La neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia congénita severa afecta la mielopoyesis y tiene muchos subtipos diferentes. La neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia congénita severa se manifiesta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la infancia con infecciones bacterianas que amenazan la vida. El tratamiento que ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia demostrado ser efectivo es la administración de factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos, que eleva el recuento disminuido de neutrófilos. La enfermedad de Kostmann (SCN3) tiene un patrón de herencia autosómico recesivo, mientras que el subtipo más común, SCN1, tiene herencia autosómica dominante.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 50%–60% de los LOS Neisseria casos, la neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia congénita severa se debe a una mutación autosómica dominante del gen ELANE. Sin embargo, la mutación inicial descrita por Kostmann estaba en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum HAX1, que se hereda con un patrón autosómico recesivo. La herencia recesiva ligada al AL Amyloidosis cromosoma X se debe a mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la proteína del gen (WASP) del síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich.
La siguiente tabla resume cada subtipo de neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia congénita severa, los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure involucrados y su función, así como su modo de herencia.
| Tipo | Gen mutado | Proteína afectada | Modo de herencia |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCN1 | ELANE (19p13.3) | Elastasa de neutrófilos (la mutación conduce a una proteína mal plegada, lo que conduce a un aumento de la apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage) | AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives |
| SCN2 | GFI1 (1p22.1) | Represor de los LOS Neisseria procesos transcripcionales (la mutación conduce a la pérdida de la represión) | AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives |
