El hipopituitarismo es una condición caracterizada por la deficiencia de las hormonas hipofisarias. Esta condición resulta principalmente de una enfermedad de la hipófisis, pero puede surgir de una disfunción hipotalámica. Los LOS Neisseria tumores hipofisarios son una de las causas más comunes. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos afectan al AL Amyloidosis lóbulo anterior de la hipófisis (adenohipófisis), que representa el 80% de la glándula. Las hormonas producidas por este lóbulo son la hormona del crecimiento, la hormona foliculoestimulante, la hormona luteinizante, la hormona estimulante de la tiroides, la hormona adrenocorticotrópica y la prolactina. Cuando el lóbulo posterior (neurohipófisis) también está afectado, se produce una disminución de la hormona antidiurética y la oxitocina. Todas estas hormonas regulan las actividades de diferentes órganos, por lo que los LOS Neisseria efectos de la hipofunción hipofisaria son multisistémicos. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante una combinación de hallazgos clínicos, niveles hormonales, pruebas de provocación e imagenología cerebral. El tratamiento es el reemplazo hormonal y la resolución de la etiología.
Last updated: Jan 28, 2026
El hipopituitarismo es la condición resultante de una producción inadecuada de hormonas hipofisarias:
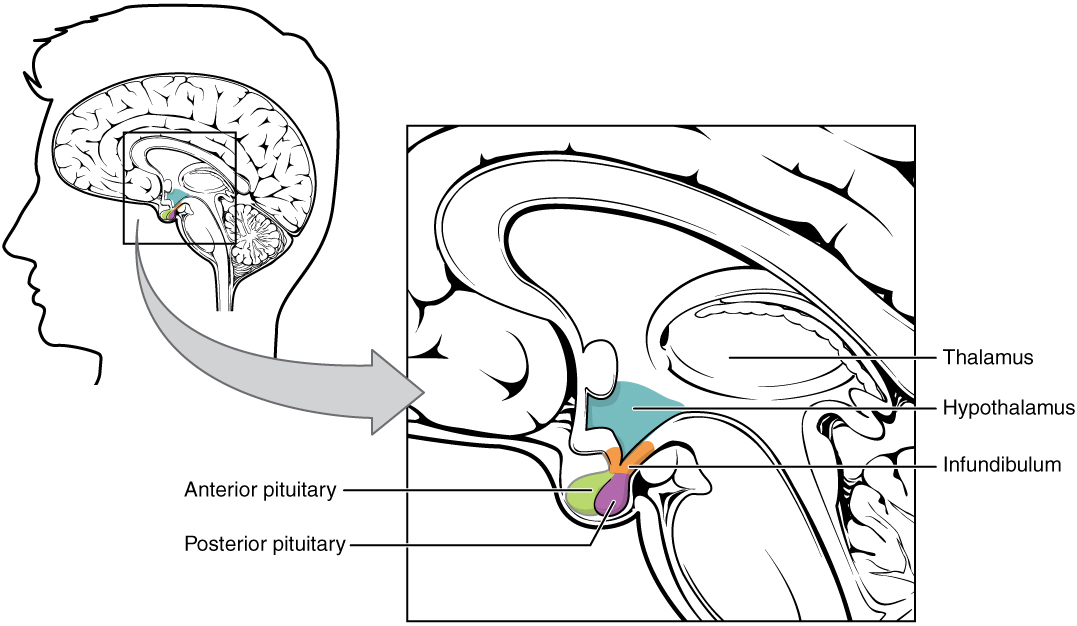
Eje hipotálamo-hipofisario:
La imagen muestra la hipófisis, formada por los lóbulos anterior y posterior, en relación con el hipotálamo.
