La leucemia/linfoma linfoblástico agudo son neoplasias malignas hematológicas caracterizadas por la proliferación descontrolada de células precursoras linfoides. La leucemia/linfoma linfoblástico agudo, son las formas más comunes de cáncer que afectan a los LOS Neisseria niños, muestran la presencia de un aumento de linfoblastos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la leucemia/linfoma linfoblástico agudo, los LOS Neisseria linfoblastos reemplazan la médula ósea normal, eventualmente ingresan a la circulación e infiltran otros órganos. La presentación clínica incluye fatiga, hemorragia, fiebre e infecciones, todas ellas relacionadas con anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, trombocitopenia y falta de leucocitos funcionales. La aparición de los LOS Neisseria síntomas tardan días o semanas. Los LOS Neisseria efectos de masa de la infiltración maligna ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum hueso, hígado, bazo) son comunes; por tanto, se observan hepatoesplenomegalia y linfadenopatía. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante frotis de sangre periférica y biopsia de médula ósea, que muestran la presencia de linfoblastos. Los LOS Neisseria estudios de inmunofenotipificación, histoquímica y genética ayudan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la clasificación y orientación del tratamiento. El tratamiento es principalmente por quimioterapia, la cual se administra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fases (inducción, consolidación y mantenimiento). El pronóstico varía según la edad de aparición y el tipo de leucemia. La tasa de curación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños es del 85%.
Last updated: Apr 14, 2022
La leucemia/linfoma linfoblástico agudo son neoplasias malignas hematológicas caracterizadas por la proliferación patológica de células precursoras linfoides (principalmente
los
LOS
Neisseria linajes de células B y T)
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea, con el desplazamiento posterior de otros precursores de células sanguíneas.
Sistema de la World Health Organization (WHO) 2016 (reemplaza la clasificación franco-estadounidense-británica):
La hematopoyesis comienza con una célula madre hematopoyética, que se incita a dividirse y diferenciarse con estímulos químicos apropiados (factores de crecimiento hematopoyéticos).
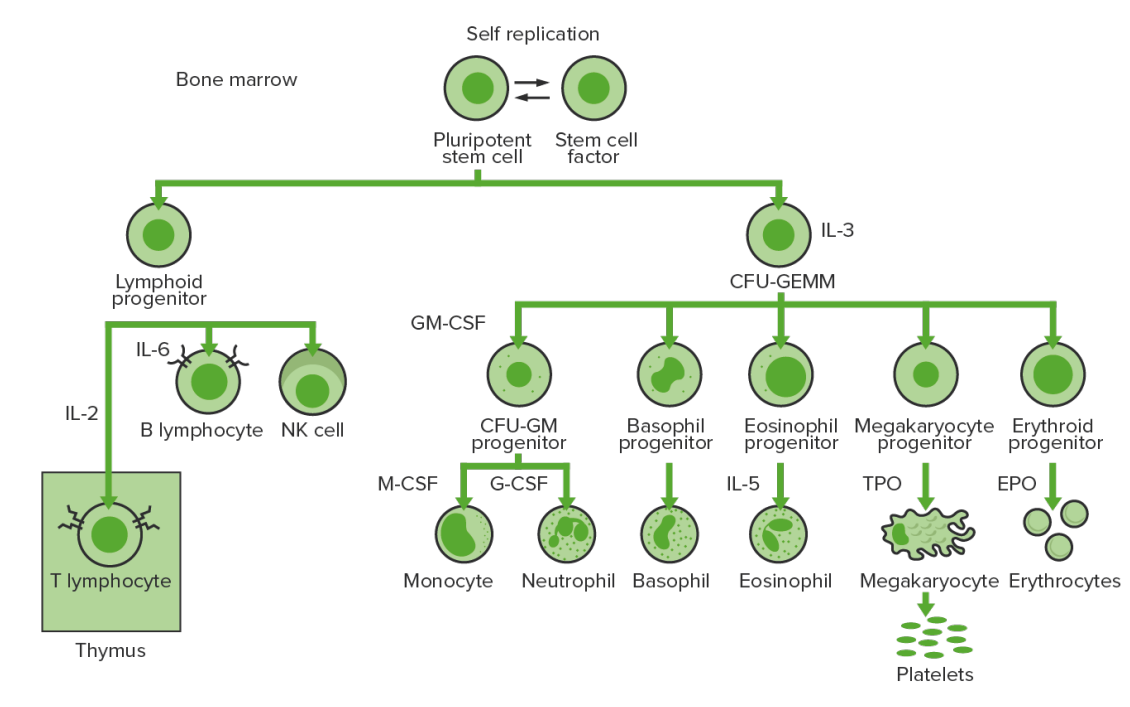
Hematopoyesis de la médula ósea:
Proliferación y diferenciación de los elementos formes de la sangre:
En la leucemia mieloide crónica, existe una proliferación sostenida de células en la línea granulocítica (mieloblastos → neutrófilos, basófilos, eosinófilos). Se ven tanto células en proceso de maduración como céulas maduras; por lo tanto, hay células que son solo parcialmente efectivas.