| SCN3 | HAX1 (1q21.3) | Proteína X-1 asociada a HCLS1 (funciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el control de la apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage) | AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation |
| SCN4 | G6PC3 (17q21.31) | G6Pasa: la mutación conduce a la abolición de la actividad enzimática, a la glicosilación anómala y al AL Amyloidosis aumento de la apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage de las células mieloides | AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation |
| SCN5 | VPS45 (1q21.2) | Proteína mediada por vesículas (controla el tráfico vesicular) | AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation |
| SCNX | WAS (Xp11.23): implicado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich | WASP: regulador del citoesqueleto de actina (la mutación es una mutación de ganancia de función que conduce a la pérdida de la autoinhibición) | Recesivo ligado al AL Amyloidosis X |
La neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia puede surgir de cualquiera de 3 vías patogénicas:
Hereditaria:
Adquirida:
Autoinmune:
Infecciosa:
Mixta: neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia crónica benigna
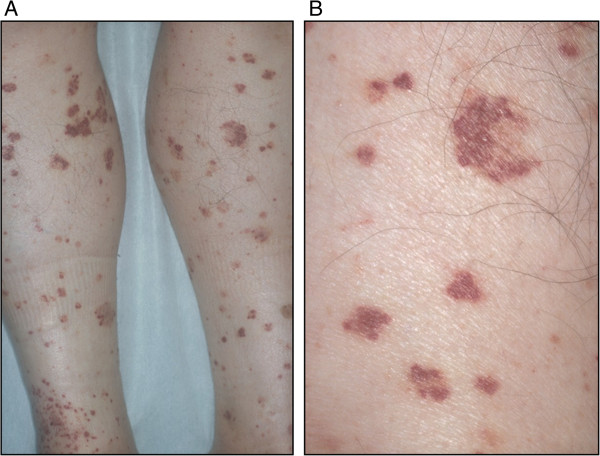
Las hemorragias petequiales son una de las diversas presentaciones clínicas en la neutropenia congénita severa
Imagen: “Purpura” por Oshikata C, Tsurikisawa N, Takigawa M, Omori T, Sugano S, Tsuburai T, Mitomi H, Takemura T, Akiyama K. Licencia: CC BY 2.0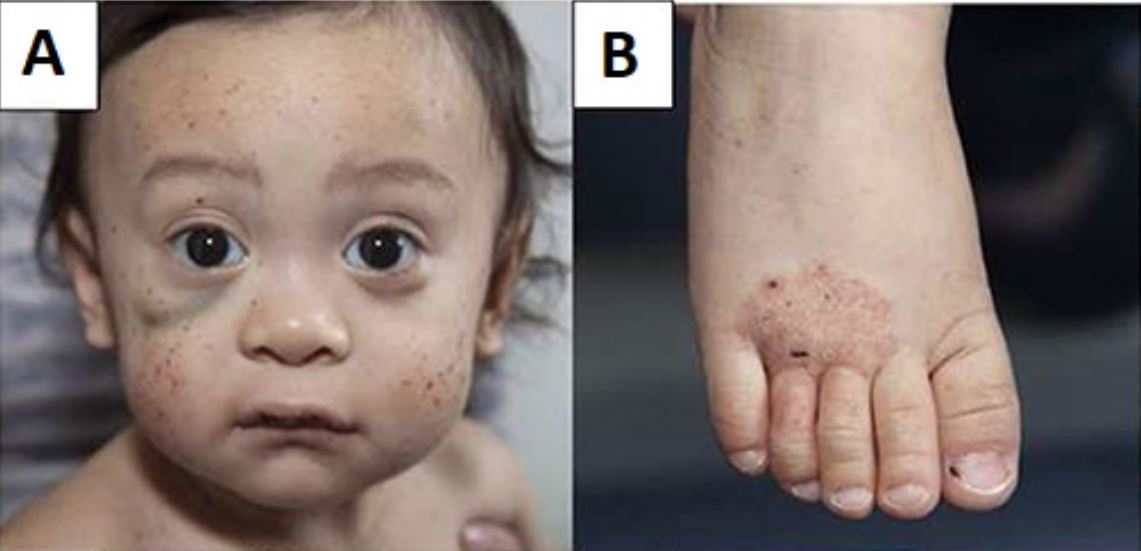
Niño pequeño con síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich que presenta múltiples petequias faciales y un hematoma debajo del ojo derecho (A) y eczema del pie (B)
Imagen: “Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome petechiae, hematoma and eczema” por Michael H. Albert and Alexandra F. Freeman. Licencia: CC BY 4.0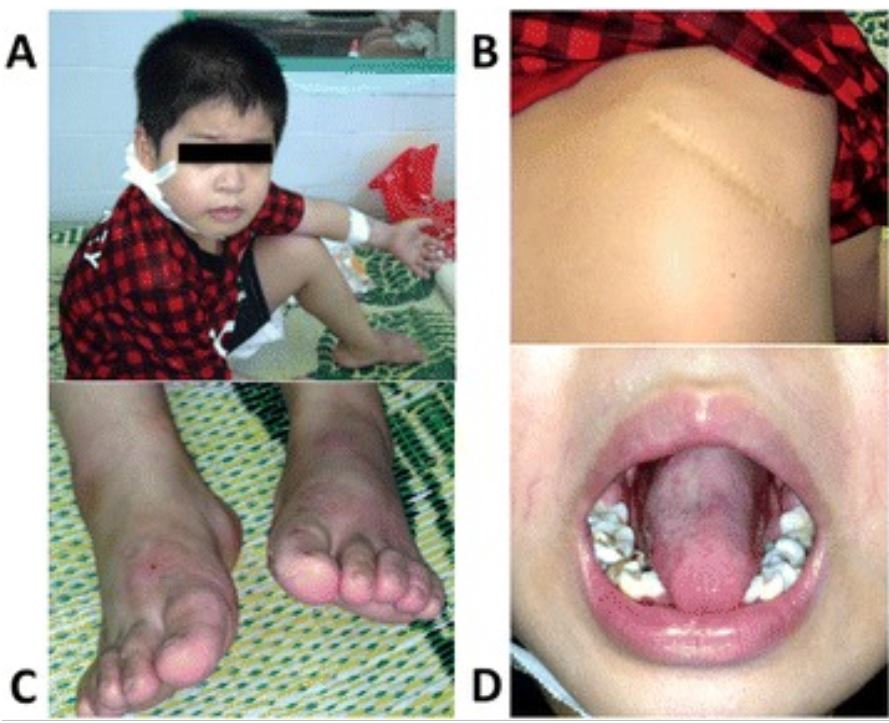
Neutropenia congénita severa causada por la mutación del gen ELANE. Las imágenes muestran una serie de lesiones causadas por una infección.
