La isquemia mesentérica es una afección poco frecuente y potencialmente mortal causada por un flujo sanguíneo inadecuado a través de los LOS Neisseria vasos mesentéricos, que provoca isquemia y necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage de la pared intestinal. La isquemia mesentérica puede ser aguda o crónica. La isquemia mesentérica aguda puede estar causada por embolia arterial, trombosis, enfermedad no oclusiva o trombosis venosa. La isquemia mesentérica crónica suele estar causada por una enfermedad aterosclerótica. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan un dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal desproporcionado con respecto a la exploración abdominal. La peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury, la sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock y la hematoquecia son indicios de infarto intestinal. La tomografía computarizada (TC) con angiografía del abdomen y la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 "hip" bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy es la modalidad diagnóstica de elección. El tratamiento suele ser quirúrgico y se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum restablecer el flujo sanguíneo intestinal, así como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la resección de cualquier intestino no viable.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La isquemia mesentérica es una afección causada por la hipoperfusión del intestino, que provoca isquemia y necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage. La isquemia mesentérica se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la evolución:
Los LOS Neisseria principales vasos afectados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la isquemia mesentérica son:
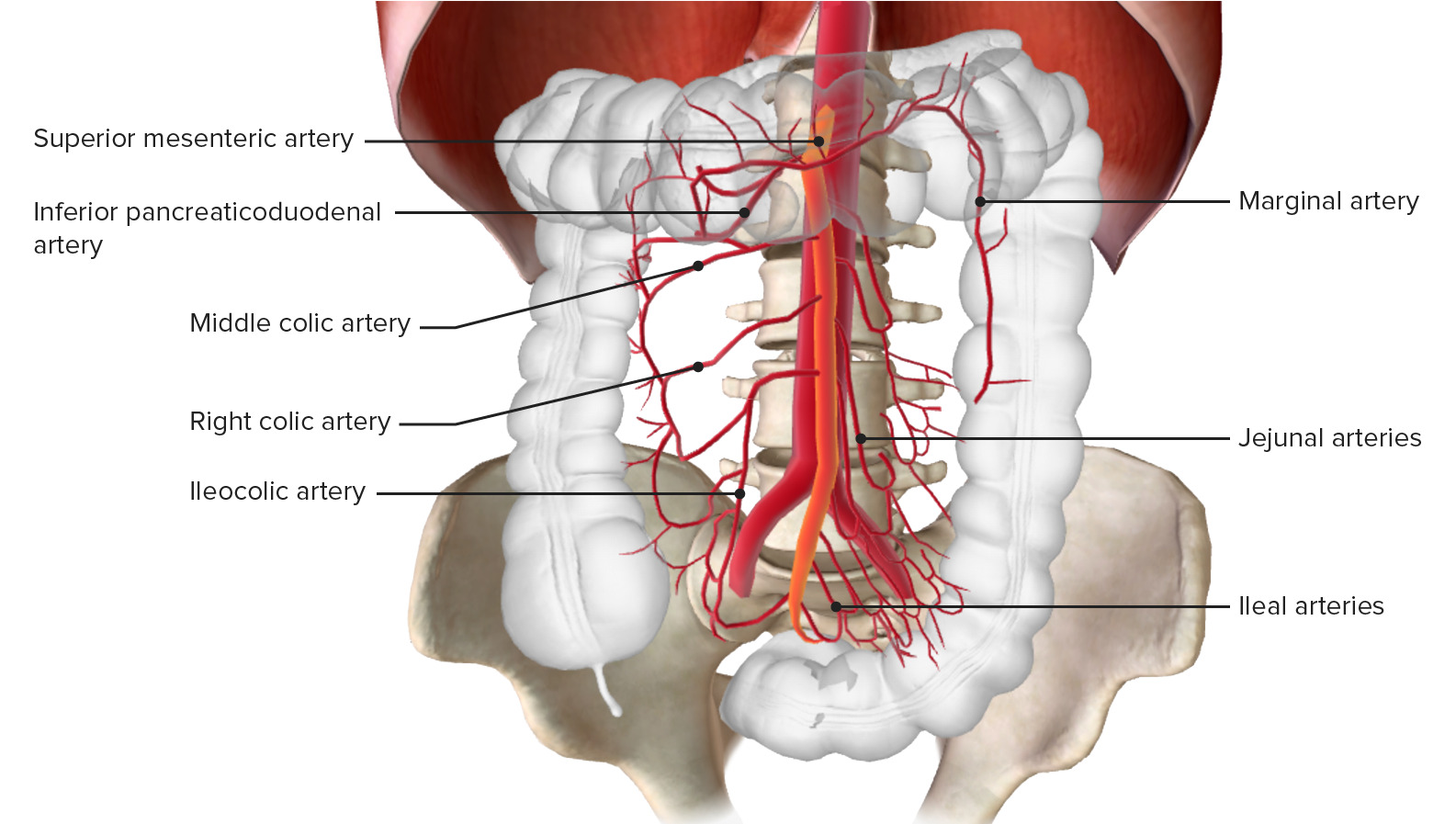
Irrigación sanguínea del colon a través de la arteria mesentérica inferior
Imagen por BioDigital, editeda por Lecturio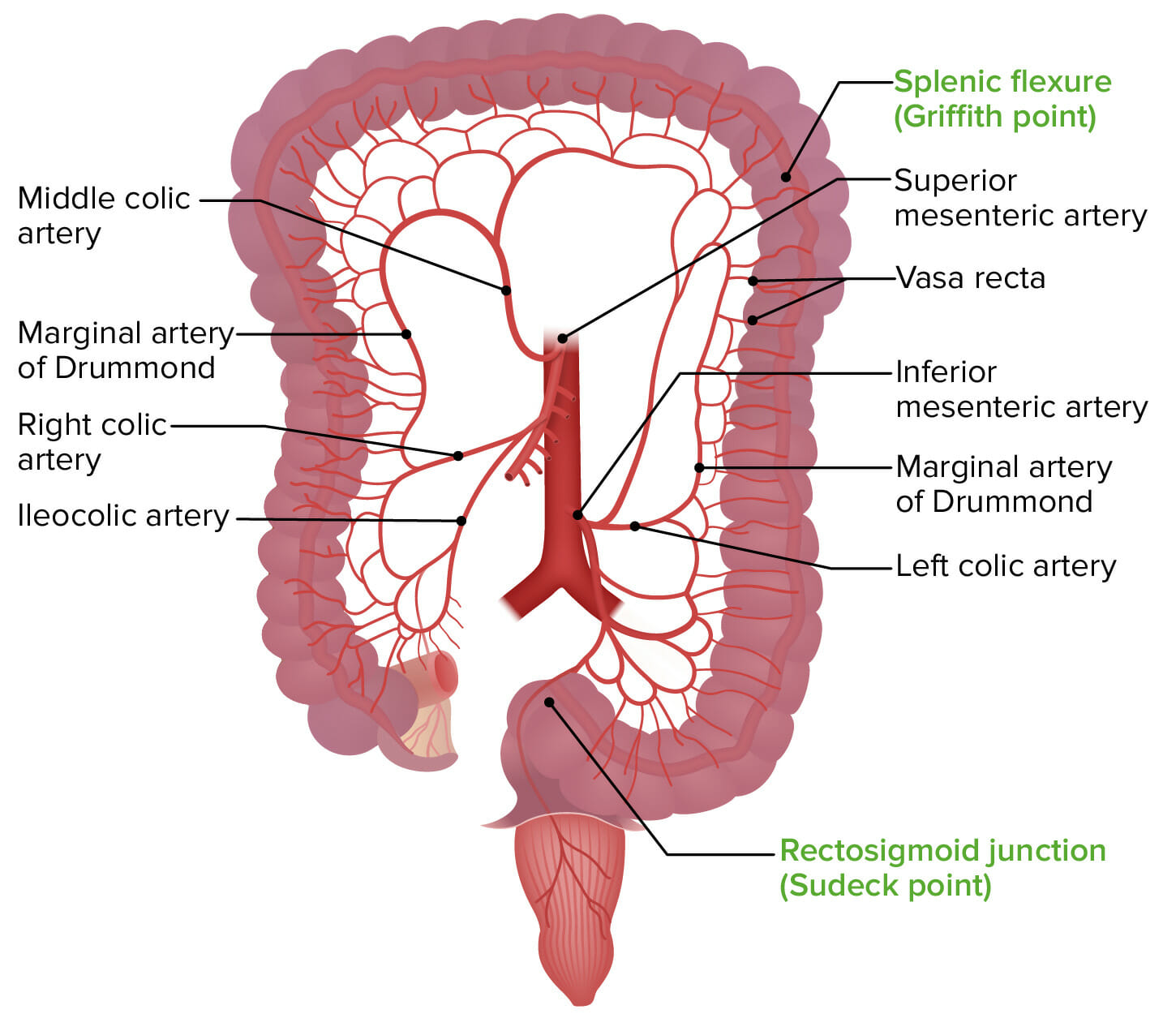
Ilustración que muestra el punto Griffith y el punto Sudeck, las zonas más vulnerables a la isquemia mesentérica
Imagen por Lecturio.La isquemia mesentérica aguda requiere un alto índice de sospecha para permitir un diagnóstico oportuno.
