Los LOS Neisseria echovirus Echovirus Echoviruses are single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses belonging to the genus Enterovirus. Transmission is most commonly through the fecal-oral route. The majority of patients are asymptomatic. Patients who are symptomatic can exhibit a wide range of illnesses ranging from nonspecific URIs and exanthems to severe and life-threatening illnesses. Echovirus son virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ARN monocatenario de sentido positivo que pertenecen al AL Amyloidosis género Enterovirus Enterovirus A genus of the family picornaviridae whose members preferentially inhabit the intestinal tract of a variety of hosts. The genus contains many species. Newly described members of human enteroviruses are assigned continuous numbers with the species designated 'human enterovirus'. Coxsackievirus. La transmisión se da comúnmente a través de la ruta fecal-oral. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes afectados son asintomáticos. Aquellos que son sintomáticos pueden presentar una amplia gama de enfermedades que van desde exantemas e infecciones respiratorias superiores inespecíficas, hasta enfermedades graves y potencialmente mortales como meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis aséptica, encefalitis y miocarditis. El diagnóstico generalmente se realiza de forma clínica, pero la confirmación de laboratorio mediante PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) y cultivo viral puede ser necesaria para pacientes con enfermedad grave. La mayoría de las infecciones son autolimitantes y no requieren tratamiento específico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la envoltura está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son positivos si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios negativos emplean la ARN polimerasa, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
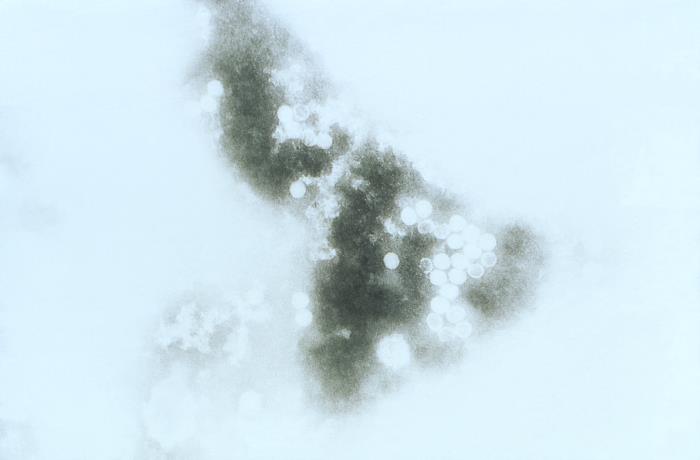

Imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión que muestra la morfología ultraestructural exhibida por los viriones echovirus tipo 6:
La muestra se sedimentó antes de la microscopía, con lo que se concentraron las partículas virales. Las partículas tienen un diámetro de 18–25 nm y contienen un núcleo de ssRNA, que está rodeado por una cápside de proteína desnuda que exhibe una simetría icosaédrica cúbica.
Hay aproximadamente 29 serotipos de Echovirus Echovirus Echoviruses are single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses belonging to the genus Enterovirus. Transmission is most commonly through the fecal-oral route. The majority of patients are asymptomatic. Patients who are symptomatic can exhibit a wide range of illnesses ranging from nonspecific URIs and exanthems to severe and life-threatening illnesses. Echovirus reconocidos:
Los LOS Neisseria humanos son el único reservorio.
Los LOS Neisseria brotes son comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
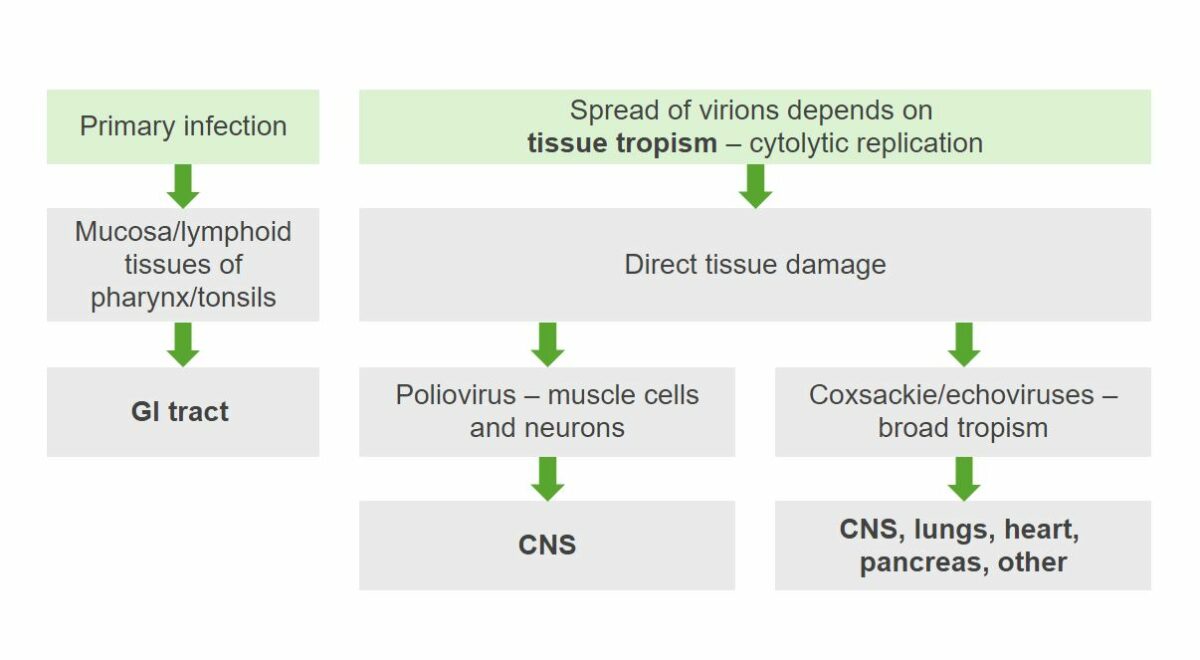
La patogenia de los enterovirus:
Los echovirus entran e infectan inicialmente los tejidos linfoides. Se produce viremia, lo que permite una eventual propagación a otros lugares, como el sistema nervioso central y el corazón.
La mayoría de las infecciones son subclínicas (50%–80% son asintomáticas) y la presentación clínica puede variar de leve a letal.
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden tener síntomas de una infección del tracto respiratorio superior:
Herpangina Herpangina Acute types of coxsackievirus infections or echovirus infections that usually affect children during the summer and are characterized by vesiculoulcerative lesions on the mucous membranes of the throat; dysphagia; vomiting, and fever. Coxsackievirus:
Los LOS Neisseria exantemas pueden ser:
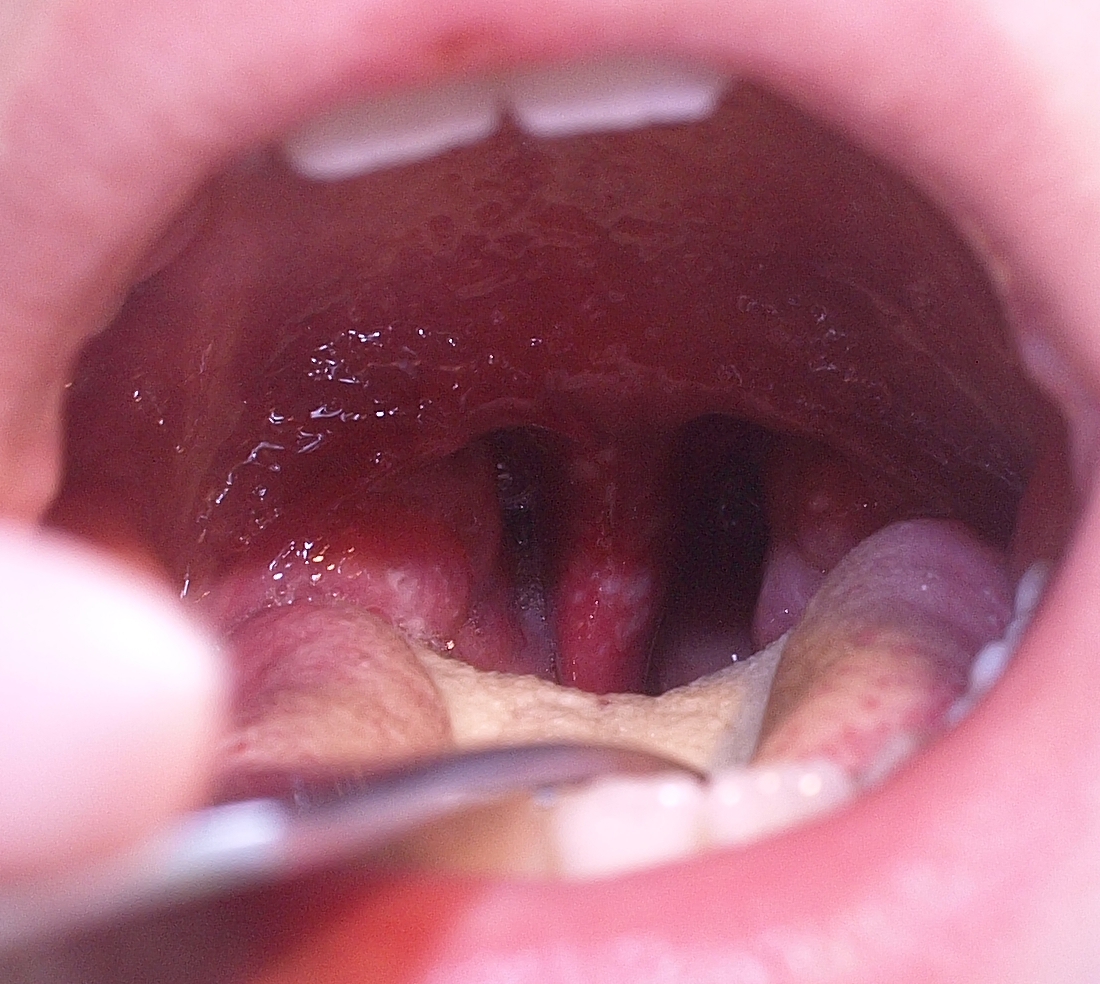
Presentación clínica de herpangina:
Afección más comúnmente asociada con los coxsackievirus del grupo A; sin embargo, también puede estar asociado con una infección por echovirus.

Un exantema viral maculopapular causado por una infección por echovirus tipo 9
Imagen: “This image depicts the right side of a young girl’s face, who was ill because of an Echovirus type-9 infection” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoMeningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis aséptica:
Encefalitis:
Otras manifestaciones neurológicas raras:
La miopericarditis puede ocurrir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una minoría de pacientes.
Los LOS Neisseria recién nacidos pueden presentar una amplia gama de presentaciones, desde leves hasta potencialmente mortales.
Síntomas inespecíficos:
Hepatitis fulminante:
La mayoría de las infecciones se diagnostican según la presentación clínica. Es posible que se necesite un diagnóstico de laboratorio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum infecciones graves.
La mayoría de las infecciones por echovirus Echovirus Echoviruses are single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses belonging to the genus Enterovirus. Transmission is most commonly through the fecal-oral route. The majority of patients are asymptomatic. Patients who are symptomatic can exhibit a wide range of illnesses ranging from nonspecific URIs and exanthems to severe and life-threatening illnesses. Echovirus son autolimitantes y el tratamiento es en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida de soporte. Opciones terapéuticas no comprobadas que se pueden considerar para pacientes con enfermedades graves o inmunocomprometidos pueden incluir:
| Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology | Coxsackievirus Coxsackievirus Coxsackievirus is a member of a family of viruses called Picornaviridae and the genus Enterovirus. Coxsackieviruses are single-stranded, positive-sense RNA viruses, and are divided into coxsackie group A and B viruses. Both groups of viruses cause upper respiratory infections, rashes, aseptic meningitis, or encephalitis. Coxsackievirus | Poliovirus Poliovirus Poliomyelitis is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. This virus is a member of the Picornaviridae family. It is a small, single-stranded, positive-sense RNA virus without a lipid envelope. Transmission occurs through the fecal-oral route and, occasionally, through respiratory aerosols. Poliovirus/Poliomyelitis | Echovirus Echovirus Echoviruses are single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses belonging to the genus Enterovirus. Transmission is most commonly through the fecal-oral route. The majority of patients are asymptomatic. Patients who are symptomatic can exhibit a wide range of illnesses ranging from nonspecific URIs and exanthems to severe and life-threatening illnesses. Echovirus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Características |
|
|
|
| Transmisión |
|
|
|
| Clínico |
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
| Tratamiento | De soporte | De soporte | De soporte |
| Prevención | Lavado de manos | Vacunación | Lavado de manos |