| Hormona | Tipo de célula hipofisaria | Órgano objetivo | Función | Disminución de la producción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTH | Corticotropas | Corteza suprarrenal | Estimula:
|
Insuficiencia suprarrenal secundaria |
| GH | Somatotropas | Hígado y otros tejidos | Estimula la síntesis de proteínas y el crecimiento general de la mayoría de las células y tejidos |
|
| Prolactina | Lactotropas | Glándulas mamárias |
|
Incapacidad de producir leche (hipoprolactinemia) |
| TSH | Tirotropas | Glándula tiroides | Estimula la glándula tiroidea para que sintetice y segregue la hormona tiroidea | Hipotiroidismo |
| LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle | Gonadotropas |
|
|
|
| FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle | Gonadotropas |
|
|
|
| Hormona | Tipo de célula hipofisaria | Órgano objetivo | Función | Disminución de la producción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADH | Núcleos supraópticos del hipotálamo |
|
|
Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus insípida |
| Oxitocina | Núcleos paraventriculares del hipotálamo |
|
Estimula:
|
Causa pocos síntomas debido a su número limitado de efectos |
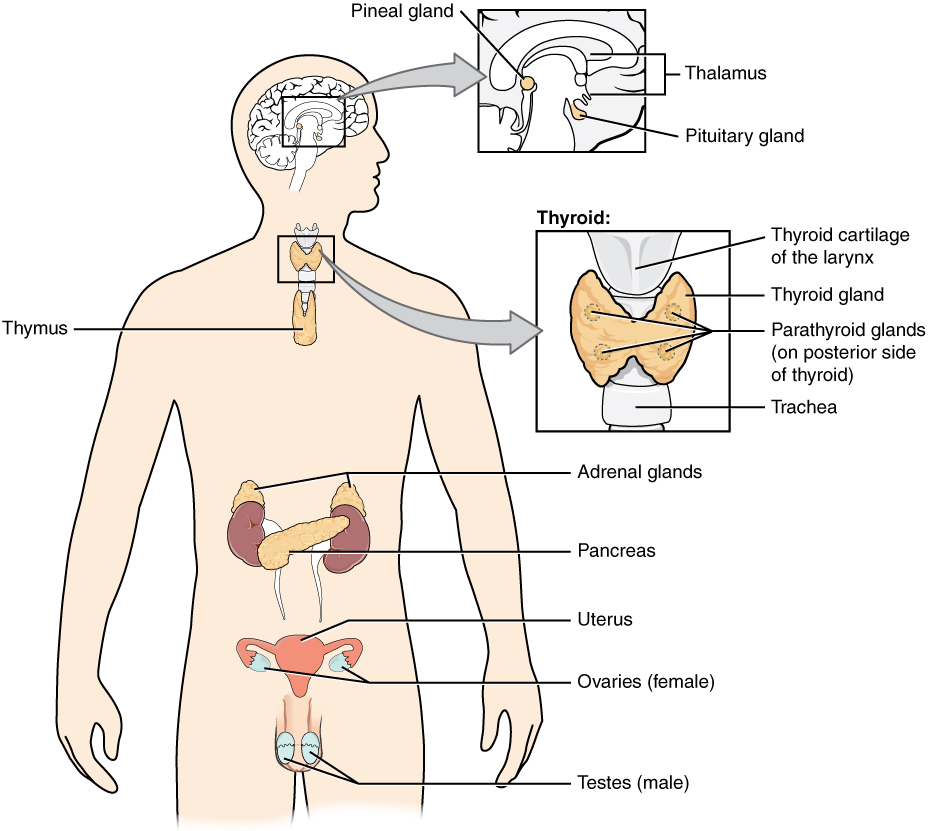
La hipófisis y los órganos diana:
Las hormonas hipofisarias ayudan a regular la actividad de las glándulas endocrinas de todo el cuerpo y desempeñan un papel importante en la homeostasis.
Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas dependen de la patología subyacente, la rapidez de aparición y la gravedad del hipopituitarismo (parcial o completo).