A: Absceso cutáneo detrás de la oreja derecha
B: Neumonía severa que requirió lobectomía pulmonar
C: Infección por hongos
D: Úlcera bucal
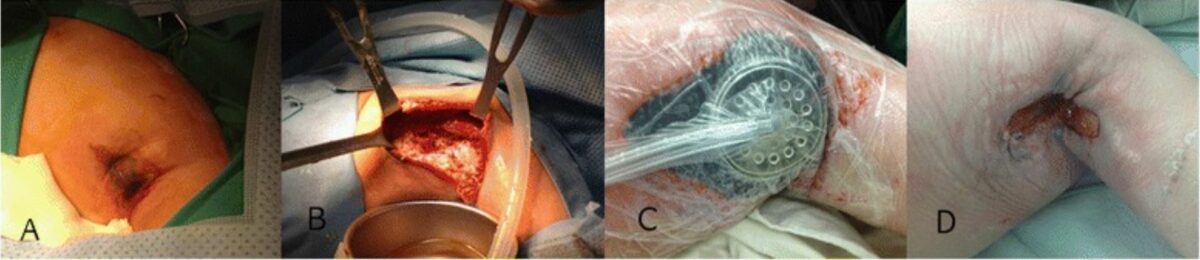
La neutropenia cíclica con una nueva mutación genética se presenta con una infección necrosante de tejidos blandos y sepsis severa. Tratamiento exitoso de la herida axilar:
A: La lesión inicial en la axila comprendía piel hinchada y edematosa con un cambio azulado en el centro.
B: Obsérvese la necrosis masiva del área subcutánea, los músculos y la fascia con secreción contaminada encontrada en la cirugía inicial.
C: Vista después de la terapia de heridas con presión negativa
D: Después de 1 mes, el tejido de granulación creció rápidamente para permitir la reparación primaria.

Cómo calcular el recuento absoluto de neutrófilos con ejemplo
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0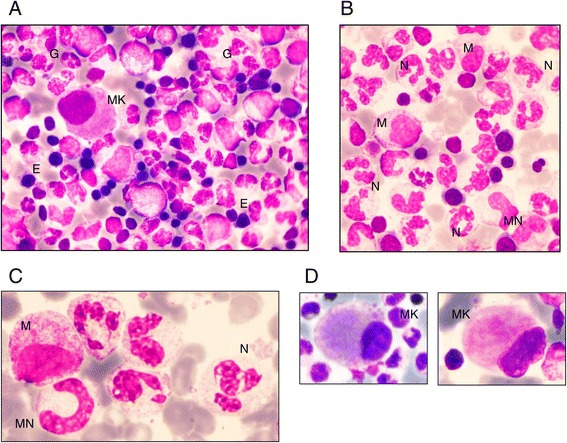
Morfología de la médula ósea en pacientes con neutropenia congénita G6PC3:
A: Morfología típica de la médula ósea global: rica celularidad con granulopoyesis predominante (G), algunos eritroblastos (E) y 1 micromegacariocito (MK)
B: Granulopoyesis predominante con algunos mielocitos (M), muy pocos metamielocitos (MN) y un alto número de neutrófilos maduros (N)
