La isquemia intestinal se produce cuando la perfusión no satisface las demandas de los LOS Neisseria intestinos, lo que provoca una lesión tisular isquémica que puede poner en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum peligro la vida si se produce una necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage intestinal y/o una perforación. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas pueden ir desde una indigestión o diarrea leve hasta un dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal intenso. Para detectar la estenosis o la oclusión se utilizan técnicas de imagen como la tomografía computarizada (TC) y la angiografía. La forma crónica de isquemia intestinal se beneficia de terapias médicas y procedimientos de revascularización (stents, cirugía de derivación gástrica), mientras que las formas agudas requieren intervenciones urgentes para restablecer el flujo sanguíneo y eliminar cualquier tejido intestinal muerto. El retraso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico y el tratamiento de la isquemia intestinal aguda da lugar a una elevada mortalidad y a complicaciones graves, como la perforación intestinal y la sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La isquemia intestinal es una disminución del flujo sanguíneo a los LOS Neisseria intestinos que da lugar a una hipoperfusión que puede provocar un infarto intestinal. La descamación de la mucosa se produce después de aproximadamente 3 horas de isquemia, y la necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage se produce después de aproximadamente 6–12 horas de isquemia.
Para todos los LOS Neisseria tipos, la isquemia intestinal afecta principalmente a los LOS Neisseria adultos de más de 60 años.
Ya sea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el intestino delgado, la isquemia intestinal aguda es el resultado de la reducción del flujo sanguíneo. Las causas incluyen:
Obstrucción del vaso debido a:
La isquemia mesentérica no oclusiva (20%–30%) puede deberse a:
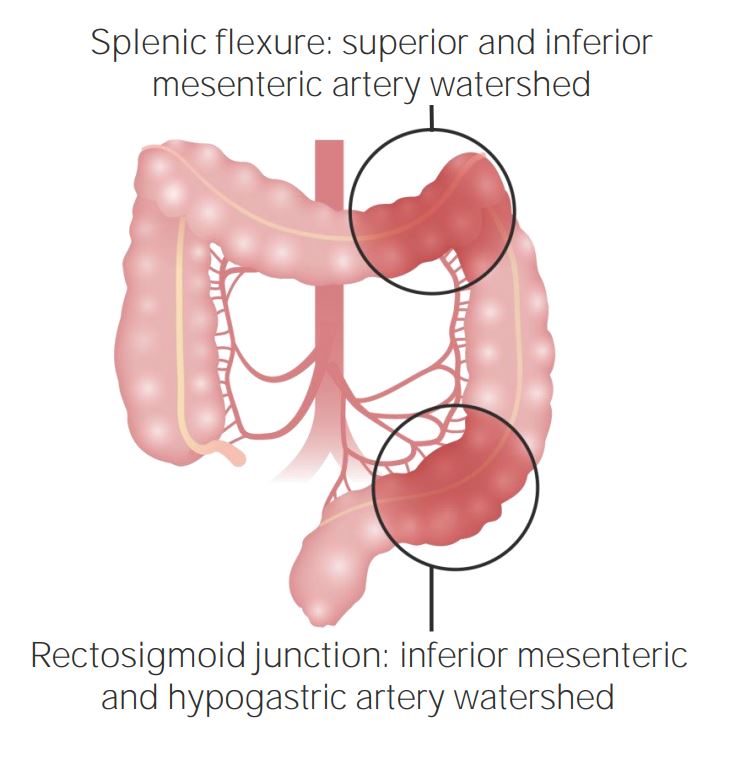
Áreas de flexión del colon
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con evidencia de infarto intestinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el examen deben tener una consulta quirúrgica urgente. Si el paciente está lo suficientemente estable, se debe realizar imagenología.
