de la hiedra venenosa y el roble venenoso), metales (e.g., níquel), medicamentos tópicos | Necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage epidérmica, inflamación, erupción cutánea y ampollas |
| Miocarditis autoinmune | Proteína de la cadena pesada de la miosina | Cardiomiopatía |
| Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo I | Proteínas de las células beta pancreáticas (posiblemente insulina, glutamato descarboxilasa) | Insulitis, destrucción de células beta |
| Granulomas Granulomas A relatively small nodular inflammatory lesion containing grouped mononuclear phagocytes, caused by infectious and noninfectious agents. Sarcoidosis | Varios, dependiendo de la enfermedad subyacente | Lesión encapsulada que contiene macrófagos y otras células |
| Algunas neuropatías periféricas | Antígeno de células de Schwann | Neuritis, parálisis |
| Tiroiditis de Hashimoto | Antígeno de tiroglobulina | Hipotiroidismo, bocio, timitis folicular |
| Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal | Microbiota entérica y/o autoantígenos | Hiperactivación de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T, liberación de citoquinas, reclutamiento de macrófagos y otras células inmunológicas, inflamación |
| Esclerosis múltiple | Antígenos de la mielina (e.g., proteína básica de la mielina) | Destrucción de la mielina, inflamación |
| Artritis reumatoide | Posiblemente colágeno y/o auto-proteínas citrulinadas | Artritis crónica, inflamación, destrucción del cartílago articular y del hueso |
| Reacción a la tuberculina (prueba de Mantoux) | Tuberculina | La induración y el eritema alrededor del lugar de la inyección indican una exposición previa |
Un caso de síndrome de Steven-Johnson después del uso de antibióticos que muestra erupción eritematosa con ampollas flácidas
Imagen: “Erythematous rash with flaccid blisters affecting the trunk” por Neila Fathallah et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) de contacto alérgica
Tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis
Lepra
Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly. Sarcoidosis
Enfermedad de Crohn
Miocarditis autoinmune
Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo I
Hipersensibilidad medicamentosa
Síndrome de Guillain-Barré