La hipercalcemia (calcio sérico > 10,5 mg/dL) puede ser el resultado de varias afecciones, la mayoría de las cuales se deben al AL Amyloidosis hiperparatiroidismo y a las neoplasias. Otras causas son los LOS Neisseria trastornos que provocan la elevación de la vitamina D, las enfermedades granulomatosas y el uso de ciertos agentes farmacológicos. Los LOS Neisseria niveles de calcio se regulan y se ven afectados por factores como la ingesta dietética y el pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance, y los LOS Neisseria niveles de la hormona paratiroidea (PTH, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), la vitamina D y la albúmina. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de los LOS Neisseria niveles de calcio y de la aparición de la hipercalcemia. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, se observan manifestaciones neuropsiquiátricas (confusión, alteración del estado mental), gastrointestinales (vómitos, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal), musculoesqueléticas ( dolor Dolor Inflammation óseo, debilidad) y renales (poliuria, polidipsia). Es necesario confirmar la hipercalcemia. La corrección del valor se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niveles de albúmina o después de determinar los LOS Neisseria niveles de calcio ionizado (la forma metabólicamente activa), a lo que sigue la determinación de los LOS Neisseria niveles de la PTH. Las pruebas de laboratorio y los LOS Neisseria estudios de imagenología posteriores se solicitan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del antecedente y la presentación. La corrección de la hipercalcemia depende de su gravedad. Los LOS Neisseria niveles de calcio > 14 mg/dL se tratan con hidratación salina isotónica intravenosa, calcitonina y bifosfonatos. La hemodiálisis se considera en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos raros. Se recomienda el tratamiento de la causa subyacente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El calcio es el mineral más abundante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo humano, y el 99% se encuentra sólo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria huesos. El calcio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre existe en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 formas:
Niveles:
La importancia del calcio:
Los LOS Neisseria huesos, el intestino y los LOS Neisseria riñones participan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death.
Elementos clave de la regulación del calcio:
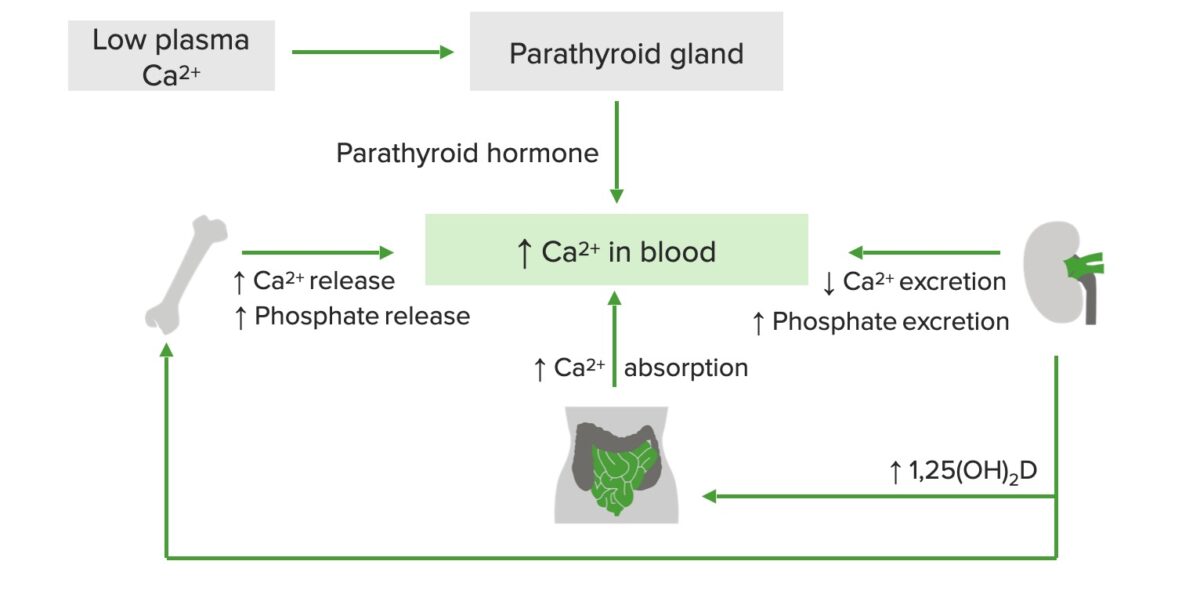
Diagrama esquemático de la regulación del calcio:
Un nivel bajo de calcio en el plasma estimula la liberación de la hormona paratiroidea, que aumenta la liberación de calcio y fosfato del hueso, la absorción de calcio en el tracto gastrointestinal y la producción de vitamina D en los riñones. La vitamina D activa, a su vez, aumenta la liberación de calcio de los huesos y la absorción de calcio en el intestino delgado.
