El impétigo es una infección bacteriana superficial altamente contagiosa causada típicamente por Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess (más común) y Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes. El impétigo se presenta con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños de 2 a 5 años con lesiones que evolucionan de pápulas a vesículas y pústulas, que eventualmente se rompen para formar costras características “color miel”. La infección puede ser primaria (infección bacteriana de piel sana e intacta) o secundaria (infección en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum abrasiones preexistentes). El diagnóstico es clínico y el tratamiento incluye antibioticoterapia tópica o sistémica. Las complicaciones del impétigo incluyen glomerulonefritis postestreptocócica, celulitis y escarlatina.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hay 3 variantes de impétigo:
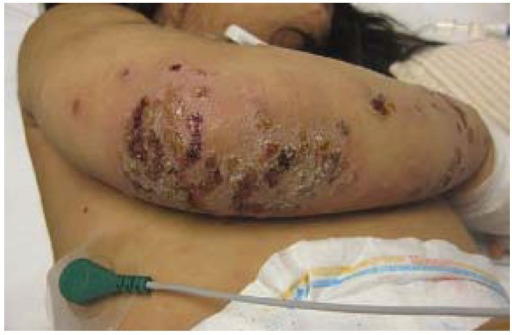
Impétigo no ampolloso con costra en la extremidad superior de un paciente pediátrico
Imagen: “Impetigo” por Saint Louis University, Cardinal Glennon Children’s Hospital, 1465 South Grand Avenue, St. Louis, MO 63104, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0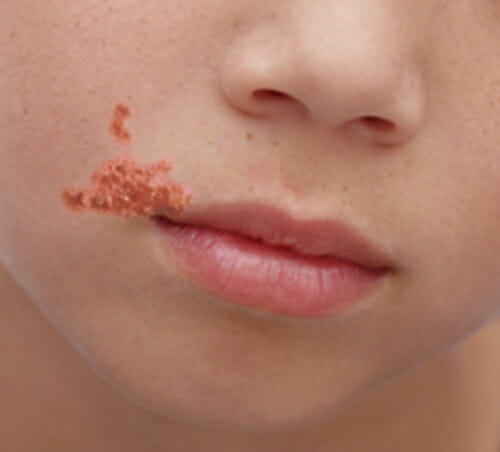
Un niño con costra de color miel debido al impétigo
Imagen: “OSC Microbio 21 02 impetigo” por CNX OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0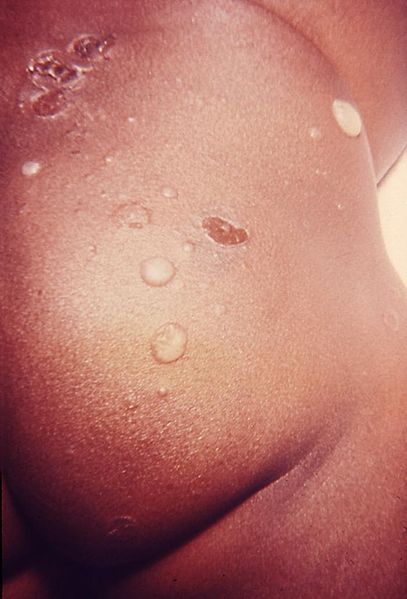
Impétigo ampolloso en la región glútea de un lactante infectado
Imagen: “Skin lesions that proved to be impetigo” por US Department of Health and Human Services. Licencia: Dominio Público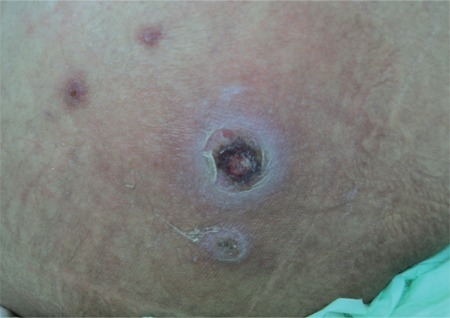
Úlcera costrosa del tamaño de una moneda típica del ectima (la fusariosis es una infección por hongos causada por Fusarium spp.)
Imagen: “Ectyhma gangrenosum” por İstanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology İstanbul, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.5El diagnóstico suele ser clínico, basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la secuencia natural de las lesiones y la presencia de costras color miel en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes pediátricos de 2–5 años.
El tratamiento depende del tipo y la gravedad de la infección.
Las siguientes afecciones también se presentan con ampollas y sirven como diagnóstico diferencial para el impétigo ampolloso:
Las siguientes afecciones son otros tipos de infecciones cutáneas superficiales que se incluyen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria diagnósticos diferenciales del impétigo: