La obstrucción del intestino delgado es una interrupción del flujo del contenido intraluminal a través del intestino delgado, y se clasifica como mecánica (debida a un bloqueo físico) o funcional (debida a la alteración de la motilidad normal). La causa más común de obstrucción del intestino delgado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria países occidentales son las adherencias postoperatorias. La obstrucción del intestino delgado se presenta típicamente con náuseas, vómitos, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, distensión, estreñimiento y/u obstrucción. El diagnóstico se establece mediante imagenología. Hasta el 80% de los LOS Neisseria casos se resuelven con un tratamiento de soporte (reposo intestinal, hidratación intravenosa y descompresión nasogástrica). Sin embargo, la cirugía es necesaria para los LOS Neisseria casos persistentes o complicados.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La obstrucción del intestino delgado es la interrupción del flujo del contenido intraluminal a través del intestino delgado (duodeno, yeyuno o íleon).
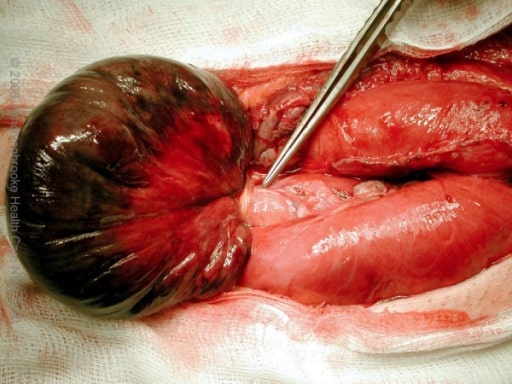
Intestino delgado gangrenoso con obstrucción en asa cerrada causada por una adherencia de banda omental
Imagen: “Intra-operative photograph” por the Department of Surgery, Hinchingbrooke Hospital, Hinchingbrooke Healthcare NHS Trust, Huntingdon, Cambridgeshire, UK. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.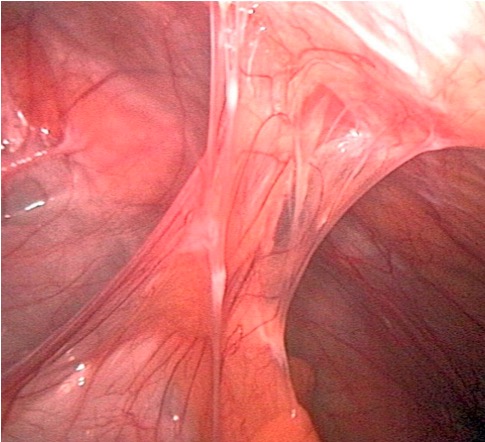
Las adherencias que pueden desarrollarse en el postoperatorio son la causa más común de obstrucción intestinal.
Imagen de Kevin Pei, PD.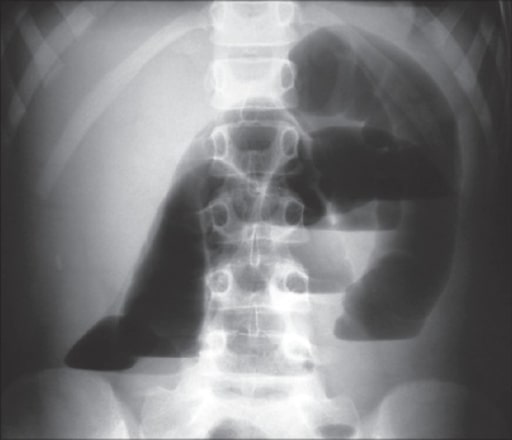
X-ray showing intestinal loops with air-fluid levels consistent with SBO
Image: “X-ray” by the Department of Surgery, University Hospital of Ioannina, Greece. License: CC BY 2.0.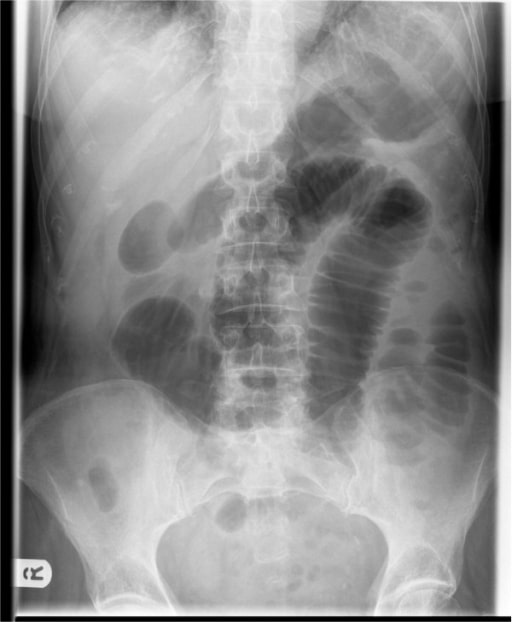
Abdominal X-ray showing dilated small bowel loops consistent with SBO
Image: “Abdominal X-ray” by the Department of General Surgery, Sunderland Royal Hospital, Kayll Road, Sunderland SR4 7TP, UK. License: CC BY 2.0.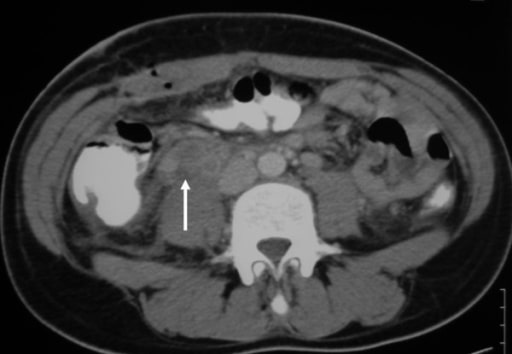
A CT scan showing the transition zone (arrow) with proximal bowel dilation and distal bowel decompression
Image: “Abdominal CT Scan” by the 2nd Department of Surgery, Athens University School of Medicine, Aretaieion Hospital, Athens, Greece. License: CC BY 2.0.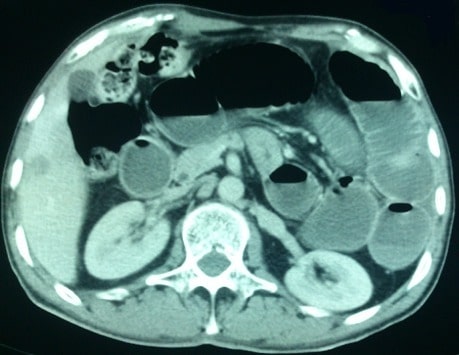
A CT scan showing a hernia causing a small obstruction with air-fluid levels
Image: “Abdominal CT scan” by the Service des Urgences Chirurgicales Viscérales, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Ibn Rochd, Casablanca, Morocco. License: CC BY 2.0.