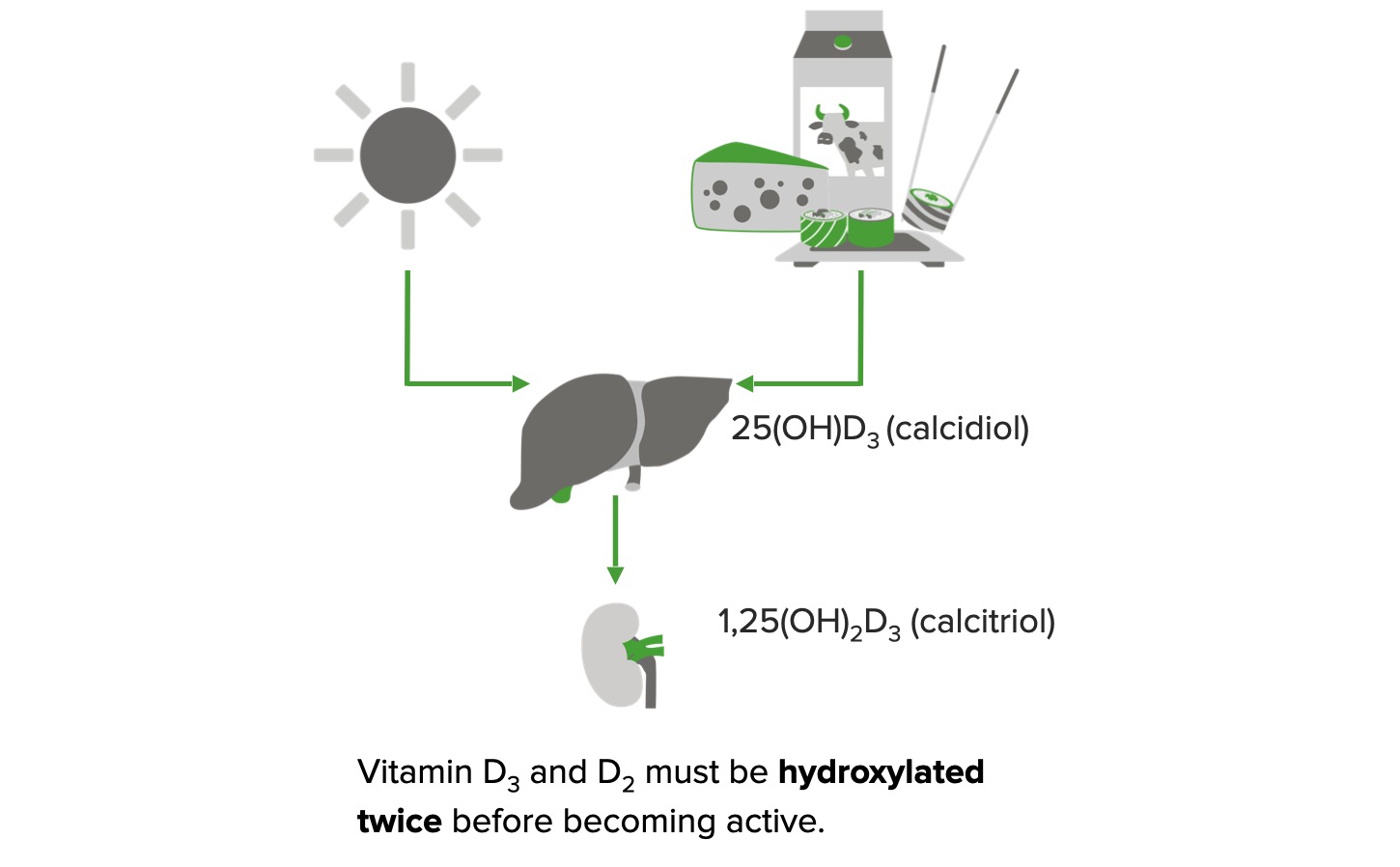
Formación de vitamina D activa:
En presencia de la luz solar, el 7-dihidrocolesterol se convierte en colecalciferol (vitamina D3) en la piel.
La vitamina D2 (fuentes vegetales/suplementos) y la vitamina D3 (fuentes animales/suplementos) se obtienen de la dieta.
Ambas formas requieren un proceso de hidroxilación enzimática de dos pasos antes de que puedan ejercer efectos biológicos.
La vitamina D2/D3 se convierte en 25-hidroxivitamina D3 (calcidiol) en el hígado. En el riñón, el calcidiol se convierte en 1,25-dihidroxivitamina D3(calcitriol), que es la forma activa.
La hipercalcemia se caracteriza por niveles elevados de calcio y suele ser el resultado de uno de estos factores o de una combinación de ellos:
Aumento de la resorción ósea:
Aumento de la absorción de calcio:
Otros:
Las manifestaciones dependen del nivel y del inicio de la hipercalcemia.
Hipercalcemia con calcio total corregido por albúmina < 12 mg/dL:
Hipercalcemia con calcio total corregido por albúmina > 12 mg/dL:
Crisis hipercalcémica/hipercalcemia grave:
Mnemotecnia:
Para recordar los LOS Neisseria síntomas clínicos comunes de la hipercalcemia, recuerde “quejidos, huesos, piedras, gemidos, tronos y síntomas psíquicos”:
| Niveles de PTH | Diagnóstico y pruebas adicionales |
|---|---|
| Elevado | Hiperparatiroidismo primario |
| Normal/ligeramente elevado |
|
| Bajo |
|