CFU-GEMM: unidad formadora de colonias de granulocitos, eritrocitos, monocitos, megacariocitos
CFU-GM: unidad formadora de colonias de macrófagos y granulocitos
GM-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
M-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de macrófagos
G-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos
NK: células asesinas naturales
TPO: trombopoyetina
| Características | Leucemia linfoblástica aguda | Leucemia mieloide aguda |
|---|---|---|
| Población | Más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños | Más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos |
| Características comunes |
|
|
| Hallazgos clínicos |
|
|
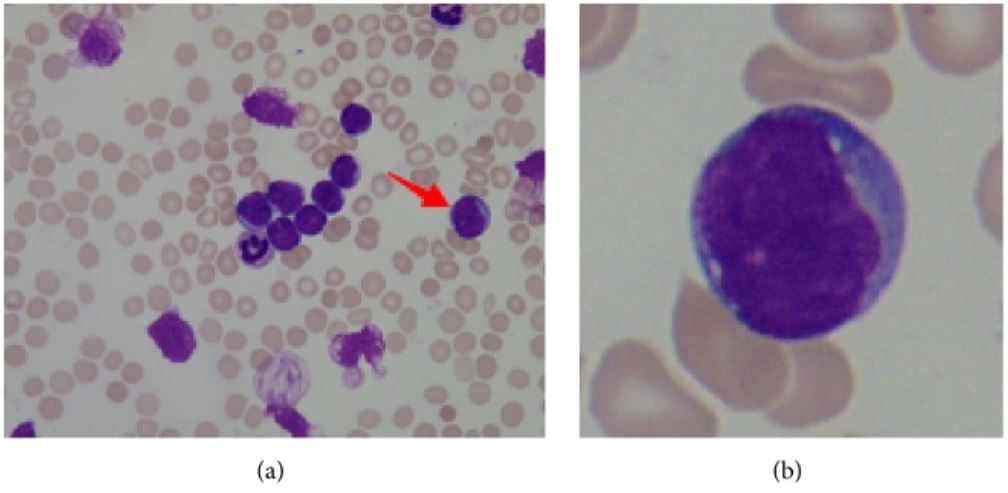
a: frotis de médula ósea de un paciente con leucemia linfoblástica aguda, flecha que apunta a linfoblasto
b: linfoblasto: núcleo grande, citoplasma escaso
| Características | Leucemia linfoblástica aguda | Leucemia mieloide aguda |
|---|---|---|
| Hallazgos de laboratorio | Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, trombocitopenia, variación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria leucocitos | |
| Frotis periférico o examen de médula ósea (morfología) | Linfoblastos:
|
Mieloblastos:
|
| Citoquímica |
|
|
| Inmunofenotipificación |
|
CD13, CD33, CD117, HLA-DR |
La quimioterapia, que puede durar de 2–3 años, es muy eficaz en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes jóvenes.
| Tratamiento | Leucemia linfoblástica aguda | Leucemia mieloide aguda |
|---|---|---|
| Inducción |
|
|
| Consolidación | Opciones:
|
Quimioterapia adicional (citarabina) |
| Mantenimiento |
|
Quimioterapia no mielosupresora y/o agente dirigido |
| Tratamiento adicional |
|
Leucemia promielocítica aguda:
|
| Trasplante de células hematopoyéticas | Para pacientes con mal pronóstico | |
| Pronóstico |
|
|