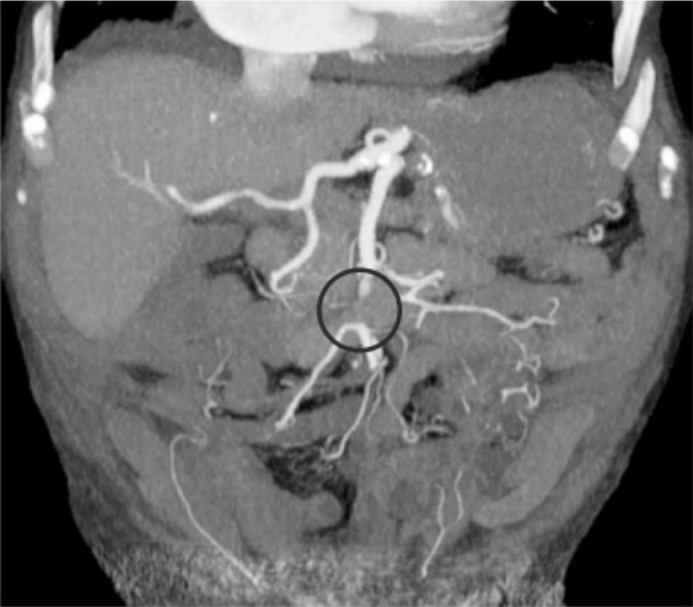
Angiografía por tomografía computarizada (TC) en la isquemia mesentérica aguda: El círculo indica una embolia oclusiva de la porción media de la arteria mesentérica superior.
Imagen: “Coronal MIP reconstructions of CTA” por Association of Radiology & Oncology. Licencia: CC BY 3.0, editada por Lecturio.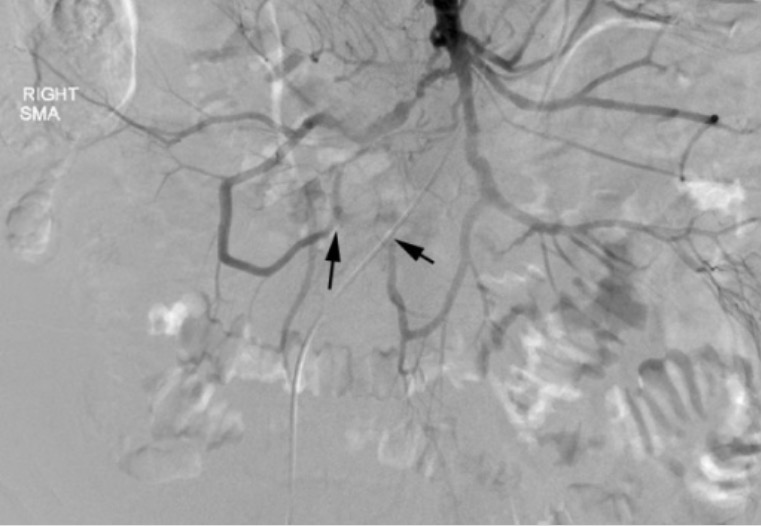
Hallazgos del angiograma mesentérico en la isquemia mesentérica aguda:
La canulación de la arteria mesentérica superior, mostrada aquí, revela una estenosis severa u oclusión de múltiples ramas de la arteria mesentérica superior (flechas negras).
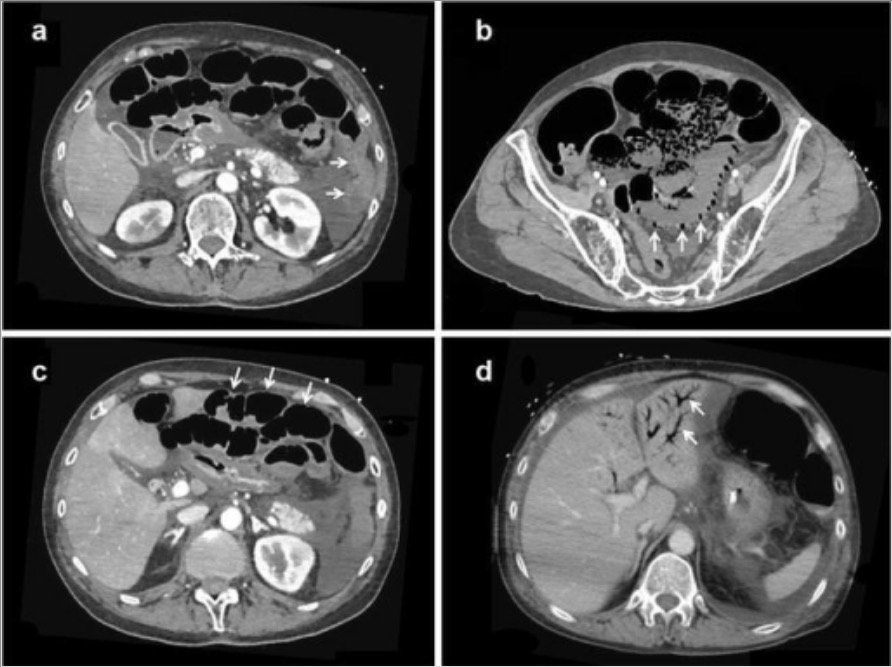
Angiografía por tomografía computarizada (TC) de la isquemia mesentérica no oclusiva:
a: La ausencia de realce de la pared intestinal inducido por el contraste (flechas) b: Neumatosis intestinal y ausencia de realce de la pared intestinal inducido por contraste (flechas) c: Dilatación del intestino y ausencia de realce de la pared intestinal inducido por contraste (flechas) d: Gas venoso portal (flechas)
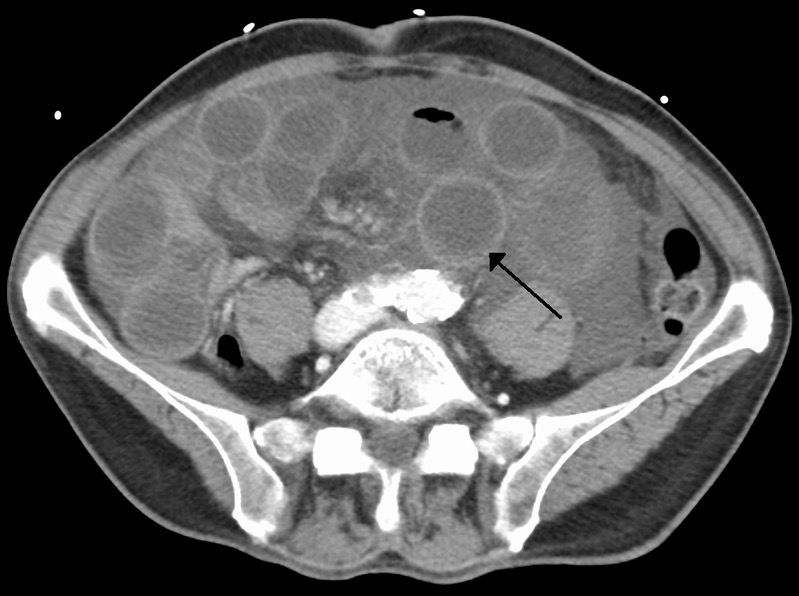
Imagen de tomografía computarizada (TC) del intestino isquémico debido a la trombosis de la vena mesentérica superior:
Obsérvese el intestino dilatado con una pared intestinal engrosada.
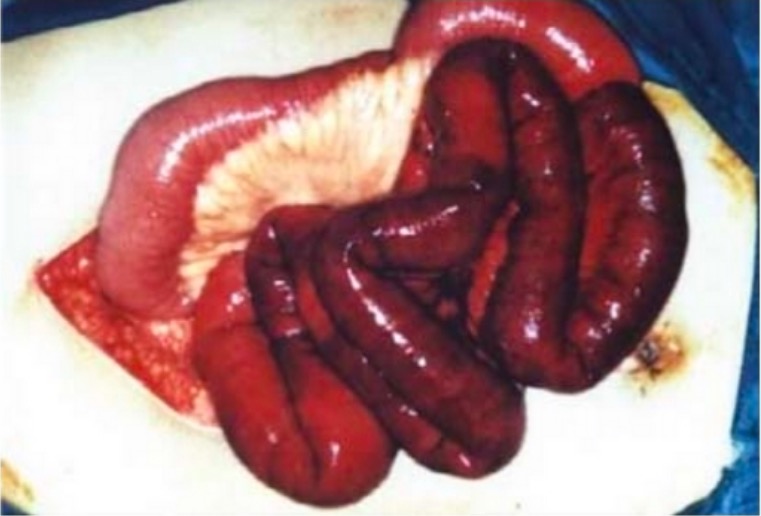
Hallazgos quirúrgicos en la isquemia mesentérica:
Imagen del intestino delgado eviscerado durante una laparotomía exploratoria con el intestino sano de color rosa en la parte superior izquierda y el intestino oscuro, oscuro e isquémico en la parte inferior derecha
La isquemia mesentérica crónica está causada por una estenosis progresiva de las arterias ≥ 2, lo que da lugar a episodios de desajuste de la oferta y la demanda de flujo sanguíneo (normalmente después de comer).
La imagenología vascular se utiliza para hacer el diagnóstico.