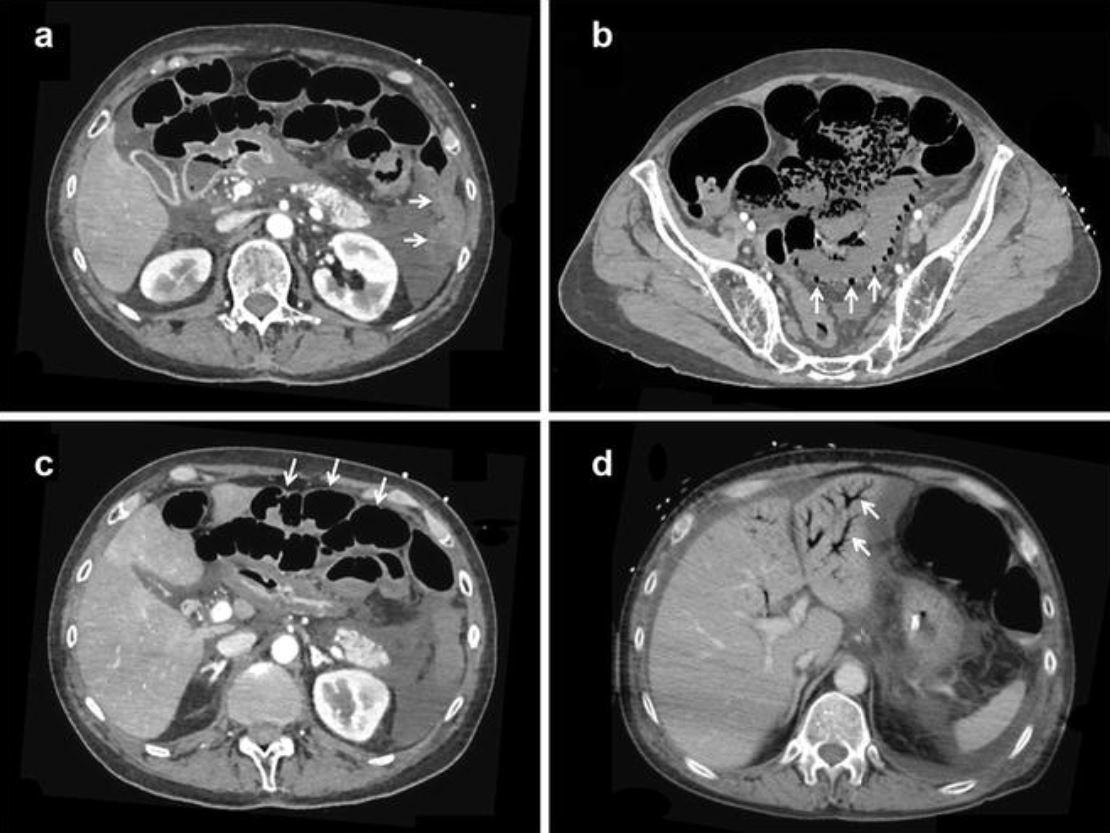
Hallazgos representativos de la tomografía computarizada de la isquemia mesentérica no oclusiva:
a: ausencia de realce de la pared intestinal inducido por contraste (flechas)
b: neumatosis intestinal y ausencia de realce de la pared intestinal inducido por contraste (flechas)
c: dilatación del intestino y ausencia de realce de la pared intestinal inducido por contraste (flechas)
d: gas en la vena porta (flechas)
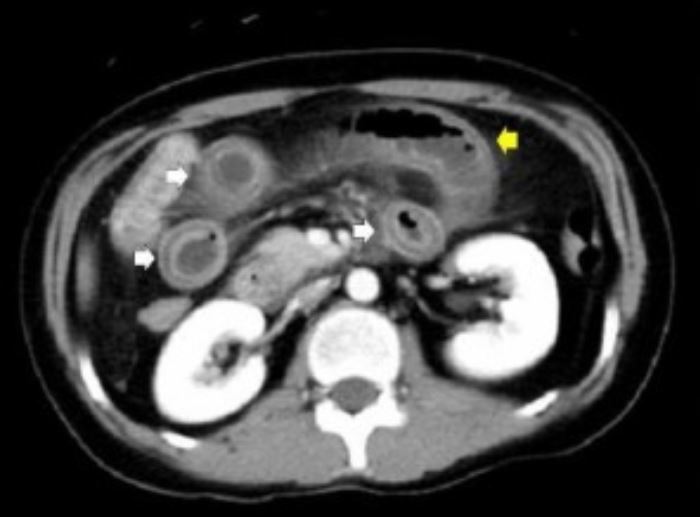
Tomografía computarizada del abdomen:
La imagen muestra distensión del intestino (flecha amarilla), engrosamiento difuso de la pared intestinal, realce anormal de la pared intestinal (signo del doble halo, o diana; flechas blancas).
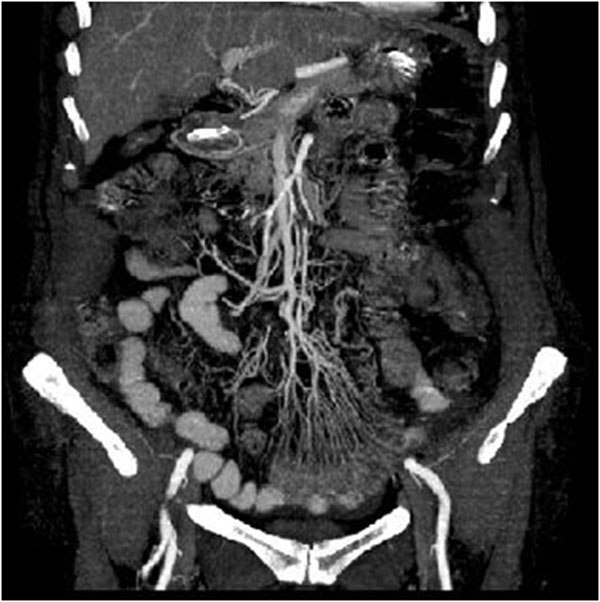
Isquemia arterial mesentérica aguda en una reconstrucción bidimensional del plano coronal de tomografía computarizada multidetector con contraste en fase temprana:
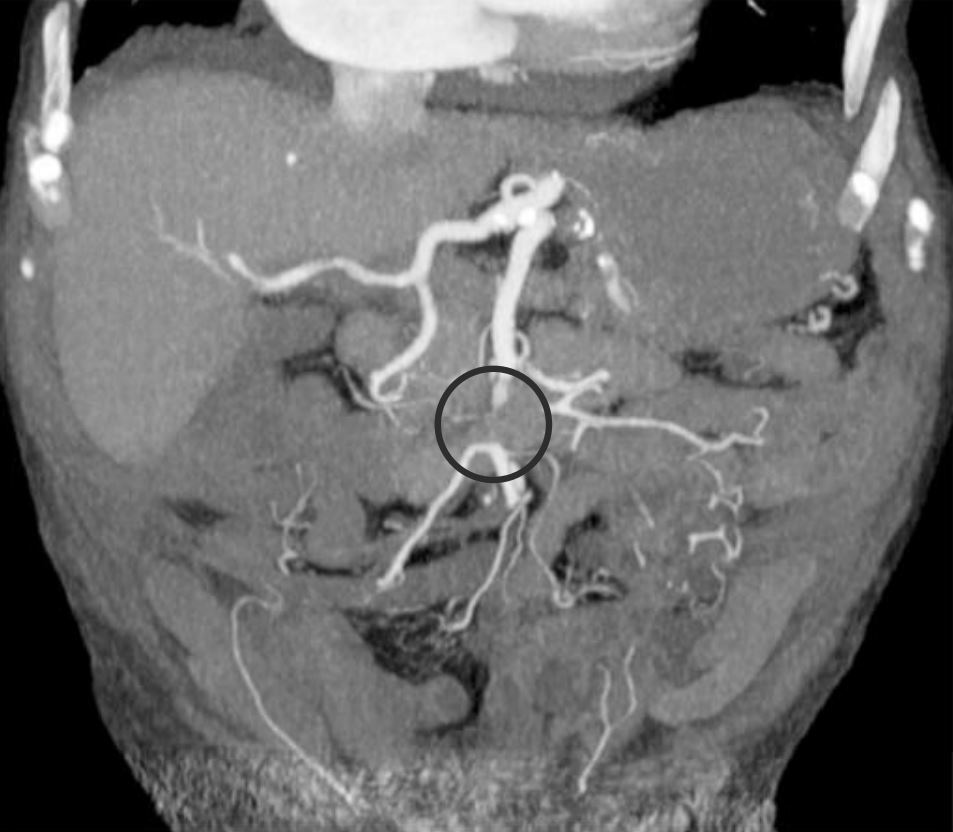
Isquemia mesentérica aguda:
Angiograma por tomografía computarizada que muestra una embolia oclusiva de la porción media de la arteria mesentérica superior (círculo)
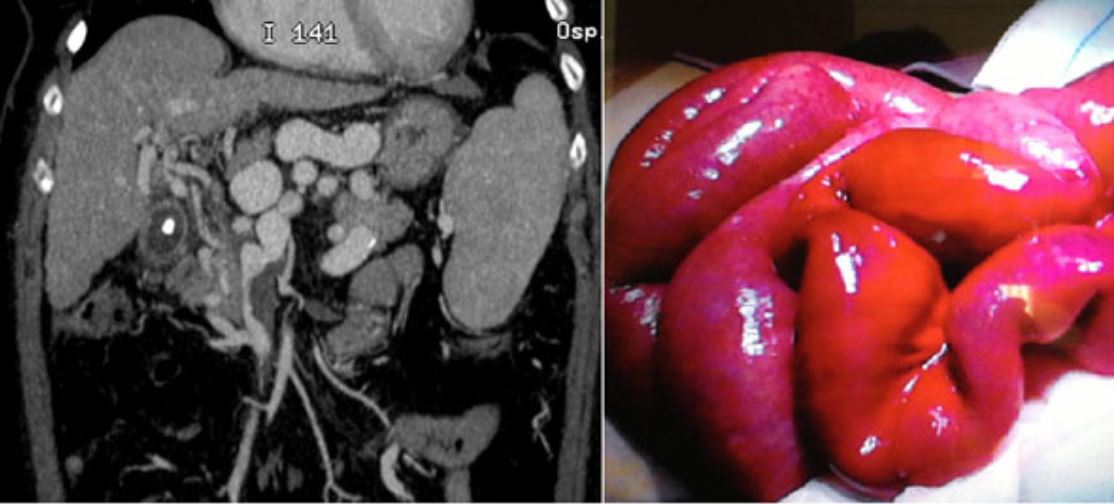
Isquemia mesentérica aguda en la reconstrucción bidimensional de tomografía computarizada multidetector con contraste. La imagen coronal de la izquierda demuestra la trombosis venosa en la vena mesentérica superior, que se confirmó en la cirugía (derecha).
Imagen: “Intestinal Ischemia: US-CT findings correlations” por Reginelli A, Genovese E, Cappabianca S, Iacobellis F, Berritto D, Fonio P, Coppolino F, Grassi R. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La isquemia mesentérica crónica es el resultado de una enfermedad vascular crónica, que puede ser causada por:
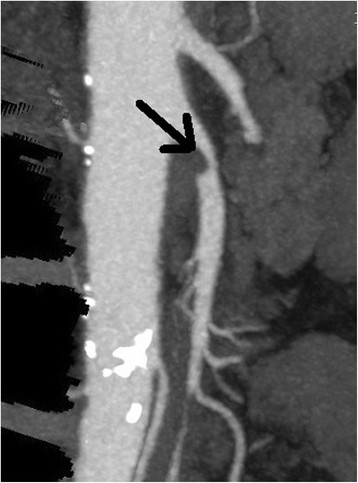
Isquemia mesentérica crónica: Angiograma por tomografía computarizada que muestra estenosis de la arteria mesentérica superior
Imagen: “Figure 1” por Spangler et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Dado que la isquemia intestinal suele presentarse con dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, el diagnóstico diferencial incluye: