El herpes zóster (también conocido como culebrilla) es una infección viral de reactivación causada por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la varicela-zóster. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la varicela-zóster permanece latente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la raíz dorsal del ganglio tras la fase de infección primaria de la varicela. La edad, el estrés o los LOS Neisseria estados inmunodeprimidos pueden desencadenar la reactivación del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology. El herpes zóster se presenta clínicamente con una distribución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum dermatoma y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de una erupción dolorosa, única y unilateral. El diagnóstico se realiza principalmente a partir de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes clínicos y la exploración física. Sin embargo, pueden realizarse pruebas de laboratorio (como la PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)) si el diagnóstico no está claro. El manejo incluye terapia antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B y tratamiento sintomático.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El herpes zóster (también conocido como culebrilla) es una infección viral de reactivación causada por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la varicela-zóster que se manifiesta como una erupción vesicular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un dermatoma, unilateral y dolorosa.
Organismo causante: virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la varicela-zóster
Transmisión:
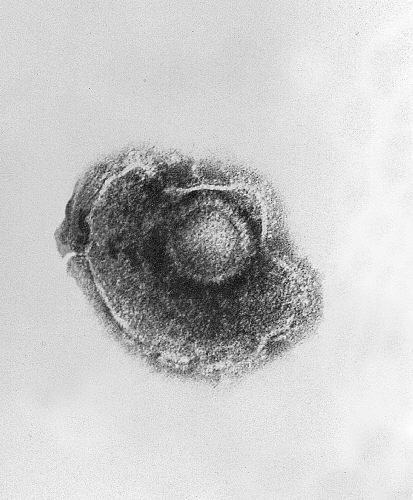
Imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión que muestra un único virus de la varicela-zóster (VZV), también conocido como herpesvirus humano 3, que causa la varicela
Imagen: “Ultrastructural features exhibited by a single varicella-zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3), the cause of chickenpox.” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la varicela-zóster causa 2 síndromes distintos:
Infección primaria (varicela):
Infección secundaria (herpes zóster):
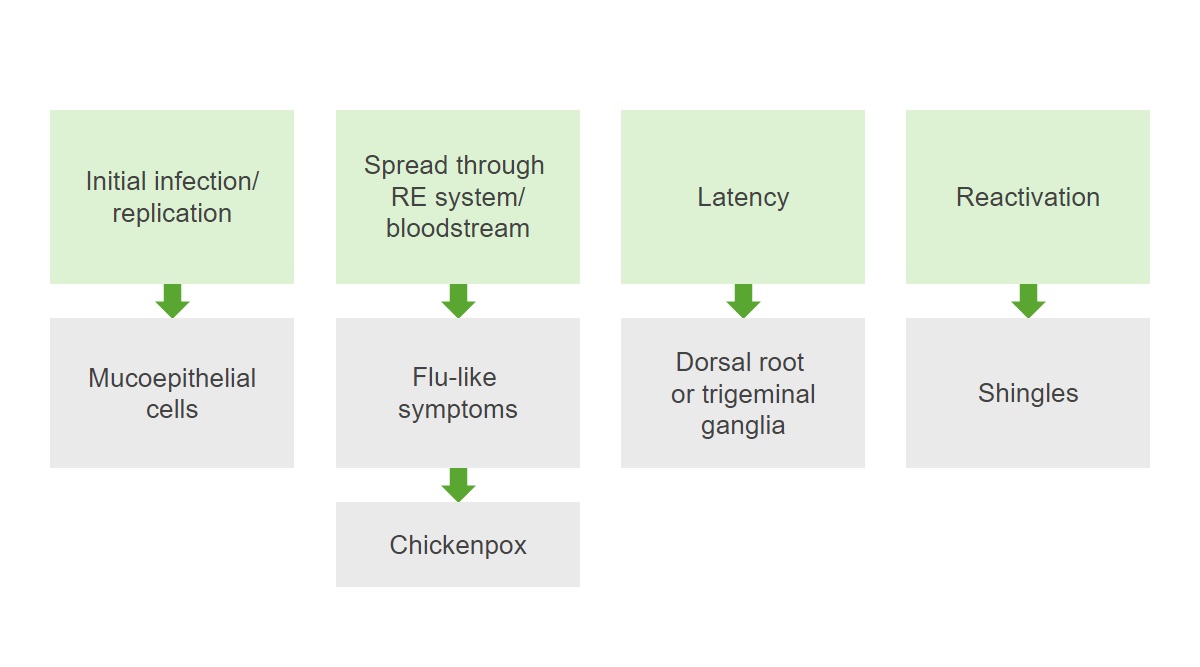
Patogénesis del virus de la varicela-zóster:
La infección replica los virus en las células mucoepiteliales y luego se extiende por el sistema reticuloendotelial (RE) y el torrente sanguíneo, provocando síntomas similares a los de la gripe y la varicela. Tras la resolución de la infección primaria, se produce un periodo de latencia y el virus permanece latente en los ganglios de la raíz dorsal. La reactivación de la infección da lugar al herpes zóster.
Neuritis aguda:
Erupción:
Síntomas sistémicos (< 20% de los LOS Neisseria casos):
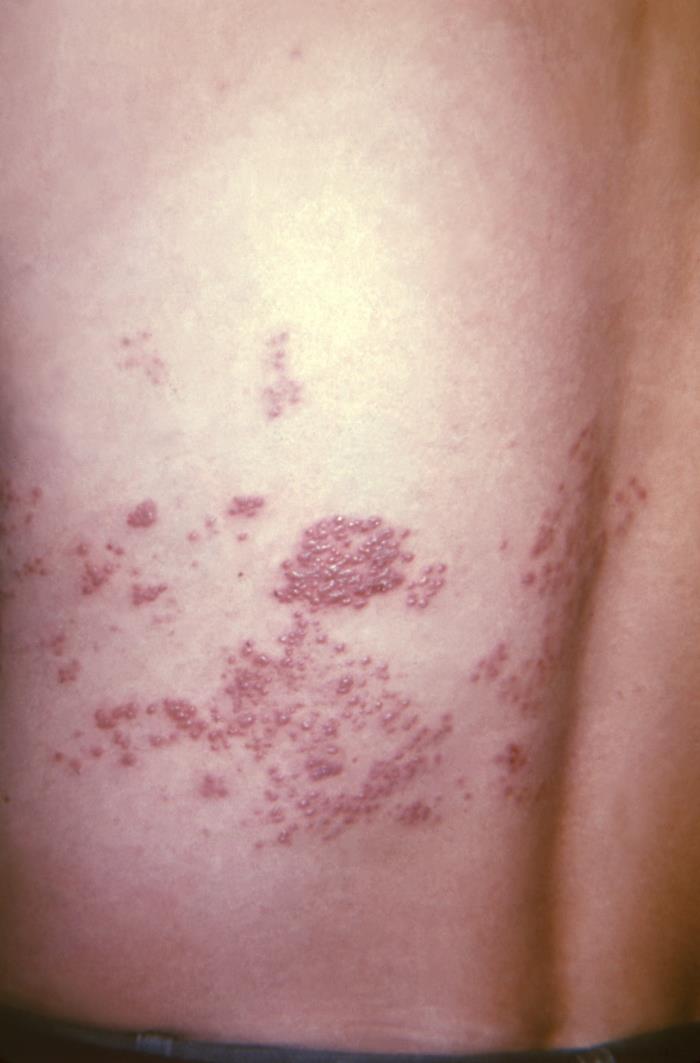
Erupción de herpes zóster en el dermatoma T10–11 a lo largo de la espalda de un paciente
Imagen: “This view of a patient’s skin, revealed a maculopapular rash, which had been due to an outbreak of shingles.” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público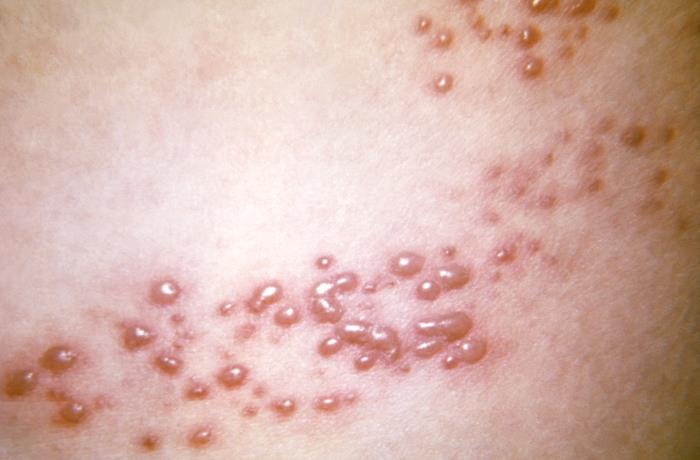
Primer plano de la erupción vesicular del herpes zóster
Imagen: “This view of a patient’s skin, revealed a maculopapular rash, which had been due to an outbreak of shingles.” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público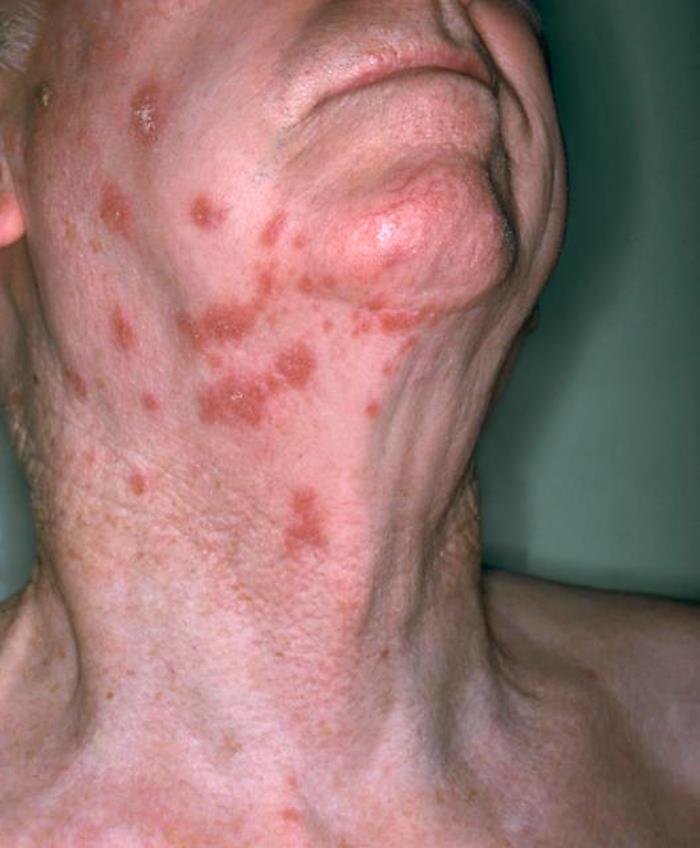
Vista anterolateral del cuello de un paciente que muestra la presencia de una erupción eritematosa debida al herpes zóster
Imagen: “Anterolateral view of this patient’s neck showing the presence of an erythematous rash due to shingles” por NIAID. Licencia: Dominio Público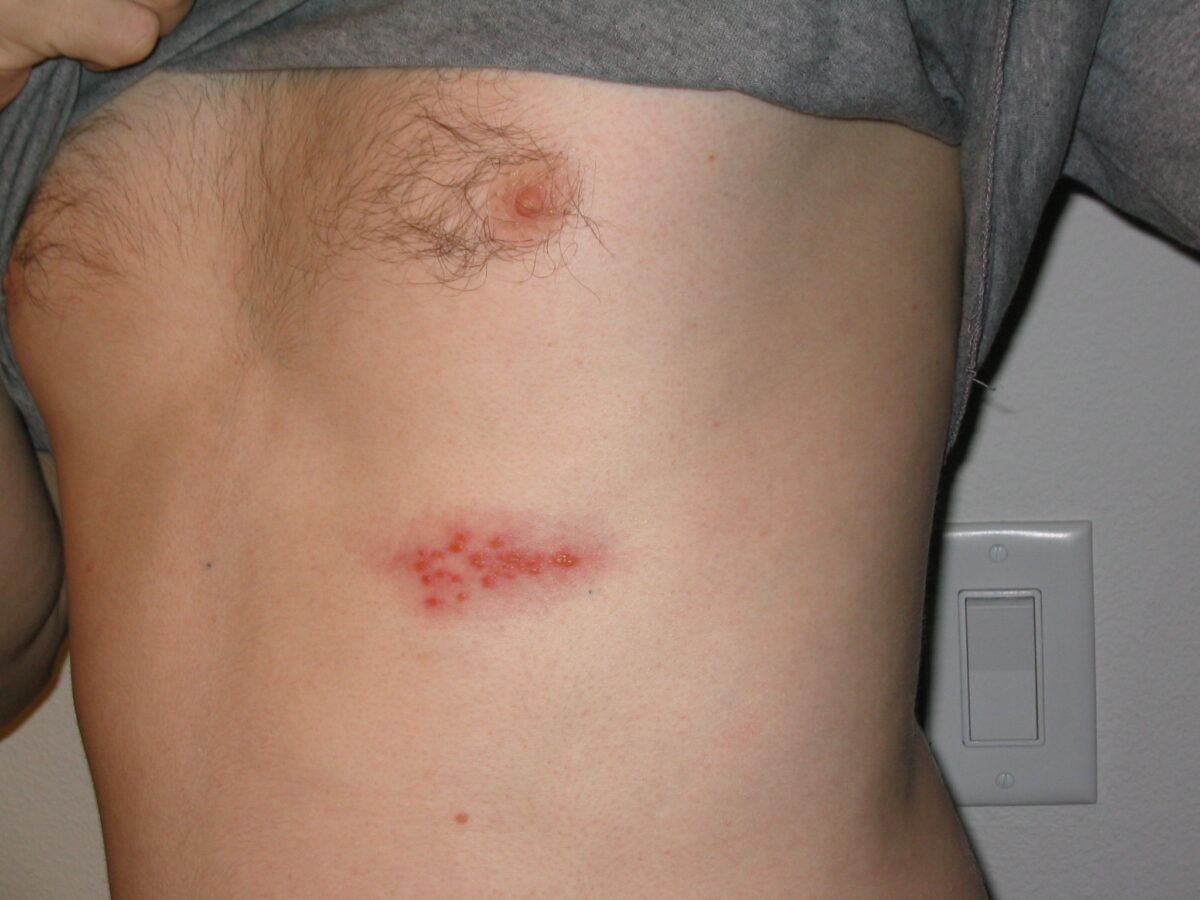
Imagen de un brote de herpes en el pecho
Imagen: “Picture of a shingles (herpes zoster) outbreak on the chest” por Preston Hunt. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Las siguientes son presentaciones graves, que pueden ocurrir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunodeprimidos:
Diseminación cutánea:
Afectación de órganos viscerales:
Herpes zóster oftálmico:
Síndrome de Ramsay Hunt (herpes zóster ótico):
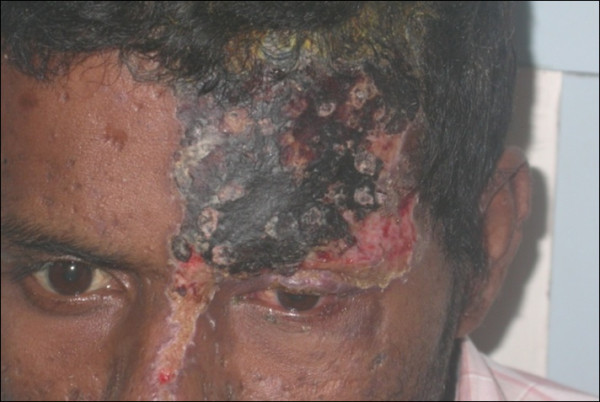
Herpes zóster oftálmico con afectación del ojo izquierdo
Imagen: “External photograph showing herpes zoster ophthalmicus” por Sudharshan S et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Neuralgia postherpética:
Necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage retiniana aguda:
Otras complicaciones:
El diagnóstico del herpes zóster se basa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación clínica. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con presentaciones atípicas, se puede utilizar lo siguiente:
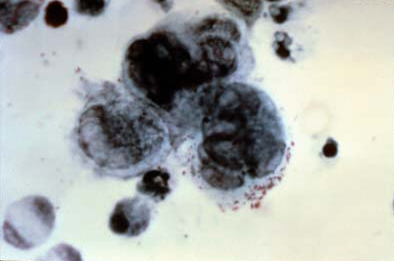
Frotis de Tzanck con 3 células gigantes multinucleadas
Imagen: “Positive Tzanck test, showing three multinucleated giant cells in center” por NIAID. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoMedidas para prevenir la transmisión:
Vacunas: