Pneumocystis jirovecii es un hongo levaduriforme que causa la neumonía por Pneumocystis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunocomprometidos. La neumonía por Pneumocystis se propaga por transmisión aérea y afecta clásicamente a los LOS Neisseria pacientes con SIDA, siendo una enfermedad definitoria del SIDA. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden presentar un inicio insidioso de fiebre, escalofríos, tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome seca, dolor Dolor Inflammation torácico y dificultad para respirar. El diagnóstico se apoya en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un aumento del nivel de β-D-glucano y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum infiltrados difusos y bilaterales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagenología torácica del paciente inmunocomprometido. El diagnóstico definitivo puede realizarse mediante la microscopía del esputo inducido o de las muestras del lavado broncoalveolar. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una terapia antimicrobiana con una combinación de trimetoprim-sulfametoxazol y cuidados de soporte. Es primordial tratar la etiología de la inmunodeficiencia. A menudo se requiere profilaxis para prevenir la infección o la reinfección.
Last updated: May 11, 2022
Pneumocystis es un hongo levaduriforme.
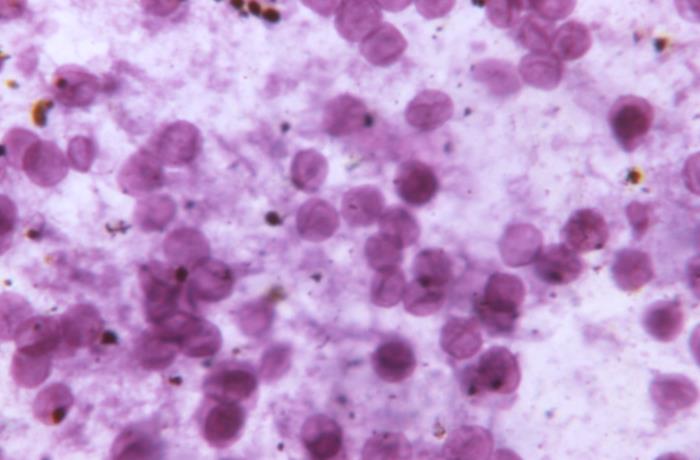
Microfotografía de una muestra de tejido pulmonar teñida con azul de toluidina que muestra numerosos quistes fúngicos de Pneumocystis jirovecii
Imagen: “This photomicrograph of a toluidine blue stained lung tissue impression smear, revealed the presence of numerous, Pneumocystis jirovecii, formerly known as Pneumocystis carinii, fungal cysts.” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoP. jirovecii (antes conocido como P. carinii P. carinii Pneumocystis jiroveci is a yeast-like fungus causing pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in immunocompromised patients. Pneumocystis pneumonia is spread through airborne transmission and classically affects patients with aids, functioning as an AIDS-defining illness. Patients may present with insidious onset of fever, chills, dry cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Pneumocystis jirovecii/Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP)) que causa la neumonía por Pneumocystis.