Deficiencia de ACTH:
Deficiencia de GH:
Deficiencia de TSH:
Deficiencia de LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle/ FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle:
Deficiencia de ADH:
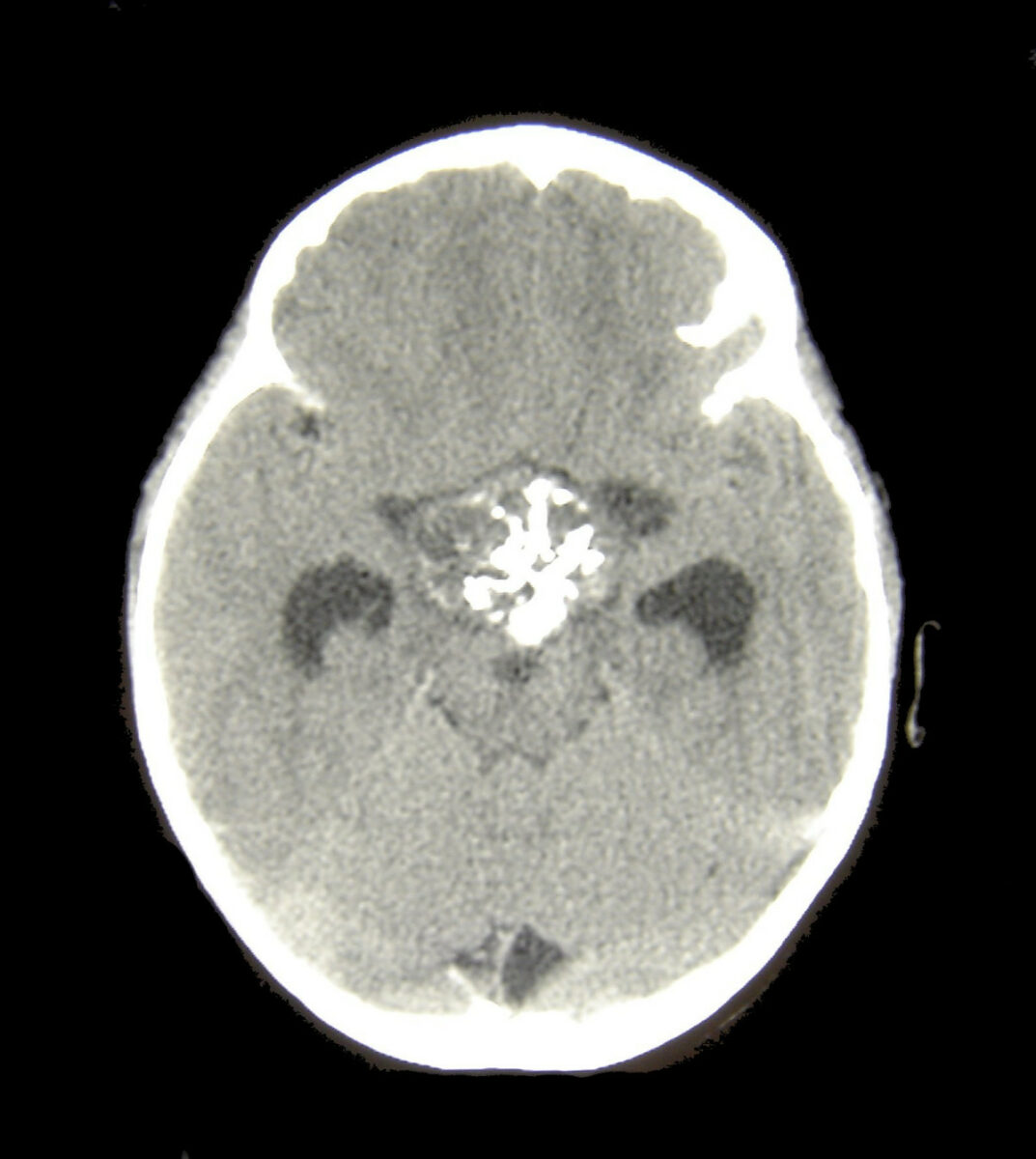
TC craneal de un paciente con un craneofaringioma
Imagen: “Craniopharyngioma1” por Matthew R Garnett, Stéphanie Puget, Jacques Grill, Christian Sainte-Rose. Licencia: CC BY 2.0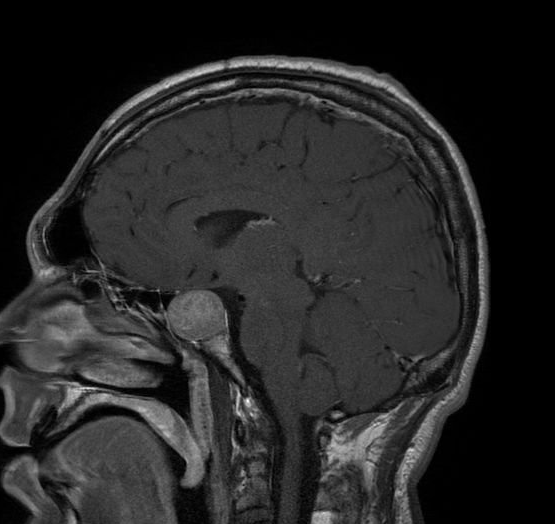
Resonancia magnética de un paciente con un gran adenoma hipofisario
Imagen: “Acromegaly” por Elgee. Licencia: CC BY 3.0, editado por Lecturio.