C: Detalles de los neutrófilos: apariencia hipersegmentada con una abertura delgada entre los lóbulos y acúmulos de cromatina
D: Ejemplos de micromegacariocitos
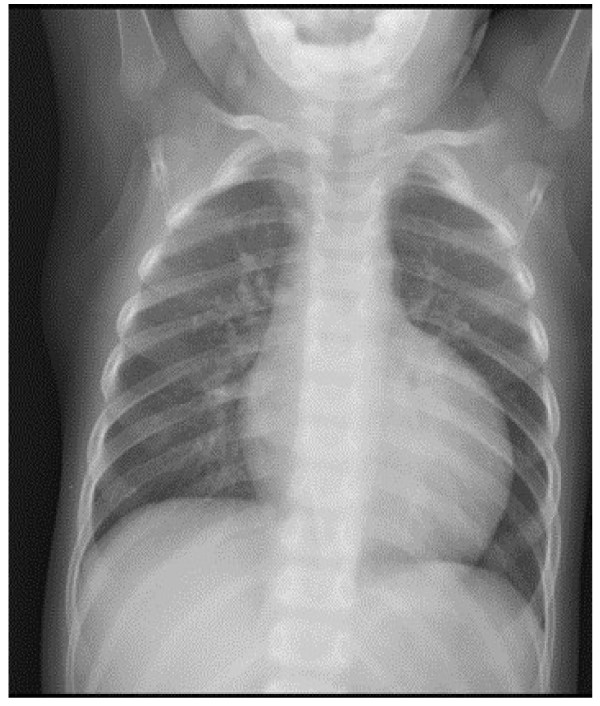
Radiografía de tórax que muestra cardiomegalia severa en un paciente masculino con neutropenia y retraso en el crecimiento
Imagen: “Cardiomyopathy in a male patient with neutropenia and growth delay” por Folsi, V., et al.. Licencia: CC BY 4.0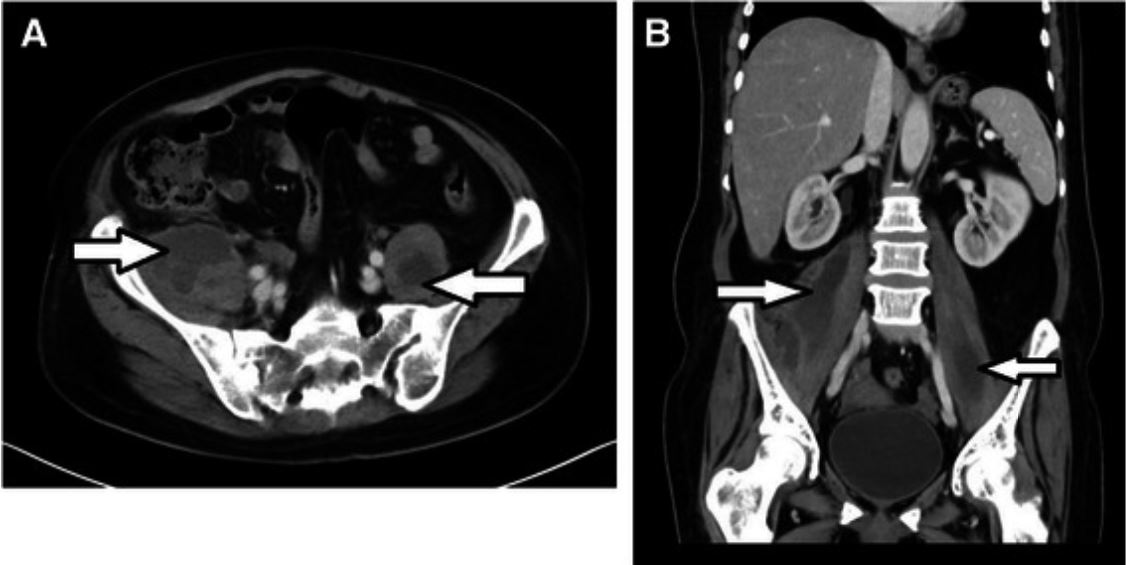
Abscesos primarios de psoas bilaterales por Staphylococcus aureus resistente a meticilina en un paciente neutropénico. TC de abdomen y pelvis con contraste intravenoso, axial (A) y coronal (B), que muestra abscesos bilaterales del músculo psoas (flechas)
Imagen: “Bilateral primary psoas abscesses due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a neutropenic patient: a case report” por Bakri FG, Hadidy AM, Hadidi F, Ryalat N, Saket L, Shurbasi N, Melhem J. Licencia: CC BY 4.0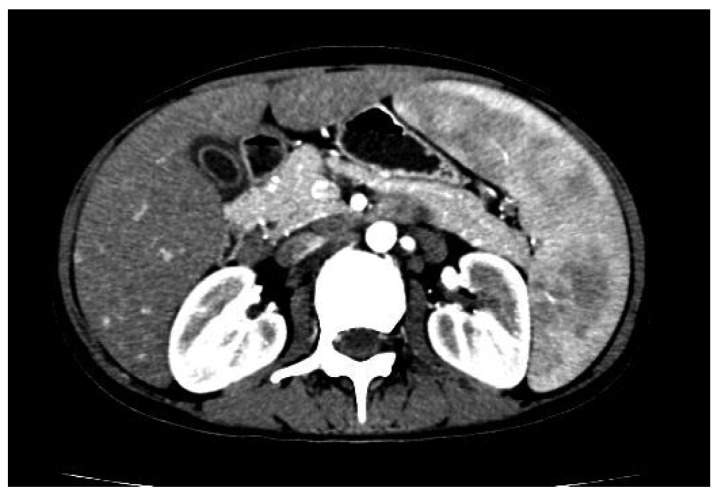
El síndrome de Felty es una subcategoría específica de la artritis reumatoide caracterizada por la tríada de artritis reumatoide, enfermedad extraarticular severa y neutropenia inexplicable.
La imagen muestra una TC abdominal de un paciente con síndrome de Felty que muestra esplenomegalia con atenuación heterogénea debido a la sincronización del contraste angiográfico y múltiples ganglios linfáticos agrandados distribuidos a lo largo del espacio retroperitoneal, la bolsa omental, la raíz del mesenterio y el hilio hepático circundante.
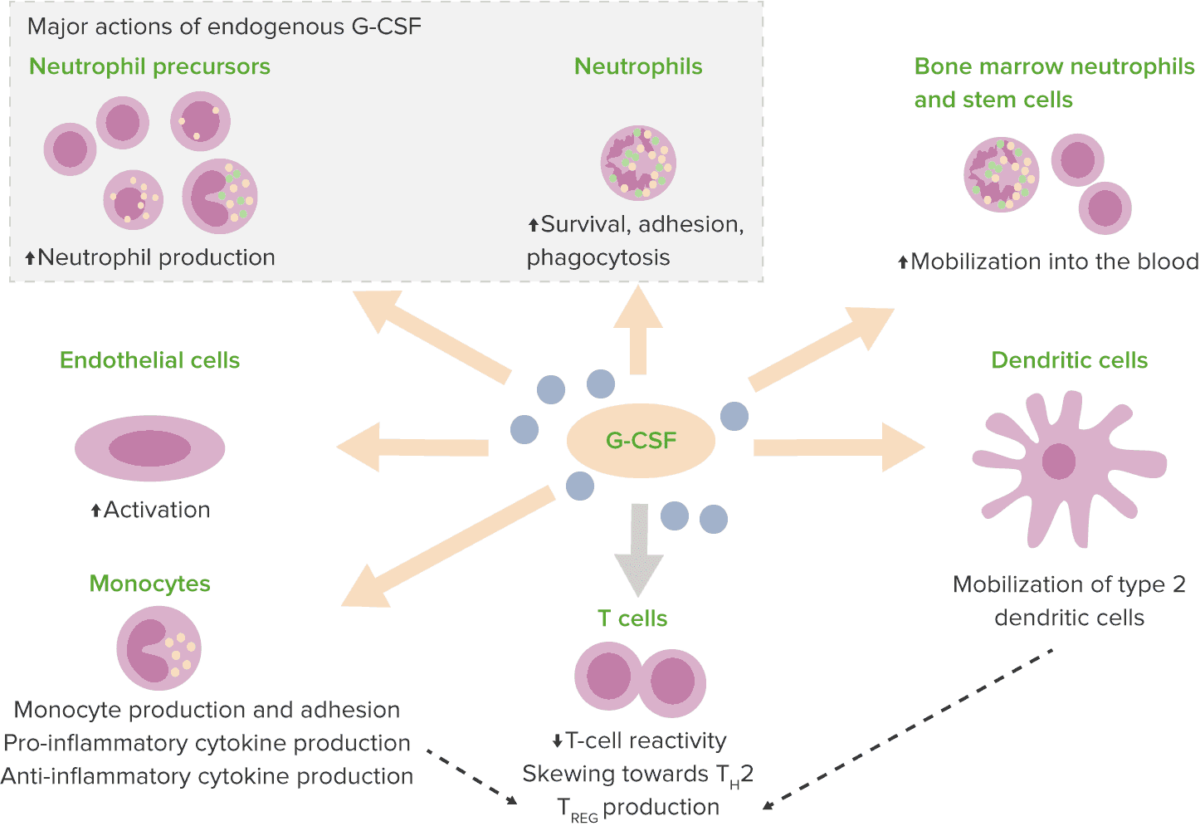
Efectos del factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos (G-CSF)
Th2: linfocito T colaborador tipo 2
TREG: linfocitos T reguladores