Se desconoce el reservorio de P. jirovecii, pero los LOS Neisseria humanos inmunocompetentes pueden desempeñar un papel importante.
P. jirovecii se propaga por transmisión aérea.
La neumonía por Pneumocystis se produce en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocomprometidos:
La neumonía por Pneumocystis puede presentarse de forma inespecífica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum comparación con otros tipos de neumonía.
La presentación puede ser subaguda y evolucionar a lo largo de varias semanas:
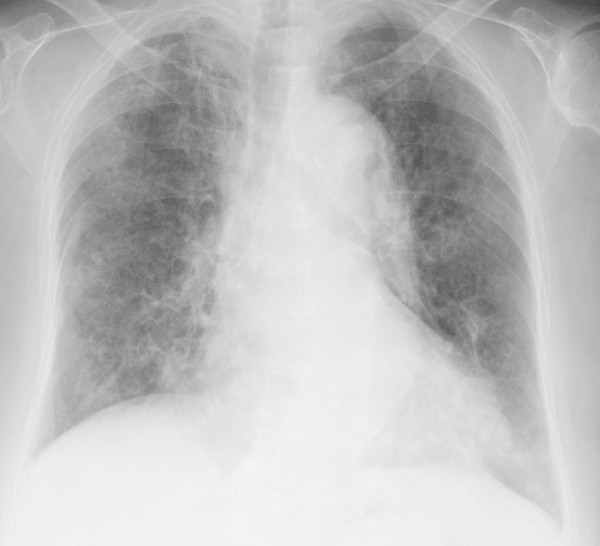
Radiografía de tórax que muestra opacidades difusas y bilaterales compatibles con una neumonía por Pneumocystis
Imagen: “Chest X-ray obtained after the diagnosis of pneumocystis pneumonia showed areas of ground-glass opacity bilaterally in almost all lung fields.” por Kato M et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0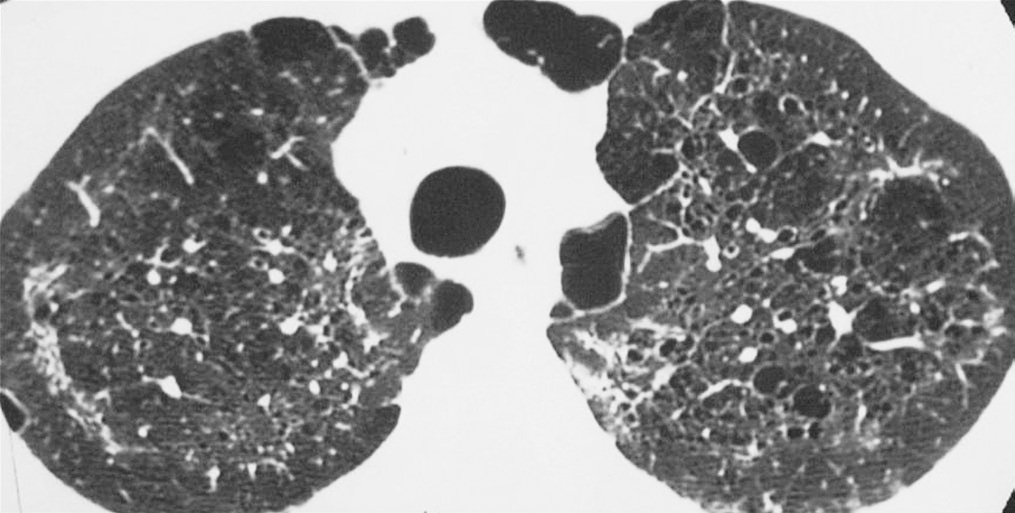
TC de alta resolución que muestra múltiples quistes pulmonares por neumonía por Pneumocystis
Imagen: “Lung cysts are usually multiple and bilateral, but range in size, shape and distribution. They are more commonly appreciated on computed tomography (CT)/high-resolution CT” por Carolyn M. Licencia: CC BY 4.0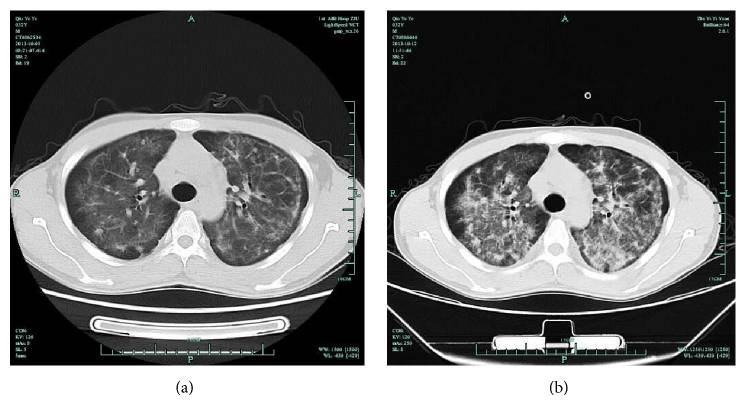
TC de tórax en un paciente con SIDA con neumonía por Pneumocystis:
(a) opacidades intersticiales bilaterales y simétricas
(b) opacidades difusas y perihilares
Diagnóstico definitivo:
Estudios de apoyo:
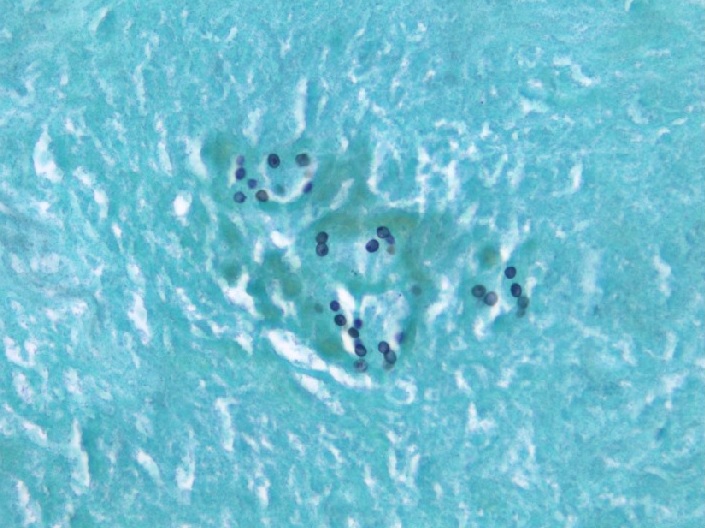

Tinción de plata metanamina que demuestra quistes de Pneumocystis jirovecii dentro de un granuloma necrosado
Imagen: “Microscopy 800x magnification: Gomori methenamine silver stain” por Patel K. Licencia: CC BY 4.0La profilaxis varía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la etiología de la inmunosupresión:
Complicaciones de la neumonía por Pneumocystis:
El reconocimiento y el tratamiento precoz mejoran el pronóstico.
Factores relacionados con un mal pronóstico: